A “Check Engine” light can be a driver’s worst nightmare, especially when it throws a cryptic code like P1457. If you own a 2002 Honda Accord and encounter this code, don’t panic! This article breaks down everything you need to know about the P1457 code, its common causes, and how to get your Accord back on track.
What Does OBD2 Code P1457 Mean?
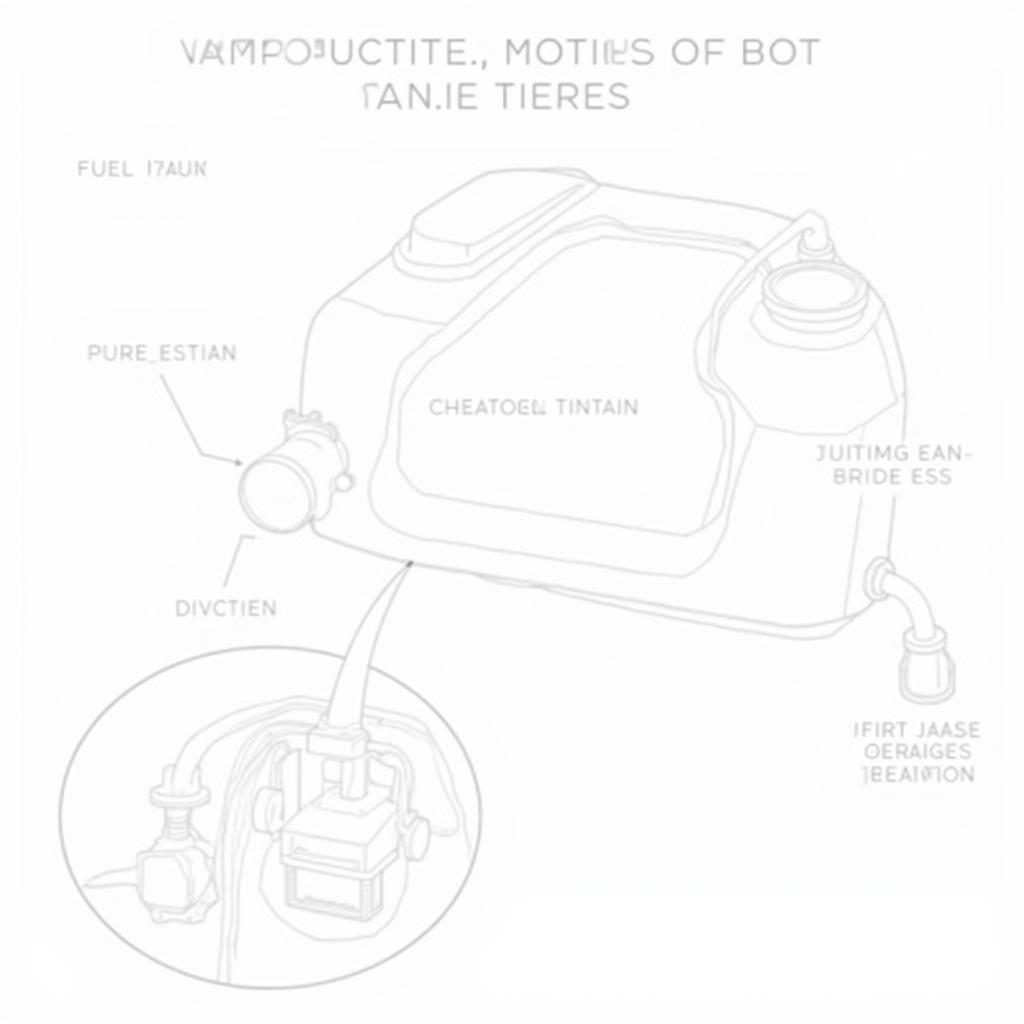
In simple terms, the P1457 code on your 2002 Honda Accord indicates a problem with the Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system. This system is crucial for preventing fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. The specific issue identified by the P1457 code relates to a “leak detected in the EVAP control system (fuel tank system).”
Common Causes of P1457 in a 2002 Honda Accord
While a leak in the EVAP system is the general culprit behind the P1457 code, several specific components can be at fault:
- Loose or Damaged Gas Cap: The most common and often overlooked cause is a loose or damaged gas cap. The gas cap seals the fuel tank, preventing vapor leaks.
- Faulty Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor: This sensor monitors the pressure inside the fuel tank. A malfunctioning sensor can misinterpret pressure changes, triggering the P1457 code.
- Damaged EVAP Canister Purge Valve: This valve controls the flow of fuel vapors from the charcoal canister to the engine for combustion. A stuck-open or closed valve can disrupt the EVAP system’s pressure balance.
- Cracked or Disconnected EVAP Hoses: The EVAP system relies on a network of hoses to transport fuel vapors. Cracks, leaks, or loose connections in these hoses can cause pressure loss.
- Damaged Charcoal Canister: The charcoal canister stores fuel vapors, preventing them from entering the atmosphere. A damaged or saturated canister can lead to leaks.
Diagnosing and Fixing the P1457 Code
Diagnosing the exact cause of the P1457 code requires a systematic approach:
- Check the Gas Cap: Start with the easiest fix – ensure the gas cap is securely tightened. Sometimes, simply re-tightening the gas cap can resolve the issue.
- Visual Inspection: Visually inspect all EVAP components, including the gas cap, hoses, and connections, for any signs of damage, cracks, or loose fittings.
- Pressure Test: If the visual inspection doesn’t reveal the problem, a pressure test using a specialized tool can pinpoint leaks in the system.
- Component Testing: Test individual components like the fuel tank pressure sensor and purge valve using a multimeter to check their electrical signals and resistance.
Expert Insight:
“Many car owners underestimate the importance of a properly functioning EVAP system,” says John Miller, a seasoned automotive technician with over 20 years of experience. “Beyond environmental concerns, a faulty EVAP system can affect your vehicle’s fuel economy and even engine performance.”
Addressing the P1457 Code: DIY or Mechanic?
While a loose gas cap might be a simple DIY fix, diagnosing and repairing other EVAP system components often require specialized tools and expertise. If you’re not comfortable working on your car, seeking help from a qualified mechanic is recommended.
Conclusion
Ignoring the P1457 code in your 2002 Honda Accord can lead to more serious issues and costly repairs down the road. By understanding the code and taking appropriate action, you can ensure your EVAP system functions properly, keeping your car running smoothly and reducing its environmental impact.