The dreaded 420 code obd2. It’s a common sight for many car owners and can be a real headache to diagnose. This code indicates a problem with your vehicle’s catalytic converter system, specifically that it’s not operating as efficiently as it should. But what does that really mean, and how do you fix it? This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the P0420 code, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions.
What Does the 420 Code OBD2 Mean?
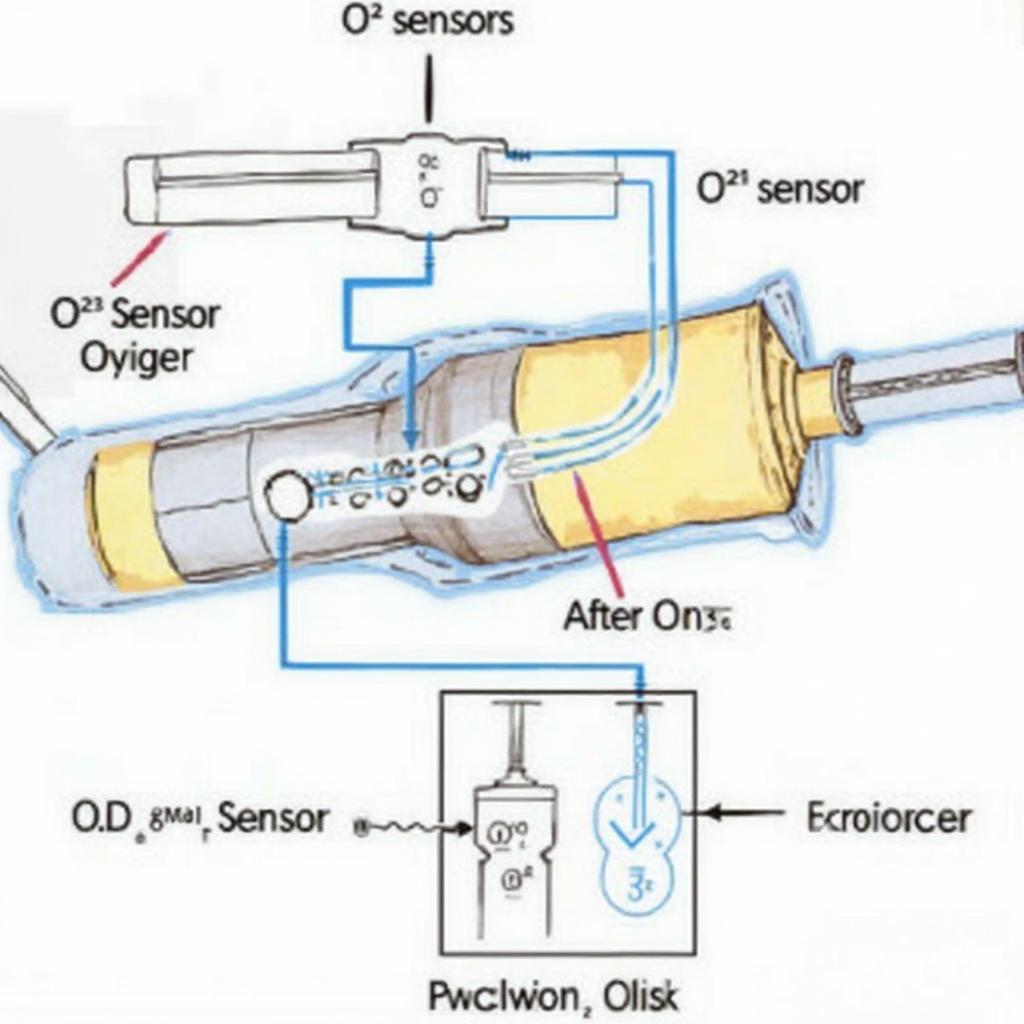
The 420 code obd2, or more specifically, the P0420 diagnostic trouble code (DTC), signifies “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1).” This means the oxygen sensors on either side of the catalytic converter are reporting similar readings, indicating the converter isn’t effectively converting harmful exhaust gases. While “Bank 1” typically refers to the side of the engine with cylinder #1, it’s crucial to consult your vehicle’s specific repair manual for confirmation. Ignoring this code can lead to further damage and potentially fail your emissions test. More information can be found on our page about code obd2 p0420.
Common Causes of the P0420 Code
Several issues can trigger the 420 code obd2. Pinpointing the exact culprit requires careful diagnosis. Here are some of the most common causes:
- Faulty Catalytic Converter: This is the most obvious and often most expensive culprit. Over time, the internal honeycomb structure of the catalytic converter can degrade, reducing its efficiency.
- Oxygen Sensor Issues: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can provide inaccurate readings to the engine control module (ECM), triggering the P0420 code. This could be due to a failing sensor or simply a loose connection.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system, especially before the catalytic converter, can disrupt the flow of exhaust gases and affect the oxygen sensor readings.
- Engine Misfires: Misfires can introduce unburnt fuel into the exhaust system, overloading the catalytic converter and potentially damaging it.
- Rich Fuel Mixture: A fuel mixture that’s too rich can also overload the catalytic converter, leading to premature failure.
- Damaged Wiring or Connectors: Damaged wiring or connectors within the exhaust system can interfere with the oxygen sensor signals and trigger the code.
Diagnosing the 420 Code OBD2
Proper diagnosis is key to resolving the P0420 code effectively. Using an OBD2 scanner is the first step. Here’s a more detailed approach:
- Check for Other Codes: Sometimes, the P0420 code can be accompanied by other codes. Addressing these other issues may resolve the P0420 code as well.
- Inspect for Exhaust Leaks: Carefully examine the exhaust system for any signs of leaks, such as holes, cracks, or loose connections.
- Check Oxygen Sensor Readings: Use an OBD2 scanner to monitor the oxygen sensor readings both before and after the catalytic converter. Comparing these readings can help determine if the converter is functioning correctly.
- Test the Catalytic Converter: A professional mechanic can perform a pressure test on the catalytic converter to determine its efficiency.
You can find more information about this code for specific car models, like the Ford, on our dedicated page for obd2 p0420 ford.
What to Do if You See a 420 Code OBD2
Seeing this code can be alarming, but there are steps you can take:
- Don’t Panic: While the P0420 code can indicate a serious issue, it doesn’t necessarily mean your car is about to break down.
- Get it Diagnosed: Take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic to have the code properly diagnosed. They’ll be able to identify the underlying cause and recommend the appropriate repairs.
Fixing the 420 Code OBD2
Depending on the diagnosis, the solution to the P0420 code can range from simple fixes to more complex repairs. Here are some potential solutions:
- Replace the Catalytic Converter: If the converter is faulty, replacement is often the only option.
- Repair Exhaust Leaks: Fixing any exhaust leaks can restore proper exhaust flow and resolve the code.
- Replace Oxygen Sensors: Faulty oxygen sensors should be replaced to ensure accurate readings.
- Address Engine Misfires: Fixing any underlying engine issues that are causing misfires can prevent further damage to the catalytic converter.
- Adjust Fuel Mixture: A mechanic can adjust the fuel mixture to ensure it’s within the correct range.
If you own a Honda CRV, check our dedicated page for obd2 code p0420 honda crv.
Conclusion
The 420 code obd2 is a common yet potentially complex issue. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures is crucial for effective resolution. While some fixes may be simple, others can be more involved, requiring professional assistance. Addressing the P0420 code promptly can prevent further damage to your vehicle and ensure it runs smoothly and efficiently. For more specific information about the P0420 code in a 2007 Civic 1.8L, you can visit our page dedicated to 2007 civic 1.8l p0420 obd2 code.
FAQ
- What is the 420 code obd2? It indicates the catalyst system efficiency is below the required threshold.
- Can I drive with a P0420 code? Yes, but it’s recommended to address the issue promptly to avoid further damage.
- How much does it cost to fix the P0420 code? The cost varies depending on the underlying cause and the required repairs.
- Can I fix the P0420 code myself? Some fixes, like repairing exhaust leaks, can be done DIY. However, more complex repairs require professional assistance.
- Will ignoring the P0420 code damage my car? Yes, ignoring the code can lead to further damage to the catalytic converter and other components.
- How can I prevent the P0420 code? Regular maintenance, including timely tune-ups and oil changes, can help prevent this code.
- Can a bad oxygen sensor cause the P0420 code? Yes, a faulty oxygen sensor can trigger this code.
Situations that may cause code P0420 to appear
- Driving short distances frequently, as this doesn’t allow the catalytic converter to reach optimal operating temperature.
- Using low-quality fuel, as this can contaminate the catalytic converter and reduce its effectiveness.
- Having a faulty fuel injector, which can cause a rich fuel mixture that damages the catalytic converter.
- Ignoring other engine trouble codes, as these can contribute to the underlying problem causing the P0420 code.
Further Reading
For more information related to the OBD2 P0420 code, you might find these articles helpful:
- How to diagnose and fix OBD2 codes
- Understanding the role of the catalytic converter
- Common OBD2 codes and their meanings
Need help with your car’s P0420 code, especially for your Toyota RAV4? Visit our specific page for your vehicle: obd2 code p0420 toyota rav4.
Need more assistance? Contact our 24/7 support team via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880 or Email: [email protected].