When your vehicle’s onboard computer detects a problem, it logs a corresponding Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in its memory. This code can be read using an OBD2 scanner, providing valuable insight into the issue. But what happens when an OBD2 scan reveals “module removed”? This article delves into the implications of a removed module on OBD2 functionality, how to identify the missing component, and steps for effective troubleshooting.
Decoding “Module Removed”
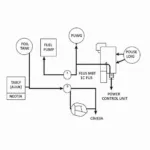
The message “module removed” appearing on your OBD2 scanner indicates that the scanner cannot communicate with a specific electronic control module (ECM) in your vehicle. Each module manages a distinct system, such as the engine, transmission, airbags, or ABS.
A module can be physically removed, or it might be experiencing a communication failure. Here’s a breakdown of potential scenarios:
- Physical Removal: The module may have been intentionally removed due to a repair, replacement, or aftermarket modification.
- Electrical Fault: A loose connection, damaged wiring, or blown fuse can disrupt communication between the OBD2 port and the module.
- Module Failure: A malfunctioning or faulty module can lead to communication errors.
Identifying the Missing Module
Pinpointing the exact missing module is crucial for effective troubleshooting. While the “module removed” message doesn’t specify the affected system, there are ways to narrow it down:
- Check Engine Light: If the check engine light is on, the missing module likely belongs to the engine or emissions control system.
- Symptoms: Observe any performance issues your vehicle might be experiencing. For example, difficulty shifting gears could indicate a problem with the transmission control module (TCM).
- OBD2 Scanner Features: Some advanced scanners can identify the specific modules they can’t communicate with, providing a more precise diagnosis.
Troubleshooting Steps
Once you suspect a missing module, follow these steps to diagnose and resolve the issue:
- Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the suspected module’s wiring harness and connectors for any signs of damage, looseness, or corrosion.
- Fuse Check: Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual to locate the fuse box and identify the fuse associated with the suspected module. Check for a blown fuse and replace it if necessary.
- Module Scan: If the visual inspection and fuse check don’t reveal any issues, connect your OBD2 scanner or visit a qualified mechanic to scan the vehicle’s computer for specific DTCs. These codes provide more detailed information about the nature of the problem.
- Professional Diagnosis: If you’re unable to pinpoint the problem, consult a qualified mechanic specializing in automotive diagnostics. They possess the expertise and specialized equipment to accurately diagnose and repair complex electrical issues.
“When dealing with potential module issues, it’s always best to start with the basics,” advises John Smith, Senior Automotive Engineer at XYZ Automotive. “A thorough visual inspection and fuse check can often pinpoint simple problems, saving you time and money.”
Impact on Vehicle Performance
A removed or malfunctioning module can significantly impact your vehicle’s performance, safety, and emissions. Depending on the affected system, you might experience:
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: A faulty engine control module (ECM) can lead to improper air-fuel mixture and ignition timing, decreasing fuel efficiency.
- Performance Issues: Problems with the transmission control module (TCM) can result in rough shifting, gear slippage, or even complete transmission failure.
- Safety Concerns: Malfunctions in modules controlling critical safety systems like airbags, ABS, or electronic stability control (ESC) can compromise your safety and that of your passengers.
- Emissions Problems: Modules related to emissions control, such as the evaporative emissions control system (EVAP) or exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system, can cause your vehicle to fail emissions tests.
 A mechanic inspecting a car engine
A mechanic inspecting a car engine
OBD2 and Module Compatibility
If you need to replace a module, ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s make, model, year, and engine type. While a used module might seem cost-effective, it can lead to compatibility issues and potential problems down the road. Opting for a new, OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) module or a reputable aftermarket alternative specifically designed for your vehicle is recommended.
Conclusion
Encountering a “module removed” message on your OBD2 scanner can be perplexing. Understanding the potential causes, knowing how to identify the affected system, and following the troubleshooting steps outlined above can help you address the issue effectively. Remember, seeking professional help from a qualified mechanic is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair, ensuring your vehicle operates safely and efficiently.
FAQs
Can I drive my car with a module removed?
It depends on the specific module. Driving with certain modules removed, such as those related to essential safety systems, can be extremely dangerous.
How much does it cost to replace a car module?
The cost varies depending on the module type, vehicle make and model, labor costs, and whether you choose a new, used, or remanufactured module.
Can a bad battery cause a module to fail?
A failing battery can lead to voltage fluctuations that may damage sensitive electronic components, including modules.
Do I need to reprogram a new module after installation?
In many cases, yes. Reprogramming ensures the new module integrates seamlessly with your vehicle’s existing systems.
Can water damage cause module problems?
Yes, water damage to the module itself or its wiring can lead to corrosion, short circuits, and communication failures.
For further assistance or if you have any questions, our team is available 24/7 via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880 or Email: [email protected].