Your cart is currently empty!
Understanding Ford Fuel Trims: A Look Back Before OBD2
Fuel trims are a critical aspect of engine performance, and Ford vehicles are no exception. For those working on older Ford models, understanding how fuel trims operated before the widespread adoption of OBD2 is essential. This article delves into the world of Ford fuel trims in the pre-OBD2 era, providing valuable insights for enthusiasts and mechanics alike.
Before diving into the specifics, it’s important to grasp the fundamental concept of fuel trims. In essence, fuel trims represent the adjustments made by the engine control unit (ECU) to fine-tune the air-fuel ratio for optimal combustion.
Ford Fuel Trims Pre-OBD2: The Basics
In the days before OBD2 became the standard in the mid-1990s, Ford vehicles relied on various systems to manage fuel delivery and adjust the air-fuel ratio.
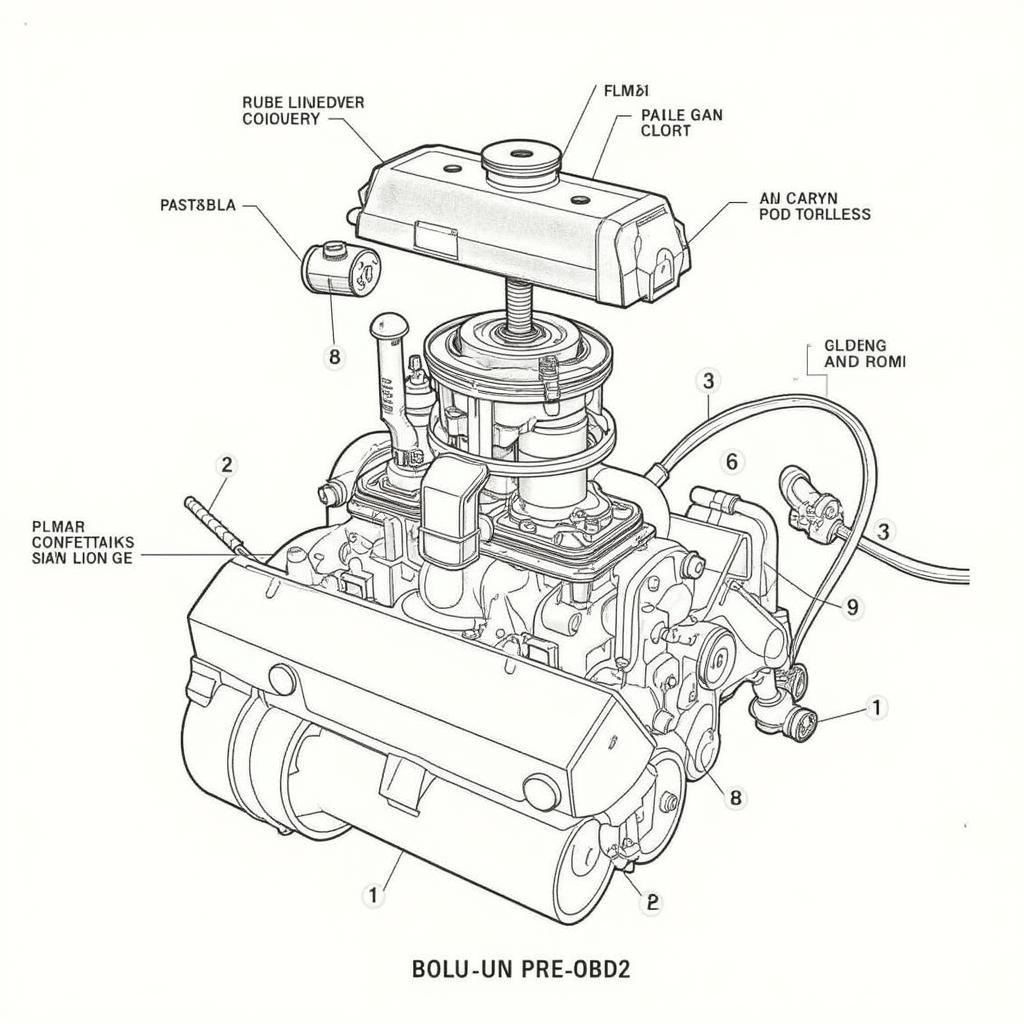
Carburetors: Many older Ford models utilized carburetors, mechanical devices responsible for mixing air and fuel before it enters the engine. Adjustments to the carburetor, often made by screws controlling fuel flow and air mixture, were the primary means of influencing fuel trims.
Early Fuel Injection Systems: As technology advanced, Ford transitioned to early electronic fuel injection systems. These systems still lacked the sophisticated sensors and diagnostic capabilities of OBD2 but allowed for some degree of electronic fuel trim control.
 Ford Fuel System (Pre-OBD2)
Ford Fuel System (Pre-OBD2)
How Pre-OBD2 Fuel Trims Were Adjusted
Unlike the live data stream and diagnostic trouble codes offered by OBD2, pinpointing fuel trim issues in pre-OBD2 Fords required a more hands-on approach:
Vacuum Gauges: Mechanics would connect a vacuum gauge to the intake manifold to get a reading of engine vacuum pressure. Fluctuations in vacuum pressure could indicate problems with the air-fuel mixture, providing clues about the direction of needed adjustments.
Exhaust Gas Analysis: Analyzing the composition of exhaust gases was another method for assessing the air-fuel ratio. Specialized equipment measured the levels of carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and oxygen (O2) in the exhaust, helping mechanics determine if the mixture was too rich or too lean.
Trial and Error: In some cases, making incremental adjustments to the carburetor or fuel injection system and observing the engine’s response was necessary. This involved tweaking settings, test-driving the vehicle, and repeating the process until a satisfactory air-fuel ratio was achieved.
Common Symptoms of Fuel Trim Issues (Pre-OBD2)
Even without the benefit of OBD2 diagnostics, certain symptoms could point to fuel trim problems in pre-OBD2 Ford vehicles:
-
Rough Idling: A rough or erratic idle, particularly when the engine is cold, could suggest an incorrect air-fuel mixture at idle speeds.
-
Hesitation or Stumbling: If the engine hesitates, stumbles, or lacks power during acceleration, it might be struggling to receive the correct fuel mixture under load.
-
Black Smoke from Exhaust: Black smoke billowing from the tailpipe generally indicates an overly rich air-fuel mixture, meaning too much fuel is being burned compared to air.
-
Poor Fuel Economy: While not always a direct indicator of fuel trim problems, a noticeable decrease in fuel efficiency could be a symptom of an imbalanced air-fuel ratio.
The Transition to OBD2
The introduction of OBD2 in the mid-1990s revolutionized automotive diagnostics, including the way fuel trims are monitored and adjusted.
OBD2 Advantages: OBD2 standardized diagnostic connectors, communication protocols, and trouble codes, making it significantly easier to identify and troubleshoot engine management issues, including those related to fuel trims.
Live Data Monitoring: With OBD2, mechanics gained the ability to view live data streams from various engine sensors, including those directly related to fuel trims. This real-time information enabled more precise diagnosis and adjustment.
 OBD2 Scanner Connected to Ford Vehicle
OBD2 Scanner Connected to Ford Vehicle
Conclusion
Understanding Ford fuel trims in the pre-OBD2 era requires a grasp of the mechanical and early electronic systems that governed fuel delivery and air-fuel mixture control. While diagnosing fuel trim issues in these older vehicles might have been more reliant on experience and deduction, the fundamental principles remain relevant.
The transition to OBD2 simplified the process, offering standardized diagnostics and live data that revolutionized automotive repair. Nevertheless, the knowledge of how fuel trims functioned before OBD2 remains valuable for those working on classic and vintage Ford models.

Leave a Reply