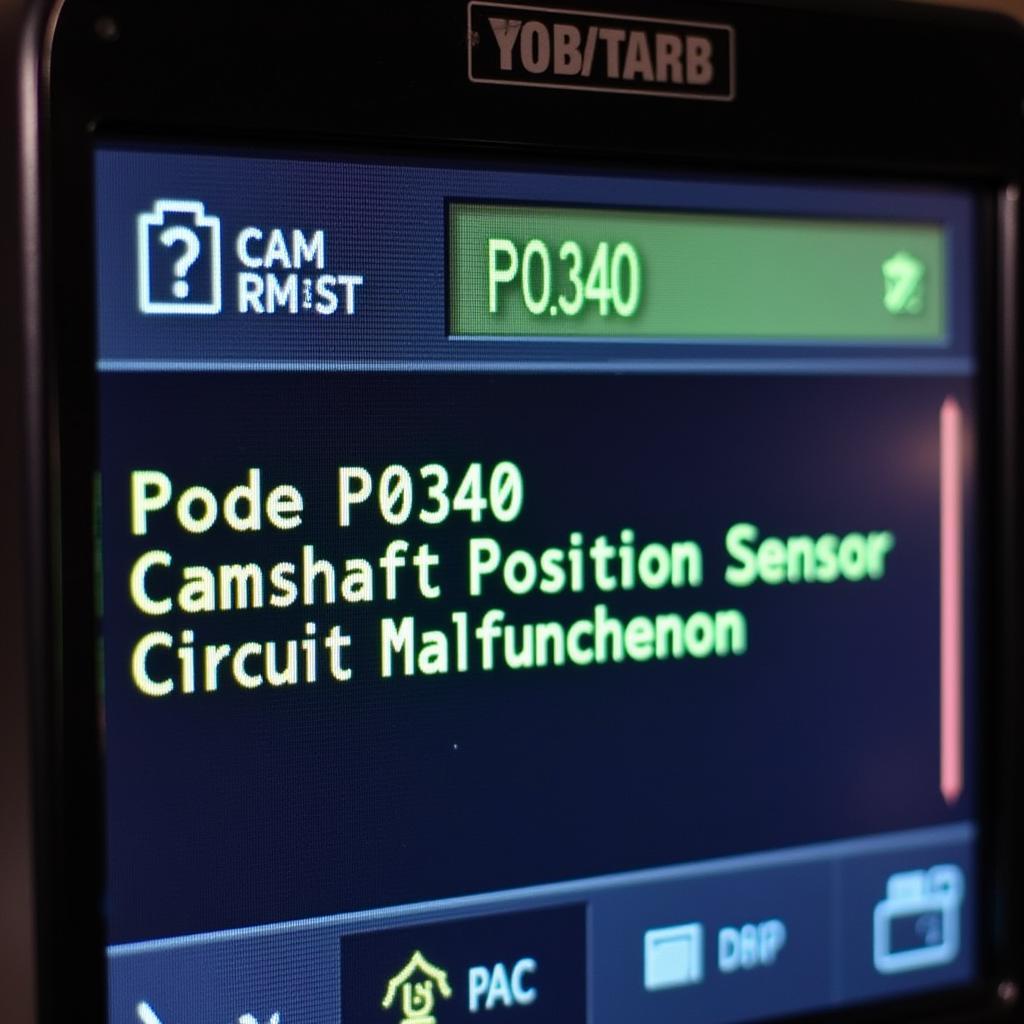
The dreaded check engine light has reared its ugly head, and your OBD2 scanner displays the cryptic code P0340. Don’t panic just yet! This article will guide you through understanding what OBD2 code P0340 means, its symptoms, common causes, and potential solutions. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a car enthusiast, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to tackle this issue head-on.
Decoding the P0340 Code
In simple terms, the P0340 code signals a problem with the camshaft position sensor circuit. This sensor is a vital component in your car’s engine management system. It monitors the rotation and position of the camshaft, providing crucial information to the Engine Control Unit (ECU). The ECU uses this data to control fuel injection timing and ignition spark, ensuring optimal engine performance and emissions.
Symptoms of a P0340 Code
When the camshaft position sensor circuit malfunctions, your car might exhibit a range of symptoms, such as:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light: This is often the first and most noticeable sign.
- Engine Stalling: The engine may stall frequently, especially when idling or coming to a stop.
- Rough Idling: You might experience vibrations or shaking when the engine is idling.
- Difficulty Starting: The car may be hard to start, requiring multiple attempts.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: The engine might consume more fuel than usual due to improper timing.
- Lack of Power: You may notice decreased acceleration and overall engine power.
Common Causes of a P0340 Code
The P0340 code can be triggered by several issues, ranging from simple wiring problems to more complex sensor failures. Here are the most common culprits:
- Faulty Camshaft Position Sensor: Over time, the sensor itself can wear out or fail due to exposure to heat, vibration, and engine fluids.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring and connectors in the sensor circuit can disrupt the signal transmission.
- Damaged Timing Belt or Chain: A worn or broken timing belt or chain can cause the camshaft to spin out of sync, leading to inaccurate sensor readings.
- Dirty or Low Engine Oil: Insufficient lubrication or contaminated oil can damage the sensor and affect its operation.
- Faulty ECU: While less common, a malfunctioning ECU can also trigger this code.
Diagnosing and Fixing a P0340 Code
“Diagnosing a P0340 code requires a systematic approach to pinpoint the root cause,” says John Smith, Senior Automotive Technician at ABC Mechanics. “Don’t jump to conclusions and start replacing parts randomly. It’s crucial to inspect and test each component thoroughly.”
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you troubleshoot the issue:
- Read the Code: Connect your OBD2 scanner best obd2 diagnostic tool and retrieve the stored codes. Note any other codes present, as they might be related.
- Inspect the Camshaft Position Sensor: Locate the sensor (refer to your vehicle’s repair manual) and examine it for any visible damage, such as cracks or corrosion.
- Check the Wiring and Connectors: Carefully inspect the wiring harness connected to the sensor for any signs of wear, cuts, or loose connections.
- Test the Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance and voltage output according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Inspect the Timing Belt/Chain: If you suspect a timing issue, consult a mechanic to inspect the belt or chain for proper tension and condition.
- Check the Engine Oil: Ensure that the engine oil level is adequate and that the oil is clean.
Conclusion
The P0340 code, while concerning, is a solvable problem. By understanding its causes and following the diagnostic steps outlined in this article, you can identify the issue and get your car back on the road. Remember, if you’re not comfortable working on your car, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
FAQs about OBD2 Code P0340
1. Can I still drive with a P0340 code?
While you might be able to drive short distances with a P0340 code, it’s not recommended. Driving with this issue can potentially lead to further engine damage and safety hazards.
2. How much does it cost to fix a P0340 code?
The repair cost depends on the underlying cause. A simple sensor replacement might cost around $100-$200, while a timing belt/chain replacement can range from $500 to over $1000.
3. Can a bad battery cause a P0340 code?
While a weak battery can sometimes cause sensor-related issues, it’s unlikely to be the primary cause of a P0340 code.
4. What other codes are related to P0340?
Other codes that might appear alongside P0340 include P0335 (Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction) and P0016 (Crankshaft Position – Camshaft Position Correlation).
5. Can I clean the camshaft position sensor?
While cleaning the sensor connector with electrical contact cleaner can sometimes help, if the sensor itself is faulty, it needs to be replaced.
6. Is it difficult to replace the camshaft position sensor myself?
The difficulty level varies depending on the car model. In some vehicles, it’s a relatively straightforward DIY task, while in others, it might require more advanced mechanical skills.
7. How often should the camshaft position sensor be replaced?
There’s no set replacement interval for the camshaft position sensor. It’s generally considered a reliable component with a long lifespan. However, it’s good practice to inspect it during regular maintenance checks.
Need help with a P0340 error code? Check out these resources:
- p0340 error codes for obd2 2004 dodge ram 1500
- what is obd2 code p0340
- dodge obd2 code p0340
- check timing belt obd2
For immediate assistance, contact our 24/7 support team via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880 or Email: [email protected].