The dreaded check engine light is illuminated on your dashboard, and you’ve connected your OBD2 scanner to see what’s wrong. You see the code P0151 staring back at you. What does it mean, and more importantly, what should you do about it?
This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the OBD2 code P0151, explaining its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions.
Understanding OBD2 Code P0151
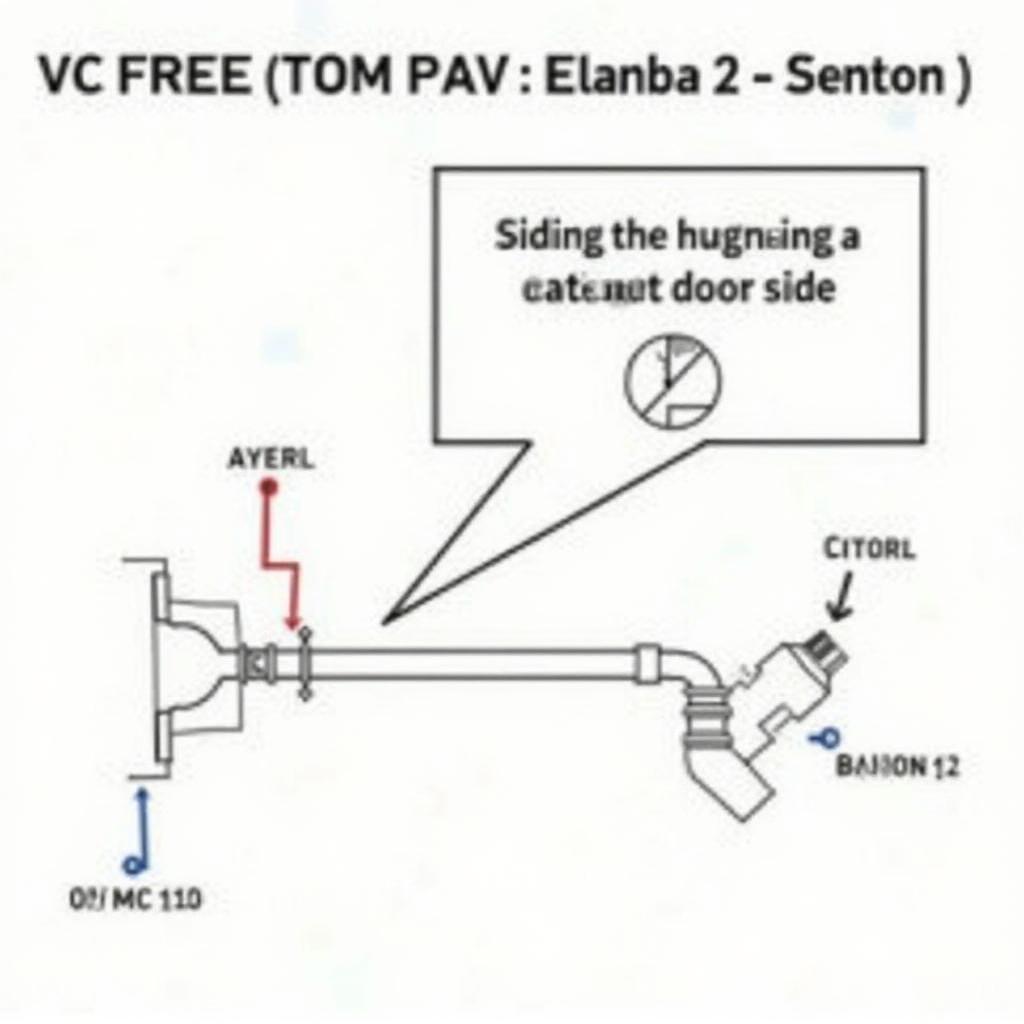
In essence, the P0151 code indicates a problem with the oxygen sensor (O2 sensor) circuit on Bank 2 Sensor 1. Let’s break this down:
- OBD2 Code: This refers to the standardized system your car uses to diagnose engine and emissions-related issues.
- P0151: This specific code signals a problem with the oxygen sensor circuit, specifically a slow response time.
- Bank 2: This refers to the side of the engine that doesn’t contain cylinder #1.
- Sensor 1: This indicates the upstream oxygen sensor, positioned before the catalytic converter.
What Causes a P0151 Code?
A slow response from the oxygen sensor often points to one of several issues:
- Failing Oxygen Sensor: Over time, oxygen sensors wear out, leading to sluggish responses and inaccurate readings. This is a common cause of the P0151 code.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust manifold, pipes, or near the sensor can introduce fresh air, disrupting the sensor’s ability to accurately measure oxygen levels.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring in the sensor circuit can disrupt the signal transmission, triggering the code.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the engine vacuum system can alter air/fuel ratios, indirectly affecting oxygen sensor readings.
- Faulty Fuel Pressure Regulator: An incorrect fuel pressure can lead to a rich or lean fuel mixture, impacting sensor performance.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU) Issues: While less common, problems with the ECU, which interprets data from the sensor, can sometimes be a factor.
Symptoms of a P0151 Code
Apart from the illuminated check engine light, you might experience some of these symptoms:
- Decreased Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to a less-than-optimal air-fuel mixture, reducing fuel efficiency.
- Rough Idle or Engine Stalling: An inaccurate oxygen sensor reading can disrupt the engine’s idle speed and stability.
- Failed Emissions Test: Since oxygen sensors are crucial for emissions control, a faulty sensor can cause your vehicle to fail emissions testing.
- Reduced Engine Performance: You might notice a decrease in engine power or acceleration due to the improper air/fuel mixture.
Diagnosing a P0151 Code
While this guide provides valuable information, it’s important to remember that self-diagnosis should be done cautiously. If you’re not comfortable working on your vehicle, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic.
Here’s a general approach to diagnosing a P0151 code:
-
Read the Code: Use your OBD2 scanner to retrieve the trouble code. Make note of any other codes stored, as they can provide additional clues.
-
Inspect for Visible Damage: Visually examine the oxygen sensor wiring harness, connectors, and the sensor itself for any signs of damage, corrosion, or looseness.
-
Check for Exhaust Leaks: Listen for any hissing sounds coming from the exhaust system, which could indicate a leak.
-
Test Sensor Voltage: Using a multimeter, check the voltage signal from the oxygen sensor. A healthy sensor should fluctuate between 0.1 volts (lean) and 0.9 volts (rich) when the engine is warm.
-
Inspect Vacuum Lines: Look for cracks, loose connections, or damage to the vacuum lines and components.
Fixing a P0151 Code
The solution to a P0151 code depends entirely on the underlying cause. Here are the most common fixes:
- Oxygen Sensor Replacement: If the sensor is worn out, replacing it is the most effective solution.
- Exhaust Leak Repair: Depending on the location and severity, exhaust leaks can be repaired by welding, sealing, or replacing damaged components.
- Wiring Repair/Replacement: Fix any damaged, corroded, or loose wiring in the sensor circuit.
Expert Insight: “When replacing an oxygen sensor, always use a high-quality OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or equivalent sensor. Cheap aftermarket sensors can lead to inaccurate readings and recurring problems,” advises John Miller, ASE Certified Master Technician.
Conclusion
The OBD2 code P0151 signals a potential issue with your vehicle’s oxygen sensor circuit, which can lead to reduced performance, increased emissions, and decreased fuel efficiency. By understanding this code, its causes, and potential solutions, you can take the necessary steps to diagnose and fix the problem, keeping your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
FAQs
1. Can I drive my car with a P0151 code?
It’s not advisable to drive for extended periods with a P0151 code. While it might seem like a minor issue, a malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to further engine problems or catalytic converter damage.
2. How much does it cost to replace an oxygen sensor?
Oxygen sensor replacement costs can vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle and labor rates. Generally, you can expect to pay between $200 and $400 for parts and labor.
3. How often should oxygen sensors be replaced?
Oxygen sensors typically last between 60,000 and 90,000 miles. However, it’s best to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific recommendations.
4. Can a bad catalytic converter cause a P0151 code?
While a faulty catalytic converter can cause other oxygen sensor codes, it’s less likely to directly trigger a P0151 code.
5. Can I clean my oxygen sensor instead of replacing it?
While some people attempt to clean oxygen sensors, it’s generally not a long-term solution. A worn-out sensor needs to be replaced.
Need Further Assistance?
Have more questions or need help diagnosing your car trouble? Contact our expert team via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, or Email: [email protected]. We offer 24/7 support to get you back on the road!
Explore More:
For more helpful OBD2 code explanations and troubleshooting guides, check out our other articles on OBDFree.com.