OBD2 IM, short for On-Board Diagnostics 2 Immobilizer, is a critical security feature in modern vehicles. This system plays a crucial role in preventing vehicle theft by disabling the engine’s starting or fuel system unless the correct key is present. This article delves into the intricacies of OBD2 IM systems, exploring their functionalities, diagnostic procedures, and common issues encountered.
How OBD2 IM Systems Work
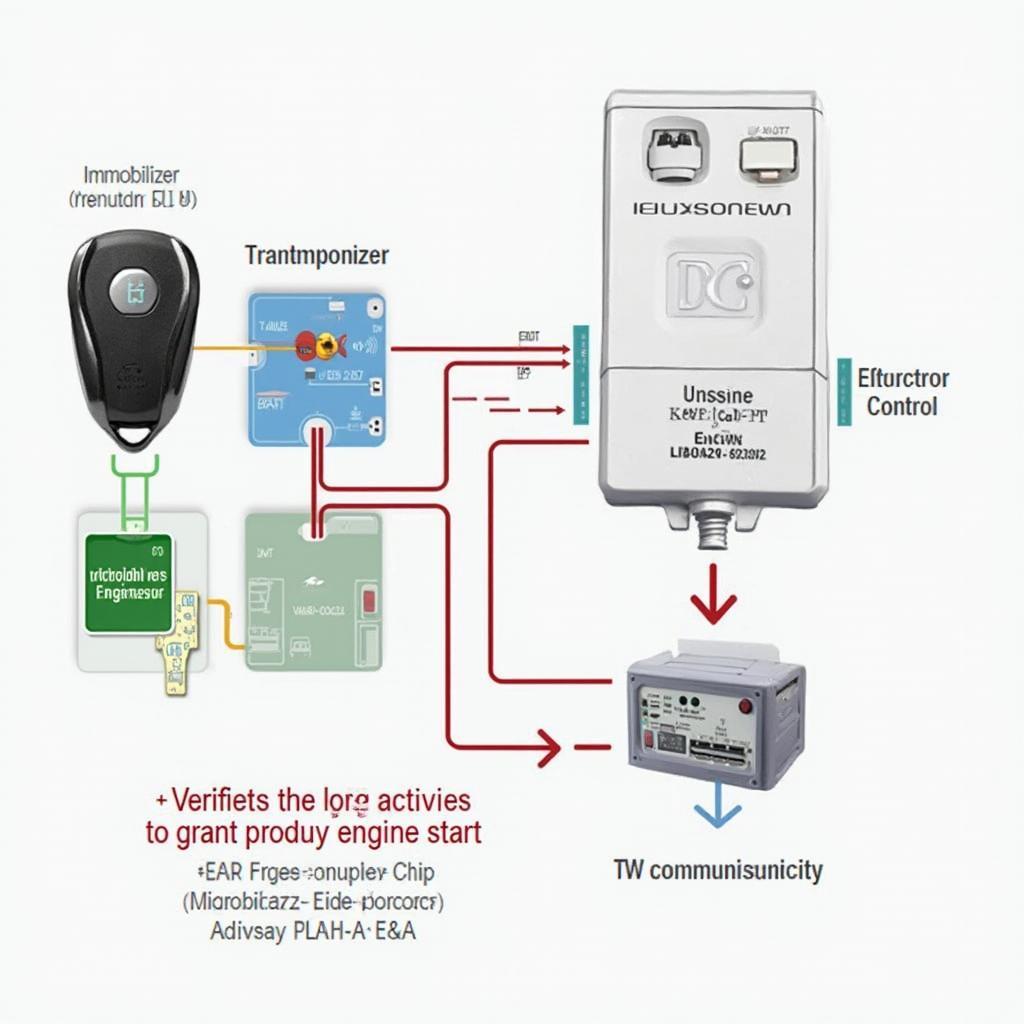
At the heart of the OBD2 IM system lies a transponder chip embedded within the vehicle’s ignition key. This chip communicates with the vehicle’s immobilizer control unit (ICU) when the key is inserted or in close proximity. The ICU, in turn, interacts with the engine control unit (ECU) to either permit or deny engine operation.
Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Key Insertion: When you insert the key into the ignition, the ICU emits an electromagnetic signal, energizing the transponder chip in the key.
- Chip Activation: The activated chip transmits a unique identification code back to the ICU.
- Code Verification: The ICU compares the received code with its stored database of authorized keys.
- Authorization: If the codes match, the ICU sends a signal to the ECU, authorizing the engine to start.
- Immobilization: If the codes don’t match or there’s a communication error, the ICU blocks the engine start by interrupting vital engine functions like fuel delivery or ignition.
Diagnosing OBD2 IM Issues
Troubleshooting OBD2 IM problems often involves using an OBD2 scanner capable of reading immobilizer-related diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes provide valuable insights into the nature of the fault, aiding in efficient repairs.
Here are some steps involved in diagnosing OBD2 IM issues:
- Connect OBD2 Scanner: Begin by connecting a compatible OBD2 scanner to your vehicle’s 16-pin diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Read DTCs: Power on the scanner and access the vehicle’s computer system. Select the option to read diagnostic trouble codes. Note down any IM-related codes displayed.
- Interpret Codes: Consult your vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online database to decipher the meaning of the retrieved codes. Each code corresponds to a specific fault within the immobilizer system.
- Further Diagnosis: Based on the code interpretation, you can proceed with further diagnostic procedures. This may involve inspecting wiring harnesses for damage, testing sensors, or checking the integrity of the transponder chip in the key.
Common OBD2 IM Problems
OBD2 IM systems, though generally robust, can encounter issues that prevent the engine from starting. Here are some frequent culprits:
- Faulty Transponder Chip: A damaged or deprogrammed transponder chip in the key is a common reason for immobilizer problems. This can occur due to wear and tear, physical damage to the key, or exposure to electromagnetic interference.
- Malfunctioning ICU: The immobilizer control unit itself can fail due to electrical faults, software glitches, or exposure to harsh environmental conditions.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring connections between the key, ICU, and ECU can disrupt communication, leading to immobilizer malfunctions.
- Weak Key Battery: Some vehicles utilize keys with batteries that power the transponder chip. A weak or dead key battery can prevent proper communication with the ICU.
vag drive box edc15 me7 obd2 immo
Certain specialized tools and devices are available for more advanced diagnostics and repairs related to OBD2 IM systems. These tools can offer functionalities beyond those of standard OBD2 scanners.
Conclusion
OBD2 IM systems have become an integral part of modern vehicle security, effectively deterring theft and unauthorized access. Understanding the workings of these systems, their diagnostic procedures, and common issues can prove invaluable for both vehicle owners and automotive professionals. Regular maintenance, proper key handling, and timely diagnosis of any immobilizer-related problems can go a long way in ensuring the smooth operation of your vehicle’s security system.