OBD2 control module codes, those cryptic combinations of letters and numbers displayed on your OBD2 scanner, can feel like a foreign language. But understanding these codes is crucial to diagnosing and fixing your vehicle’s issues. This guide dives deep into the world of OBD2 control module codes, providing you with the knowledge to decipher these digital messages and take control of your car’s health.
What are OBD2 Control Module Codes?
Your car is a complex network of electronic systems, each controlled by a dedicated module. These modules constantly communicate with each other, ensuring everything runs smoothly. When a module detects a problem, it generates an OBD2 control module code, storing it in the vehicle’s onboard computer.
Think of these codes as your car’s way of saying, “Hey, something’s not right here.” An OBD2 scanner acts as the translator, allowing you to understand these messages and pinpoint the source of the problem.
Types of OBD2 Control Module Codes
There are several types of OBD2 control module codes, each indicating a different type of issue:
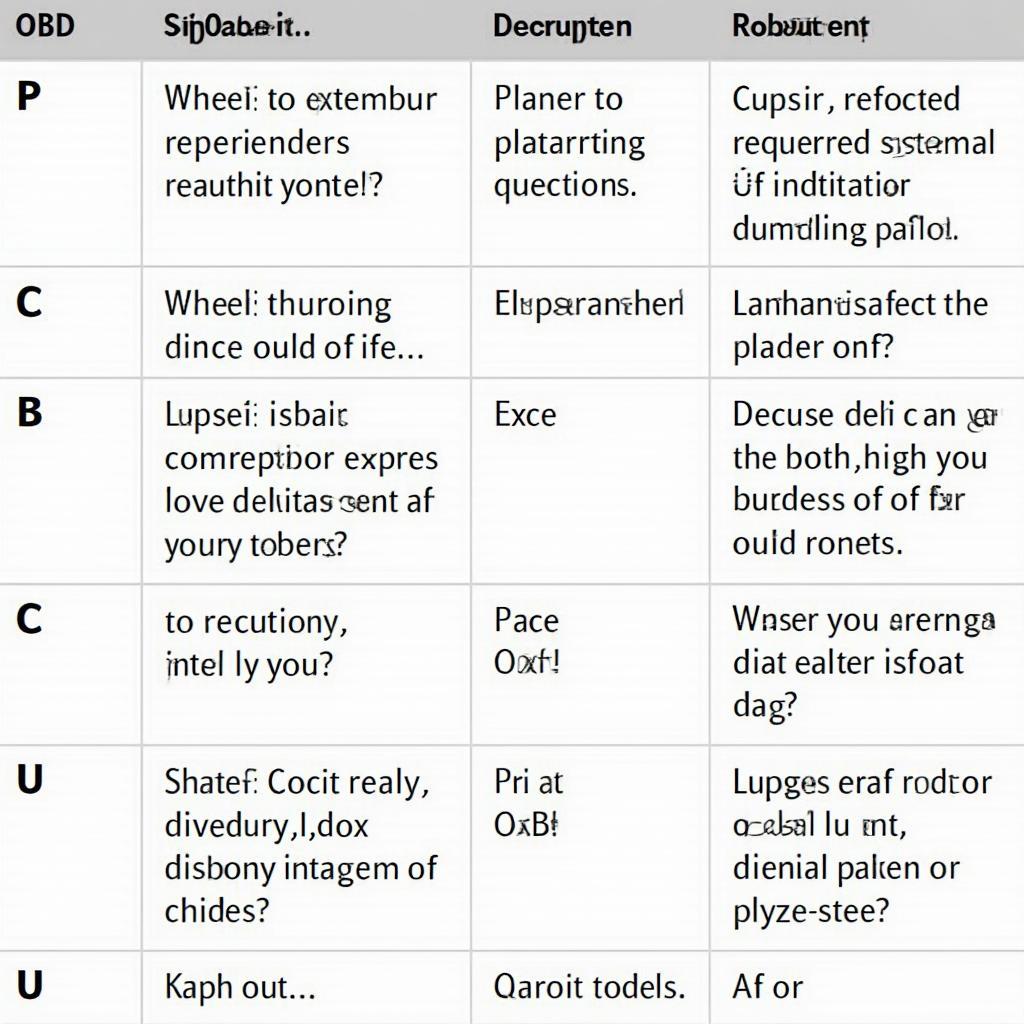
- Powertrain (P Codes): These codes relate to the engine, transmission, and emission control systems. They are the most common type of OBD2 code.
- Body (B Codes): B codes point to problems with body electronics, such as power windows, airbags, and central locking.
- Chassis (C Codes): These codes signal issues with the chassis systems, including anti-lock brakes (ABS), traction control, and suspension.
- Network Communication (U Codes): U codes indicate problems with the communication network between different modules in the vehicle.
 Types of OBD2 Codes
Types of OBD2 Codes
Understanding OBD2 Control Module Code Structure
Each OBD2 control module code follows a specific structure, providing valuable clues about the problem:
- The First Character: This letter indicates the system where the fault lies (P, B, C, or U).
- The Second Character: This number signifies whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- The Third Character: This number identifies the specific system or subsystem affected (e.g., 1 for fuel and air metering, 3 for ignition system).
- The Last Two Characters: These numbers represent the specific fault within the identified system.
For example, the code “P0301” translates to:
- P: Powertrain
- 0: Generic code
- 3: Ignition System
- 01: Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
Common OBD2 Control Module Codes and Their Meanings
While countless OBD2 control module codes exist, some appear more frequently than others. Here are a few examples:
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) – This code indicates a problem with the catalytic converter, often caused by a faulty oxygen sensor or engine misfires.
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1) – This code suggests the engine is running lean, meaning there’s too much air compared to fuel. This could be due to a vacuum leak, a faulty mass airflow sensor, or a fuel delivery issue.
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected – This code indicates that one or more cylinders in the engine are misfiring, which can cause rough idling, poor acceleration, and reduced fuel economy.
What to Do When You Encounter an OBD2 Control Module Code
Discovering an OBD2 control module code can feel daunting, but it doesn’t necessarily spell disaster. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Don’t Panic: A code doesn’t always mean an immediate breakdown is imminent. It serves as an early warning system, giving you time to address the issue.
- Record the Code: Write down the exact code displayed on your OBD2 scanner. This information is crucial when researching the problem or consulting with a mechanic.
- Research the Code: Numerous online resources, including OBDFree, provide detailed information about specific OBD2 control module codes.
- Check for Loose Connections or Damaged Wiring: Sometimes, a simple loose connection or damaged wire can trigger a code. Before delving deeper, visually inspect the affected system for any obvious issues.
- Reset the Code: After addressing the potential problem, reset the code using your OBD2 scanner. This clears the code from the computer’s memory and allows you to monitor if it returns.
- Seek Professional Help: If the code persists or you’re uncomfortable diagnosing the issue yourself, consult a qualified mechanic. They possess the expertise and tools to diagnose and repair your vehicle effectively.
OBD2 Control Module Codes: Your Car’s Cryptic Language, Now Decoded
Understanding OBD2 control module codes empowers you to take charge of your vehicle’s maintenance and repair. By recognizing the warning signs and taking prompt action, you can prevent minor issues from escalating into major headaches down the road. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to keeping your car running smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Control Module Codes
1. Can I drive my car with an OBD2 control module code?
It depends on the code’s severity. Some codes indicate minor issues that might not affect drivability immediately. However, ignoring codes can lead to further damage and more costly repairs. It’s best to research the code’s potential impact and err on the side of caution.
2. Can I reset an OBD2 control module code myself?
Yes, you can reset codes using an OBD2 scanner. However, simply clearing the code doesn’t fix the underlying problem. If the issue persists, the code will reappear.
3. Are generic OBD2 scanners as good as manufacturer-specific ones?
Generic scanners can read and reset most common OBD2 codes. However, manufacturer-specific scanners might offer more detailed information and access to proprietary codes.
4. How often should I check for OBD2 control module codes?
It’s a good practice to check for codes periodically, especially if you notice any changes in your vehicle’s performance. Many experts recommend checking at least once a month or before long trips.
5. Can extreme temperatures affect OBD2 control module codes?
Yes, extreme temperatures can impact sensor readings and potentially trigger codes. If you live in an area with extreme weather, be mindful of this possibility.
6. Do all cars have the same OBD2 control module codes?
While the OBD2 system is standardized, manufacturers may have specific codes for their vehicles. However, the most common codes are generally universal.
7. Can I prevent OBD2 control module codes from appearing?
Regular vehicle maintenance, such as oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug replacements, can help prevent many common codes.
p219a chevy silverado obd2 fault code
Need further assistance with OBD2 control module codes? Contact our team of automotive experts via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected]. We’re available 24/7 to help you decode your car’s messages and get back on the road with confidence!