Your cart is currently empty!
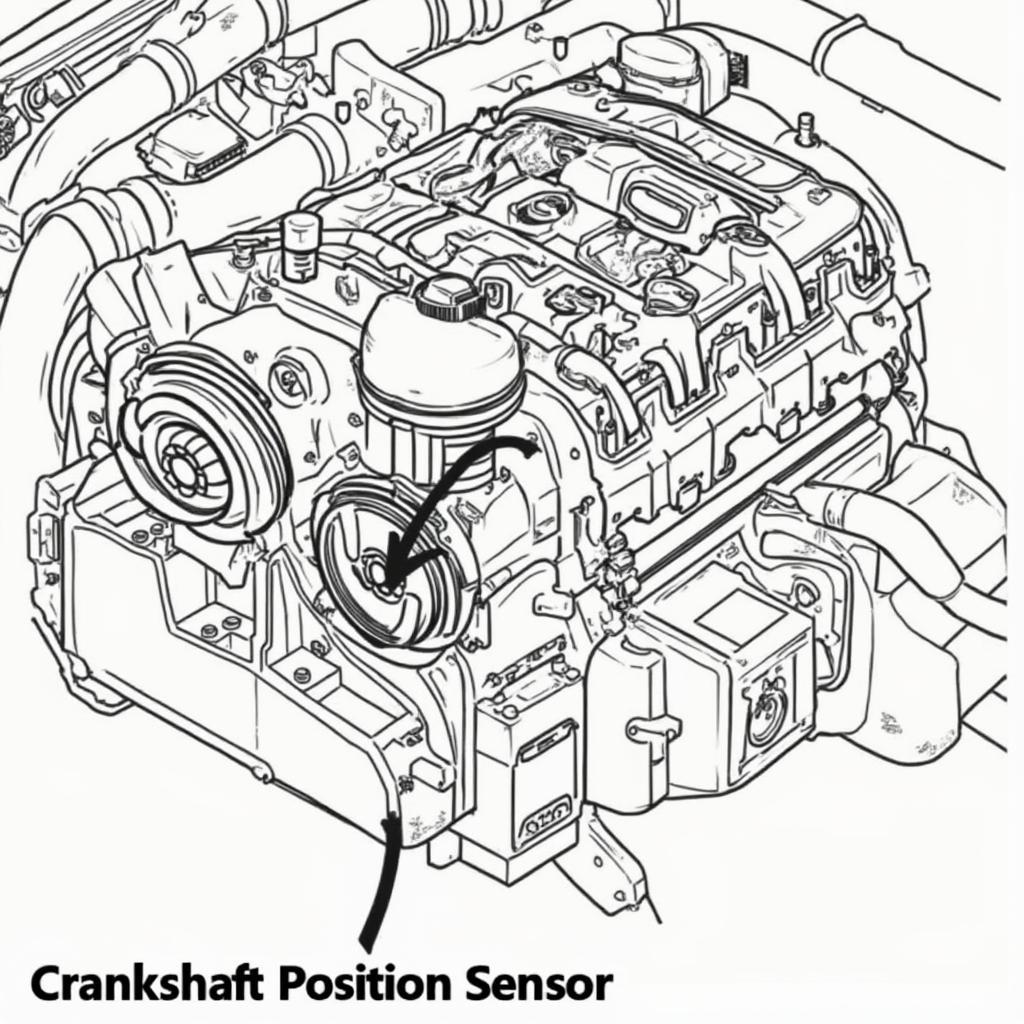
OBD2 Crankshaft Positioning Sensor: What It Is and Why It’s Crucial
The crankshaft positioning sensor (CKP) is a vital component of your vehicle’s engine management system. This small but mighty sensor provides critical information to the engine control unit (ECU), allowing it to determine the position and speed of the crankshaft. This data is essential for the ECU to control ignition timing and fuel injection, ensuring your engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
Understanding the Role of a Crankshaft Position Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor acts like the eyes of your engine, constantly monitoring the crankshaft’s rotation. Imagine a bicycle: the faster you pedal, the faster the crankshaft rotates. In a car, the CKP sensor detects this rotation and relays this information to the ECU. The ECU uses this data to calculate the engine speed (RPM) and the precise position of each piston.
 crankshaft sensor location
crankshaft sensor location
Why is this important? Without accurate information from the CKP sensor, the ECU wouldn’t know when to spark the spark plugs or inject fuel. This can lead to a range of engine performance issues, from misfires to a complete stall.
Common Symptoms of a Failing Crankshaft Position Sensor
A failing crankshaft position sensor can manifest itself through a variety of symptoms, often making it difficult to diagnose without proper tools. Here are some common signs:
- Engine Stalling: One of the most common and frustrating symptoms is engine stalling. This occurs because the ECU loses track of the crankshaft’s position and can’t provide the correct ignition timing, leading to the engine cutting out unexpectedly.
- Difficult Starting: Similar to stalling, a bad CKP sensor can make it difficult to start your car. Since the ECU relies on the sensor to determine the engine’s starting position, a faulty sensor can prevent the ignition system from functioning correctly.
- Misfires and Rough Idle: When the CKP sensor provides inconsistent signals, it can lead to mistimed ignition sparks and fuel injection. This can cause the engine to misfire, resulting in a rough idle, vibrations, and decreased engine performance.
- Check Engine Light: Often, a failing crankshaft position sensor will trigger the check engine light on your dashboard. This is the ECU’s way of alerting you to a problem within the engine management system, and it’s essential to get it checked out immediately.
- Reduced Fuel Economy: Inconsistent signals from the CKP sensor can disrupt the optimal air-fuel mixture, leading to reduced fuel efficiency.
Diagnosing a Crankshaft Position Sensor Problem
Diagnosing a crankshaft position sensor issue typically requires specialized equipment like an OBD2 scanner. This tool allows you to read the error codes stored in the ECU, which can pinpoint the problem to the CKP sensor.
However, even with an OBD2 scanner, it’s essential to rule out other potential issues that could cause similar symptoms, such as:
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring to the CKP sensor can disrupt the signal transmission.
- Faulty ECU: While less common, a malfunctioning ECU can also lead to problems with the crankshaft position sensor readings.
Importance of Using a Reliable OBD2 Scanner
Using a reliable OBD2 scanner is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair. A quality scanner will provide:
- Accurate Error Code Reading: Ensuring you get the right codes for the CKP sensor.
- Live Data Stream: Allowing you to monitor the sensor’s readings in real time.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your car’s make and model.
Conclusion
The crankshaft position sensor plays a crucial role in your vehicle’s engine management system. Understanding its function and the symptoms of a failing sensor can help you address problems quickly and prevent potential engine damage. Remember, a reliable OBD2 scanner is your best friend when it comes to diagnosing and resolving CKP sensor issues, keeping your engine running smoothly for miles to come.

Leave a Reply