The OBD2 port, often found under the driver’s side dashboard, is the gateway to your car’s internal network. Understanding the “OBD2 pinout male” is crucial for anyone who wants to delve into vehicle diagnostics, troubleshoot issues, or even customize their car’s performance. This guide will take you through every pin on the male OBD2 connector, explaining its function and significance in detail.
Decoding the OBD2 Pinout Male
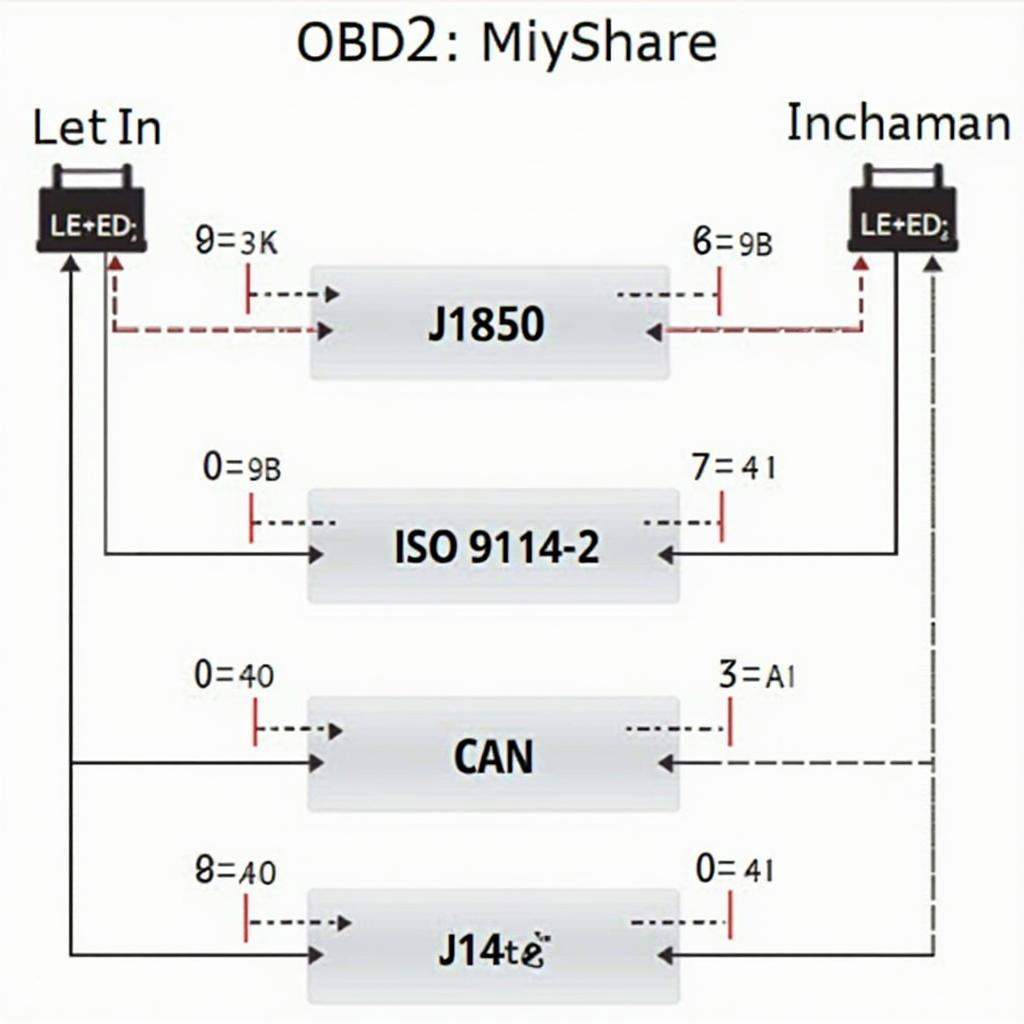
The OBD2 connector is a standardized 16-pin interface, with each pin assigned a specific function. Let’s break down the role of each pin:
-
Pin 1 (Manufacturer Discretionary): As the name suggests, the use of this pin varies depending on the car manufacturer. Some manufacturers might use it for communication protocols specific to their vehicles, while others might leave it unused.
-
Pin 2 (J1850 Bus+): Primarily used by US-based car manufacturers, this pin facilitates communication on the J1850 Bus+, a network protocol for data transmission within the vehicle.
-
Pin 3 (Manufacturer Discretionary): Similar to Pin 1, the functionality of this pin is determined by the manufacturer and can vary across different car makes and models.
-
Pin 4 (Chassis Ground): This pin provides a ground connection for the chassis, ensuring a stable electrical reference point for the OBD2 system.
-
Pin 5 (Signal Ground): Unlike Pin 4, this pin serves as a ground for signals transmitted through the OBD2 connector, crucial for accurate data interpretation.
-
Pin 7 (ISO 9141-2 K-Line): Found in many European and Asian vehicles, this pin facilitates communication using the ISO 9141-2 protocol, another standard for data transmission in vehicles.
-
Pin 8 (Battery Power): This pin provides a direct connection to the vehicle’s battery, supplying power to the OBD2 scanner and enabling communication with the vehicle’s computer.
-
Pin 9 (Manufacturer Discretionary): Like Pins 1 and 3, this pin’s function is manufacturer-specific and might not be used in all vehicles.
-
Pin 10 (J1850 Bus-): Working in conjunction with Pin 2, this pin completes the J1850 Bus communication pathway used in certain vehicle makes.
-
Pin 11 (Manufacturer Discretionary): Another manufacturer-specific pin whose use can differ significantly between vehicle brands and models.
-
Pin 12 (Manufacturer Discretionary): Similar to the previous pins, the functionality of Pin 12 is at the discretion of the manufacturer.
-
Pin 13 (ISO 9141-2 L-Line): Complementing Pin 7, this pin forms the second line required for communication using the ISO 9141-2 protocol, commonly found in specific car models.
-
Pin 14 (CAN High (CAN-H)): This pin represents the high signal line for the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus, a robust and widely used communication protocol in modern vehicles.
-
Pin 15 (CAN Low (CAN-L)): Completing the CAN bus communication pathway, this pin carries the low signal line, working in tandem with Pin 14 to transmit data efficiently.
-
Pin 16 (Battery Positive): This pin acts as a secondary power source, providing an alternative connection to the battery positive terminal for increased reliability.
Importance of Understanding the OBD2 Pinout Male
Knowing the pin configuration of the OBD2 connector is not just for professional mechanics. It’s invaluable for any car enthusiast or owner for several reasons:
-
DIY Diagnostics: By understanding which pins correspond to specific functions, you can use a multimeter or other diagnostic tools to troubleshoot basic car problems, potentially saving you time and money.
-
Vehicle Customization: For those interested in modifying their cars, knowing the OBD2 pinout allows for connecting aftermarket devices like performance tuners or data loggers, unlocking further control over your vehicle.
-
Choosing the Right Scanner: With numerous OBD2 scanners available, understanding the different communication protocols and their corresponding pins helps you select a scanner compatible with your specific car model.
“Knowing the OBD2 pinout is like having a map to your car’s brain,” says automotive electronics expert, Robert Hernandez. “It empowers you to understand how your car communicates and allows you to tap into its potential for diagnostics and modifications.”
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Applications of OBD2 Pinout
The knowledge of OBD2 pinout male unlocks a world of possibilities beyond basic diagnostics. Here are some advanced applications:
-
Data Logging and Analysis: By tapping into specific data streams through the corresponding pins, you can collect valuable information about your car’s performance, fuel efficiency, and even driving habits. This data can be analyzed to optimize your car’s performance and identify potential issues before they escalate.
-
Custom Wiring Projects: For complex modifications, understanding the pinout allows you to integrate custom wiring harnesses or connect external devices seamlessly, expanding the capabilities of your vehicle’s electrical system.
-
Troubleshooting Communication Errors: When encountering communication issues between your scanner and the car’s computer, familiarity with the pinout helps you pinpoint potential problems like faulty wiring or incompatible protocols, streamlining the troubleshooting process.
Common Questions about OBD2 Pinout Male
1. Are all OBD2 pinouts the same?
While the physical connector is standardized, the functionality of specific pins, particularly the manufacturer discretionary ones, can vary between car manufacturers and models. It’s essential to consult your vehicle’s service manual for the exact pinout configuration.
2. Can I damage my car by probing the OBD2 pins?
While the OBD2 system is relatively protected, it’s crucial to exercise caution when probing the pins. Always use a multimeter set to the appropriate voltage and current settings to avoid potential damage to the vehicle’s electronics.
3. Can I make my own OBD2 cable?
Yes, with the right knowledge and tools, it’s possible to create your own OBD2 cables for specific applications. However, this requires careful attention to wiring diagrams, soldering techniques, and ensuring proper insulation to prevent short circuits or damage to your vehicle.
4. Where can I find reliable information about my car’s OBD2 pinout?
The most reliable source for your car’s specific OBD2 pinout is the vehicle’s service manual. Additionally, online resources like OBDFree provide comprehensive information on OBD2 systems, pinouts, and related topics.
5. Is it legal to modify my car using the OBD2 port?
The legality of modifying your car through the OBD2 port varies depending on your location and the specific modifications made. It’s crucial to research local regulations and consult with certified professionals to ensure your modifications comply with all applicable laws and safety standards.
homemade-how-to-make-obd2-to-usb-cable
Conclusion
Mastering the OBD2 pinout male opens a door to a deeper understanding of your vehicle’s inner workings. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a car enthusiast eager to delve into diagnostics and modifications, this knowledge empowers you to take control of your car’s health and performance.
Remember, while this guide provides valuable insights into the OBD2 pinout male, always consult your vehicle’s service manual and seek advice from qualified professionals when performing any diagnostics or modifications.
Need further assistance with OBD2 systems or car diagnostics? Contact our expert team through WhatsApp at +1(641)206-8880 or email us at [email protected]. We are available 24/7 to answer your questions and provide expert guidance.