The Ford OBD2 P0147 code indicates a problem with the oxygen sensor (O2 sensor) circuit low voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 3). This code specifically points to a voltage issue in the downstream oxygen sensor after the catalytic converter. Let’s delve into the details of this trouble code, understanding its causes, symptoms, and how to fix it.
What Does the Ford OBD2 P0147 Code Mean?
The P0147 code tells us that the powertrain control module (PCM) has detected a low voltage signal from the downstream oxygen sensor on bank 1. Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine where cylinder number 1 is located. Sensor 3 indicates the downstream sensor, positioned after the catalytic converter. The downstream O2 sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the efficiency of the catalytic converter. A low voltage reading suggests a problem with the sensor itself, the wiring, or the sensor’s heater circuit.
Causes of the Ford OBD2 P0147 Code
Several factors can trigger the P0147 code in your Ford vehicle. Here are some of the most common culprits:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The sensor itself may be worn out or damaged, leading to inaccurate voltage readings.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged, corroded, or shorted wiring in the sensor circuit can disrupt the voltage signal.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system before the sensor can introduce outside air, affecting the sensor’s readings.
- Faulty Catalytic Converter: While less common, a failing catalytic converter can also contribute to this code.
- Blown Fuse: A blown fuse in the sensor’s circuit can interrupt power supply.
- PCM Issues: Rarely, a faulty PCM can be the underlying cause, though it’s essential to rule out other possibilities first.
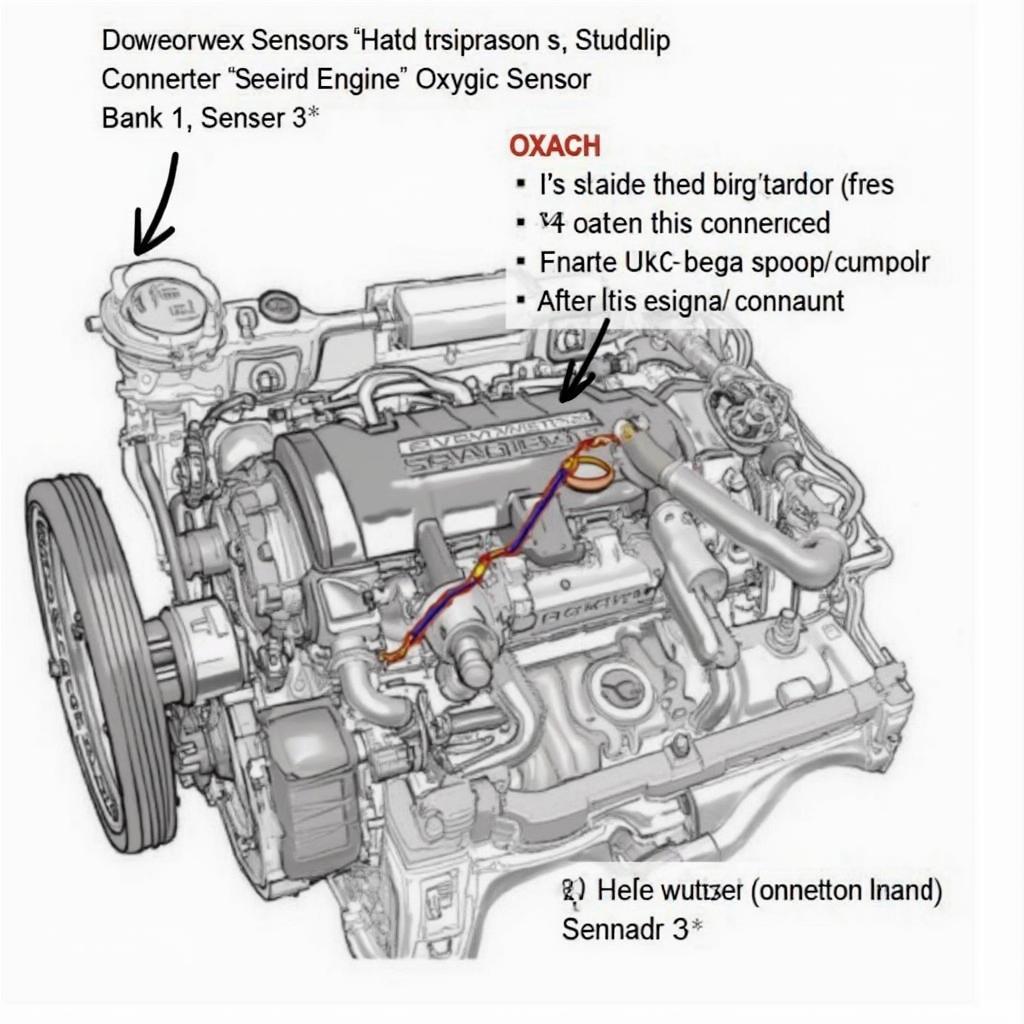 Ford OBD2 P0147 Oxygen Sensor Location
Ford OBD2 P0147 Oxygen Sensor Location
Symptoms of the Ford OBD2 P0147 Code
While the check engine light is the most obvious sign, other symptoms can accompany the P0147 code:
- Decreased Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning O2 sensor can lead to inefficient fuel consumption.
- Rough Idle or Stalling: Though less common, these issues can arise due to the inaccurate data being sent to the PCM.
- Failed Emissions Test: A faulty downstream O2 sensor can directly impact your vehicle’s emissions output.
How to Fix the Ford OBD2 P0147 Code
Addressing the P0147 code requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Retrieve the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to confirm the P0147 code and check for any other related codes.
- Inspect the Wiring: Thoroughly examine the wiring and connector for any damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Repair or replace as needed.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Inspect the exhaust system for any leaks before the downstream sensor. Repair any leaks found.
- Test the Oxygen Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s voltage output and heater circuit resistance. Replace the sensor if it fails the test.
- Check the Fuse: Inspect the fuse related to the oxygen sensor circuit. Replace if blown.
- Consult a Professional: If the issue persists, consult a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and repair. They might need to test the catalytic converter or check the PCM.
What if I Ignore the Ford OBD2 P0147 Code?
Ignoring the P0147 code can lead to further problems, including potential damage to the catalytic converter, decreased fuel efficiency, and failed emissions tests. Addressing the issue promptly can prevent these complications and ensure the optimal performance of your Ford vehicle.
Conclusion
The Ford OBD2 P0147 code signals a problem with the downstream oxygen sensor circuit. By understanding the potential causes, symptoms, and diagnostic steps, you can effectively address this issue and keep your Ford running smoothly. Don’t delay in diagnosing and fixing the problem to prevent potential damage to other components and maintain optimal fuel efficiency.
FAQ
- What does Bank 1 Sensor 3 mean? Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine with cylinder 1, and Sensor 3 is the downstream oxygen sensor located after the catalytic converter.
- Can I drive with a P0147 code? While you can technically drive, it’s best to address the issue promptly to prevent further problems.
- How much does it cost to replace an oxygen sensor? The cost varies depending on the make and model but typically ranges from $100 to $300.
- Will replacing the oxygen sensor fix the problem? Replacing the sensor is often the solution, but other issues, such as wiring problems or exhaust leaks, might also be involved.
- Can I replace the oxygen sensor myself? Yes, with basic mechanical skills and tools, you can often replace the sensor yourself.
- How can I prevent the P0147 code from recurring? Regular maintenance, including checking for exhaust leaks and ensuring proper wiring connections, can help prevent this code.
- What other codes are related to the P0147 code? Related codes can include P0136, P0137, P0138, and P0139, which also relate to oxygen sensor issues.
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, or Email: [email protected]. Our customer support team is available 24/7.
