OBD2 EVAP codes are related to your vehicle’s Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system, which prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. These codes can be confusing, but understanding them is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and minimizing its environmental impact. This guide provides a detailed explanation of OBD2 EVAP codes, their causes, and how to address them.
What are OBD2 EVAP Codes?
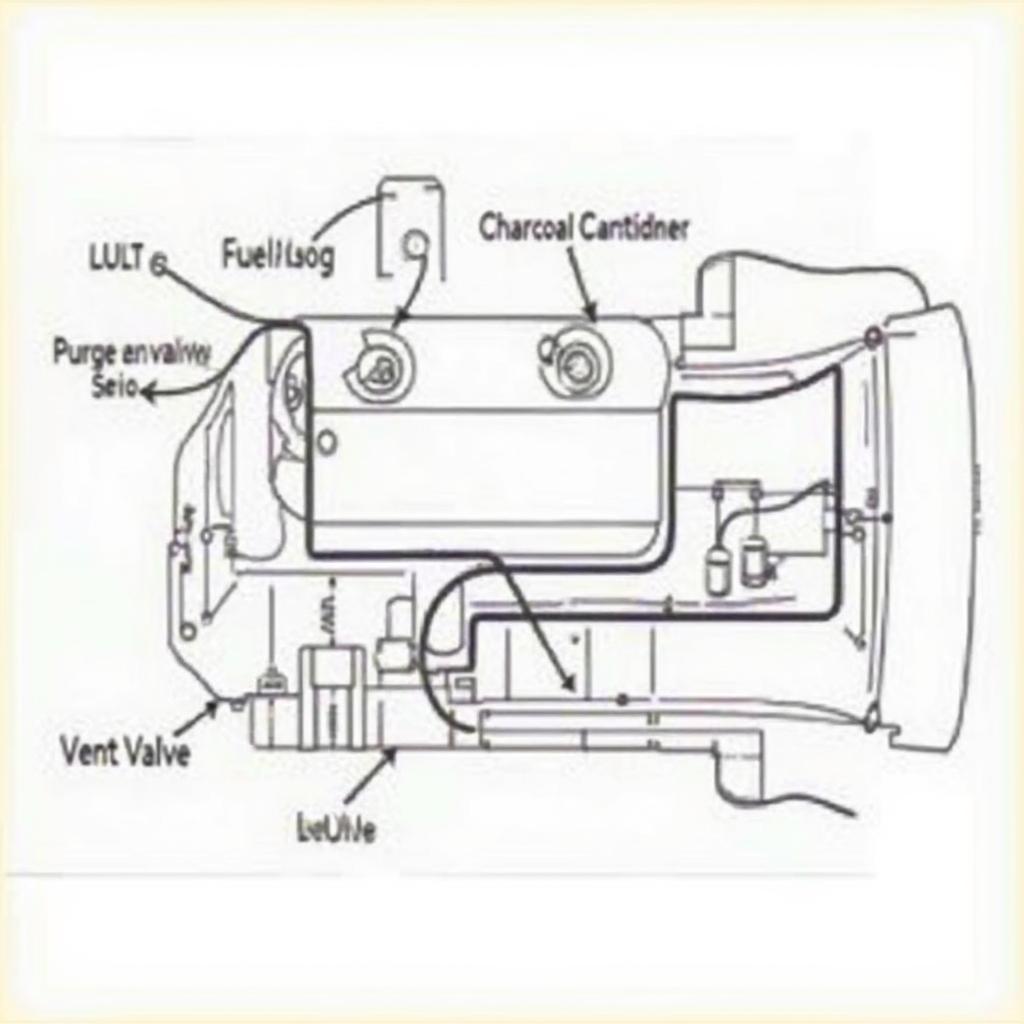
The EVAP system captures fuel vapors from the fuel tank and stores them in a charcoal canister. When the engine is running, these vapors are purged from the canister and burned in the engine. The OBD2 system monitors this process and triggers a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), or an EVAP code, if it detects a leak or malfunction. These codes help pinpoint the issue within the complex EVAP system. Knowing what these codes signify can save you time and money on repairs. For instance, an lt1 obd2 evap code relates to a specific type of engine and can narrow down your troubleshooting process.
Common OBD2 EVAP Codes and Their Meanings
Several EVAP codes can appear, each indicating a different problem area. Some of the most common include:
- P0440: Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction. This is a general code indicating a problem somewhere in the EVAP system.
- P0441: Incorrect Purge Flow. This code suggests an issue with the purge valve or its control circuit.
- P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak). This indicates a small leak in the system, often a loose gas cap.
- P0446: Evaporative Emission Control System Vent Control Circuit Malfunction. This points to a problem with the vent valve or its circuit.
- P0455: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Gross Leak). This code signifies a large leak, such as a cracked hose or damaged canister. Addressing these issues quickly helps protect the environment and ensures your vehicle runs smoothly.
Understanding these common codes is the first step to diagnosis. However, pinpointing the exact cause requires further investigation. Remember, a small leak detected now can prevent more serious issues later.
Diagnosing OBD2 EVAP Codes: A Step-by-Step Guide
Diagnosing EVAP codes often involves a systematic approach:
- Check the Gas Cap: The most common cause of a P0442 code is a loose or damaged gas cap. Ensure it’s tightly sealed.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect all EVAP system components, including hoses, lines, and the canister, for cracks, damage, or loose connections.
- Smoke Test: A smoke test introduces smoke into the EVAP system to pinpoint leaks. This method effectively identifies even the smallest leaks.
- Scan Tool Diagnostics: Use an OBD2 scanner to read the specific code and access live data to monitor EVAP system performance. The 95 xj obd2 guide might provide valuable information for older Jeep models.
- Component Testing: Test individual components, such as the purge valve and vent valve, using a multimeter or other diagnostic tools. You might need a specialized scanner like one of the best obd2 scanners for year 1999 asian vehicles.
By following these steps, you can systematically narrow down the problem and identify the faulty component. Remember to check for related issues. For example, obd2 p0442 with p0172 p0175 might point to a combined EVAP and fuel system problem.
Why are OBD2 EVAP Codes Important?
Addressing OBD2 EVAP codes is crucial for several reasons:
- Environmental Protection: The EVAP system prevents harmful fuel vapors from polluting the atmosphere.
- Vehicle Performance: EVAP system problems can sometimes lead to drivability issues, such as rough idling or poor fuel economy.
- Passing Emissions Tests: A functioning EVAP system is essential for passing state-mandated emissions tests. Information on 00 volvo obd2 can be helpful for Volvo owners.
- Preventing Further Damage: Ignoring EVAP codes can lead to more serious and costly repairs down the line.
What Causes OBD2 EVAP Codes?
- Loose or Damaged Gas Cap: A loose or cracked gas cap is the most frequent culprit.
- Cracked or Leaking Hoses and Lines: Exposure to heat and weather can cause hoses and lines to deteriorate.
- Faulty Purge or Vent Valve: These valves control the flow of vapors within the system and can malfunction over time.
- Damaged Charcoal Canister: The canister can become saturated or damaged, preventing it from effectively absorbing vapors.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your EVAP System
Understanding OBD2 EVAP codes empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s emissions and performance. By addressing these codes promptly and effectively, you contribute to a cleaner environment and ensure your vehicle operates efficiently. Don’t ignore these seemingly minor issues, as they can escalate into significant problems if left unchecked.
FAQ
- What does EVAP stand for? EVAP stands for Evaporative Emission Control.
- What is the most common EVAP code? P0442 (Small EVAP leak) is often caused by a loose gas cap.
- Can I drive my car with an EVAP code? You can usually drive with an EVAP code, but it’s best to address it promptly.
- How much does it cost to fix an EVAP leak? The cost varies depending on the cause and can range from a few dollars for a gas cap to hundreds for more complex repairs.
- How do I prevent EVAP codes? Regularly inspect your gas cap and EVAP system components for damage.
Need further assistance with your OBD2 codes? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We offer 24/7 customer support.