Understanding the differences between OBD1 and OBD2 systems is crucial for anyone working with vehicles. These two systems represent distinct eras in automotive diagnostics, impacting how we identify and fix car problems. This article delves into the core distinctions between these systems, exploring their functionalities, capabilities, and implications for vehicle maintenance.
Decoding the Acronyms: OBD1 vs. OBD2
OBD stands for On-Board Diagnostics. OBD1, the predecessor, was an early attempt to standardize diagnostic procedures. However, it lacked uniformity, with manufacturers implementing their own proprietary systems. This meant different connectors, diagnostic tools, and trouble codes for each car make. OBD2, introduced in 1996 in the United States, revolutionized car diagnostics with a standardized system applicable across all vehicle makes and models. This universality simplified troubleshooting and repair, making it easier for mechanics and car owners alike.
Key Distinctions: Functionality and Capabilities
Several fundamental differences set OBD1 and OBD2 apart. OBD1 primarily focused on monitoring the emissions system, offering limited diagnostic capabilities. OBD2, on the other hand, monitors a broader range of vehicle systems, including the engine, transmission, and other critical components. This comprehensive approach allows for more accurate and detailed diagnostics. Furthermore, OBD2 boasts advanced features like real-time data monitoring and freeze frame data capture, providing invaluable insights into vehicle performance and fault conditions.
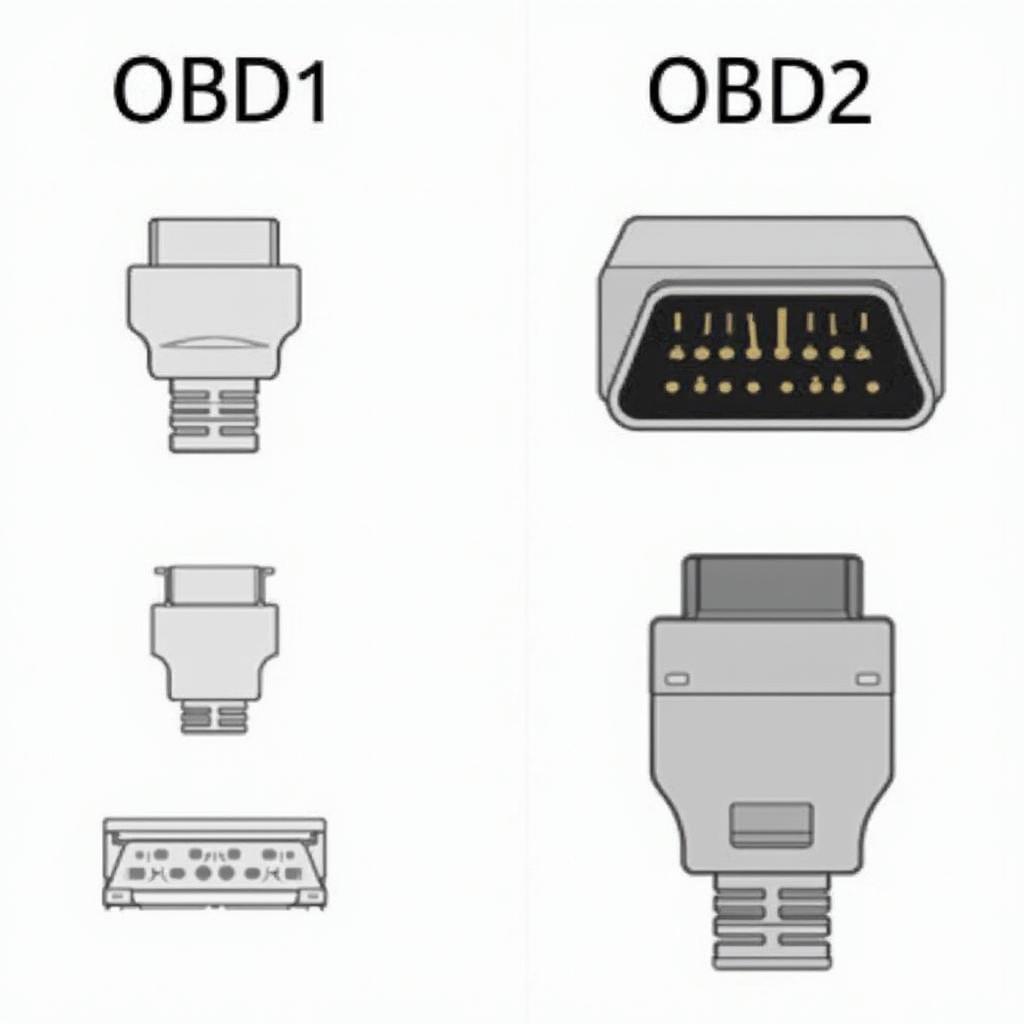 OBD1 vs OBD2 Connectors: A Visual Comparison
OBD1 vs OBD2 Connectors: A Visual Comparison
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): A Comparative Look
Another critical difference lies in the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). OBD1 DTCs varied significantly between manufacturers, leading to confusion and difficulty in interpretation. OBD2 standardized the DTC format, using a five-character alphanumeric code that provides consistent information across all vehicles. This standardized format simplifies diagnosis and repair, regardless of the vehicle’s make or model.
Data Access and Interpretation: A Simplified Approach with OBD2
Accessing and interpreting diagnostic data was significantly more challenging with OBD1. Specialized equipment and manufacturer-specific knowledge were often required. OBD2, with its standardized protocols and widely available scan tools, makes data access much simpler. Generic OBD2 scanners can retrieve and interpret DTCs, sensor data, and other crucial information, empowering car owners and mechanics with accessible diagnostic capabilities.
What Does This Mean for You?
The transition from OBD1 to OBD2 represents a significant leap forward in automotive diagnostics. For car owners, OBD2 simplifies troubleshooting and empowers them to understand their vehicle’s health better. For mechanics, OBD2 provides a standardized platform for efficient and accurate diagnosis and repair.
Embracing the Future of Automotive Diagnostics
OBD2 continues to evolve, with ongoing advancements in technology and functionality. As vehicles become increasingly complex, the role of OBD2 in diagnostics and maintenance is only set to grow, paving the way for more sophisticated and efficient vehicle care.
Conclusion
The differences between OBD1 and OBD2 are substantial, marking a significant evolution in automotive diagnostics. OBD2’s standardization, expanded capabilities, and ease of use have revolutionized how we diagnose and repair vehicles. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone involved in vehicle maintenance and repair, ensuring effective troubleshooting and optimal vehicle performance.
FAQ
-
What year did OBD2 become mandatory? OBD2 became mandatory for all new cars sold in the United States in 1996.
-
Can I use an OBD2 scanner on an OBD1 car? No, OBD1 and OBD2 systems are not compatible. You’ll need a specific OBD1 scanner or adapter.
-
Where is the OBD2 port located? The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard, near the steering wheel.
-
What is a DTC? A DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code) is a code that indicates a specific malfunction within a vehicle system.
-
How can I clear DTCs? You can clear DTCs using an OBD2 scanner or by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery for a short period.
-
Are all OBD2 scanners the same? No, OBD2 scanners vary in features and functionality. Some offer basic code reading, while others provide advanced data logging and analysis.
-
Do I need a professional to use an OBD2 scanner? Basic OBD2 scanners are user-friendly and can be used by car owners. However, more advanced scanners may require professional expertise.
Do you have other questions about OBD systems? Check out these related articles on our website:
- OBD2 Codes Explained
- Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- Troubleshooting Common Car Problems with OBD2
Need assistance? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: cardiagtechworkshop@gmail.com or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.

