Understanding OBD2 PIDs (Parameter IDs) is like having a secret decoder ring for your car. These codes unlock a wealth of information about your vehicle’s performance, emissions, and overall health. Learning to use OBD2 PID effectively empowers you to diagnose issues, monitor critical systems, and even enhance your car’s performance.
Many car owners feel intimidated by the complexity of OBD2 PIDs. However, with a little guidance, anyone can learn to interpret this valuable data. This guide will walk you through the basics of OBD2 PIDs, from understanding their structure to using them with an OBD2 scanner. We’ll cover everything you need to know to start decoding your car’s data and take control of your vehicle’s maintenance. You’ll soon be able to identify potential problems before they become major headaches, saving you time and money in the long run.
What are OBD2 PIDs and Why Should I Care?
OBD2 PIDs are standardized codes used by your car’s onboard computer to identify specific parameters. These parameters can range from engine speed and coolant temperature to oxygen sensor readings and fuel pressure. Think of them as the language your car’s computer uses to communicate its status. By accessing these PIDs with an OBD2 scanner, you gain valuable insights into the inner workings of your vehicle. Why should you care? Because understanding these PIDs can help you:
- Diagnose problems: Is your check engine light on? OBD2 PIDs can pinpoint the source of the issue, helping you avoid unnecessary repairs.
- Monitor performance: Track your car’s fuel efficiency, engine performance, and emissions output to ensure optimal operation.
- Prevent future issues: By regularly monitoring critical parameters, you can identify potential problems before they escalate.
- Customize your car: For the technically inclined, understanding OBD2 PIDs opens doors to customizing certain vehicle functions.
Ready to dive in? Let’s start with the basics of OBD2 commands. You can find a complete list of OBD2 commands at obd2 command.
Decoding the Structure of OBD2 PIDs
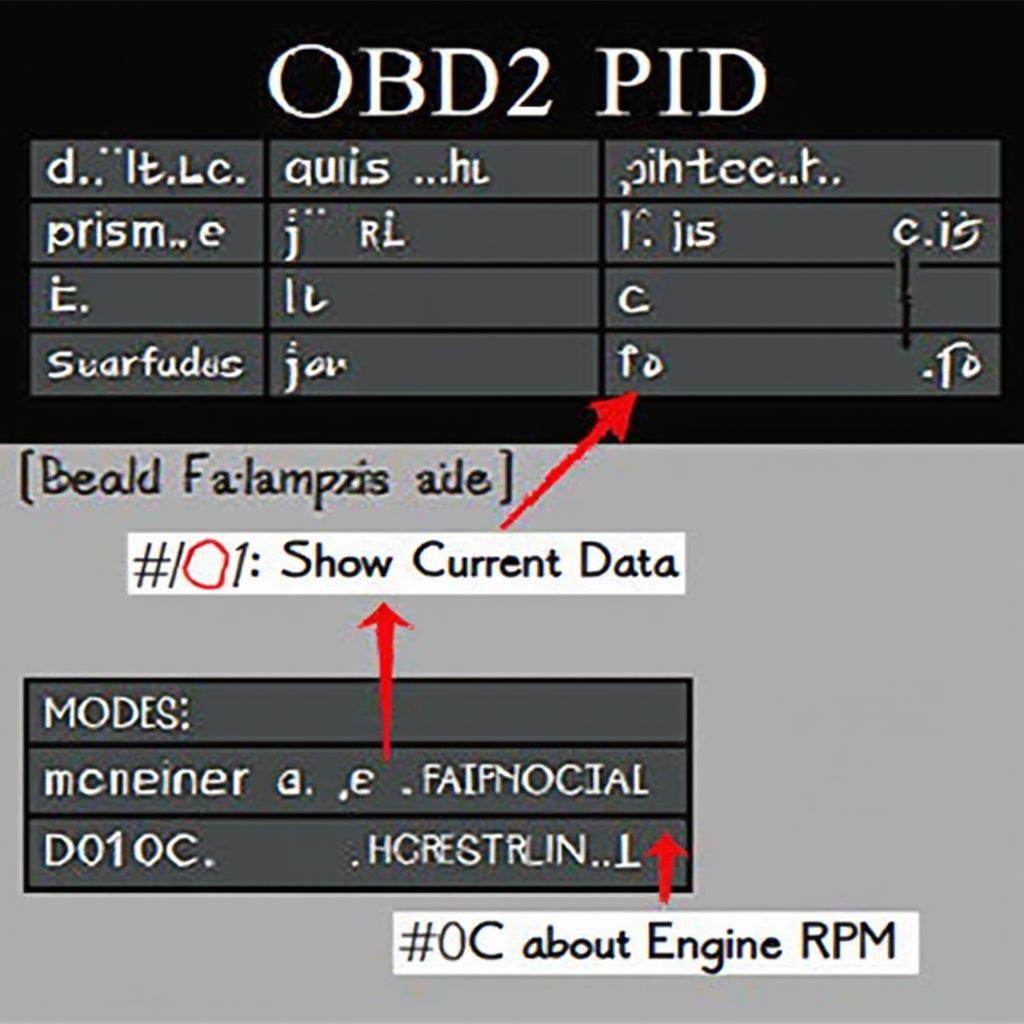
OBD2 PIDs are typically represented by a four-character hexadecimal code. The first two characters represent the mode, which defines the type of request being made. The remaining two characters identify the specific parameter being requested. For example, Mode $01 refers to “Show Current Data,” and PID $0C represents “Engine RPM.” So, the PID $010C requests the current engine speed. It’s like asking your car, “How fast is your engine spinning right now?”
Understanding the different modes is crucial for using OBD2 PIDs effectively. While Mode $01 is the most common for retrieving real-time data, other modes allow you to access diagnostic trouble codes, freeze frame data, and other valuable information. You can learn how to perform live logging using the Torque OBD2 scanner in our guide how to live log on torque obd2 scanner.
How to Use OBD2 PIDs with a Scanner
Using OBD2 PIDs with a scanner is straightforward. First, connect your OBD2 scanner to your car’s OBD2 port, usually located under the dashboard. Turn on the ignition, and the scanner will establish communication with your car’s computer. Next, select the desired mode and enter the PID you want to read. The scanner will then display the corresponding data. Some scanners even allow you to graph data in real-time, making it easier to monitor changes and identify trends. Refer to our article on obd2 pid liste for a comprehensive list of available PIDs.
Understanding the units of measurement associated with each PID is essential. For example, engine speed is typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), while coolant temperature is measured in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit. Knowing the correct units allows you to interpret the data accurately.
Common OBD2 PIDs and Their Uses
Some commonly used OBD2 PIDs include:
- $010C (Engine RPM): Monitors engine speed.
- $0105 (Coolant Temperature): Checks engine temperature to detect overheating issues.
- $010D (Vehicle Speed Sensor): Reads the speed of the vehicle. More on VSS monitoring can be found here: does obd2 monitor vss.
- $0111 (Throttle Position): Monitors the position of the accelerator pedal.
- $011F (Intake Air Temperature): Measures the temperature of the air entering the engine.
Understanding these basic PIDs can help you diagnose a wide range of issues, from a faulty thermostat to a misfiring engine.
Calculating and Interpreting OBD2 PID Data
Sometimes, the raw data retrieved from OBD2 PIDs needs to be converted using specific formulas to get meaningful values. For example, some PIDs return data in hexadecimal or binary format, which needs to be converted to decimal or other units. Our guide on obd2 pids calculations provides in-depth information on these calculations.
“Accurate interpretation of OBD2 data requires understanding the specific formula for each PID,” says automotive expert, Dr. Emily Carter, Ph.D. “Using the wrong formula can lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs.”
Conclusion: Mastering OBD2 PIDs for Car Enthusiasts
Learning to use OBD2 PID opens a world of possibilities for car enthusiasts. By understanding these codes, you can diagnose problems, monitor performance, and gain a deeper understanding of how your car works. While it may seem daunting at first, with the right resources and a little practice, anyone can learn to use OBD2 PID effectively. So grab your OBD2 scanner, start exploring, and unlock the secrets of your car!
FAQ
- What is the difference between OBD2 and OBD1? OBD2 is a standardized system used in most vehicles manufactured after 1996, while OBD1 is an earlier, less standardized system.
- Do all cars support all OBD2 PIDs? No, different car manufacturers may support different sets of PIDs.
- What is a good OBD2 scanner to use? There are many good OBD2 scanners available, ranging from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools.
- Can I damage my car by using an OBD2 scanner? Using an OBD2 scanner correctly is generally safe and will not damage your car.
- Where can I find a complete list of OBD2 PIDs? Numerous online resources provide lists of OBD2 PIDs, including manufacturer websites and automotive forums.
- What are some common mistakes to avoid when using OBD2 PIDs? Common mistakes include misinterpreting data due to incorrect units or formulas, and failing to consider other factors that may affect readings.
- Are there any advanced applications of OBD2 PIDs? Advanced applications include performance tuning, data logging, and custom vehicle modifications.
For further support please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.