Your cart is currently empty!
Understanding OBD2 Sensor Data: A Comprehensive Guide
Obd2 Sensor Data is the lifeblood of modern vehicle diagnostics. It provides a wealth of information about your car’s performance, allowing you to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems. This article dives deep into the world of OBD2 sensor data, explaining what it is, how it works, and why it’s so important.
Understanding OBD2 sensor data is crucial for any car owner or mechanic. It allows you to pinpoint the root cause of car problems, saving you time and money on repairs. From monitoring engine performance to tracking fuel efficiency, OBD2 data opens a window into the inner workings of your vehicle. Learn how to leverage this valuable information to keep your car running smoothly and efficiently. Check our article on Chevy Avalanche OBD2 sensor data for a specific example.
What is OBD2 Sensor Data?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system that allows external devices, like OBD2 scanners, to access data from a vehicle’s various sensors. These sensors are strategically placed throughout the vehicle and continuously monitor critical parameters such as engine speed, coolant temperature, oxygen levels, and much more. The data collected is then transmitted to the vehicle’s computer, which uses it to control engine functions and emissions.
This data, when accessed through an OBD2 scanner, can be invaluable for troubleshooting. It allows you to see real-time values from various sensors, helping you pinpoint the exact component causing a problem. For example, if your check engine light is on, an OBD2 scanner can read the corresponding diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and display related sensor data, enabling you to quickly identify the faulty sensor or component. Do you know if OBD2 monitors VSS? Our article provides the answer.
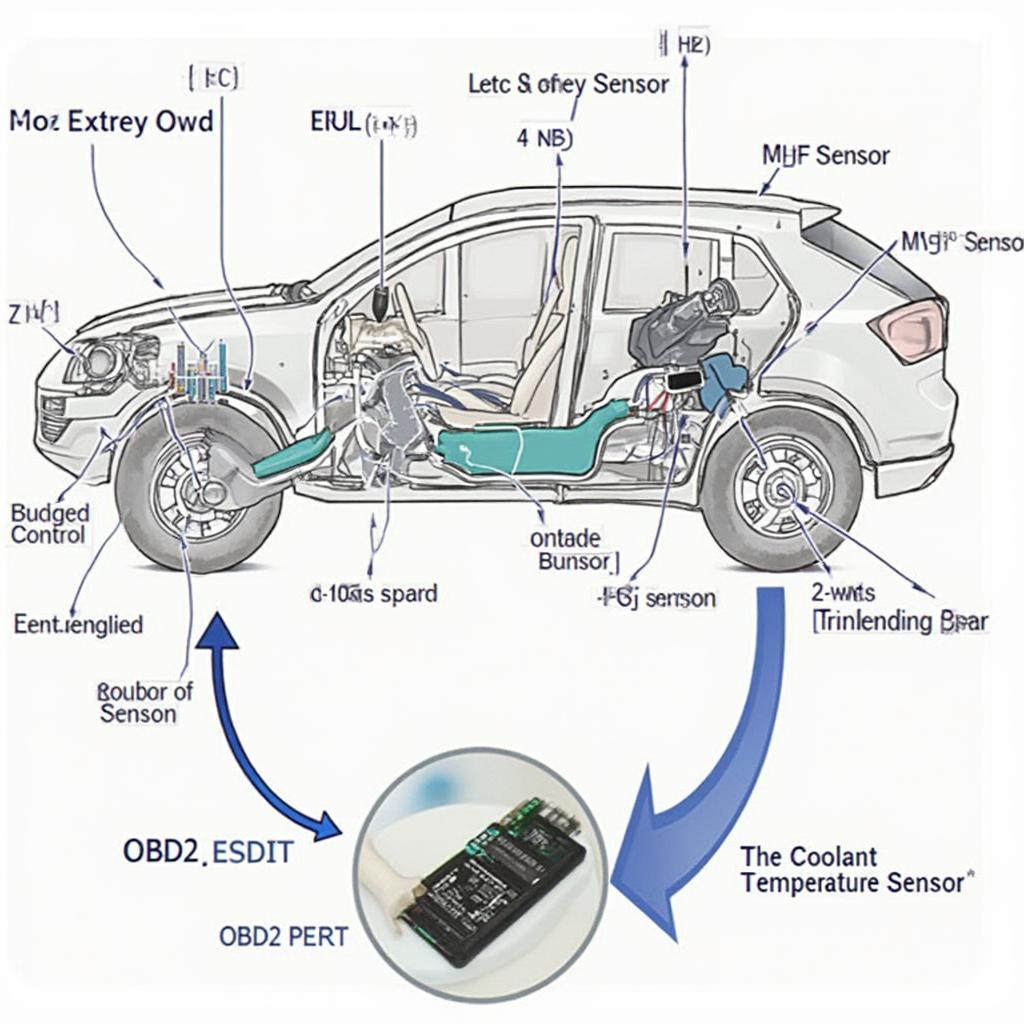
 OBD2 Sensor Data Flow Diagram
OBD2 Sensor Data Flow Diagram
How OBD2 Sensor Data Works
The OBD2 system works by constantly monitoring a vehicle’s sensors and comparing their readings to pre-programmed parameters. When a sensor reading deviates significantly from the expected range, the system triggers a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), which is stored in the vehicle’s computer.
Accessing this data with an OBD2 scanner allows you to retrieve these DTCs and view the corresponding sensor data. This can be extremely helpful in diagnosing a wide range of issues, from minor sensor malfunctions to more serious engine problems. Understanding the different types of sensor data and their implications is essential for effective diagnostics. Thinking about using Torque Pro? Find the best OBD2 sensor for Torque Pro in our guide.
Why is OBD2 Sensor Data Important?
OBD2 sensor data is crucial for a number of reasons:
- Diagnostics: As mentioned, it helps pinpoint the cause of vehicle problems.
- Maintenance: By monitoring sensor data, you can identify potential issues before they become major problems, allowing for preventative maintenance.
- Performance Tuning: Enthusiasts and racers can use OBD2 data to monitor engine performance and make adjustments to optimize power output.
- Fuel Efficiency: Tracking fuel consumption and related sensor data can help identify areas for improvement in fuel economy.
- Emissions Monitoring: OBD2 data is used to ensure vehicles comply with emissions regulations.
Common OBD2 Sensor Data Types
Here are some common types of OBD2 sensor data you might encounter:
- Engine Speed (RPM): Measures the engine’s rotational speed.
- Coolant Temperature: Monitors the engine’s operating temperature.
- Oxygen Sensor (O2): Measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases, indicating the air-fuel ratio. Check our article on OBD2 live data O2s for more information.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF): Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
- Throttle Position (TPS): Indicates the position of the throttle plate, controlling air intake.
- Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP): Measures the pressure in the intake manifold.
What knock sensor data will OBD2 scanners report? Find out in our comprehensive guide.
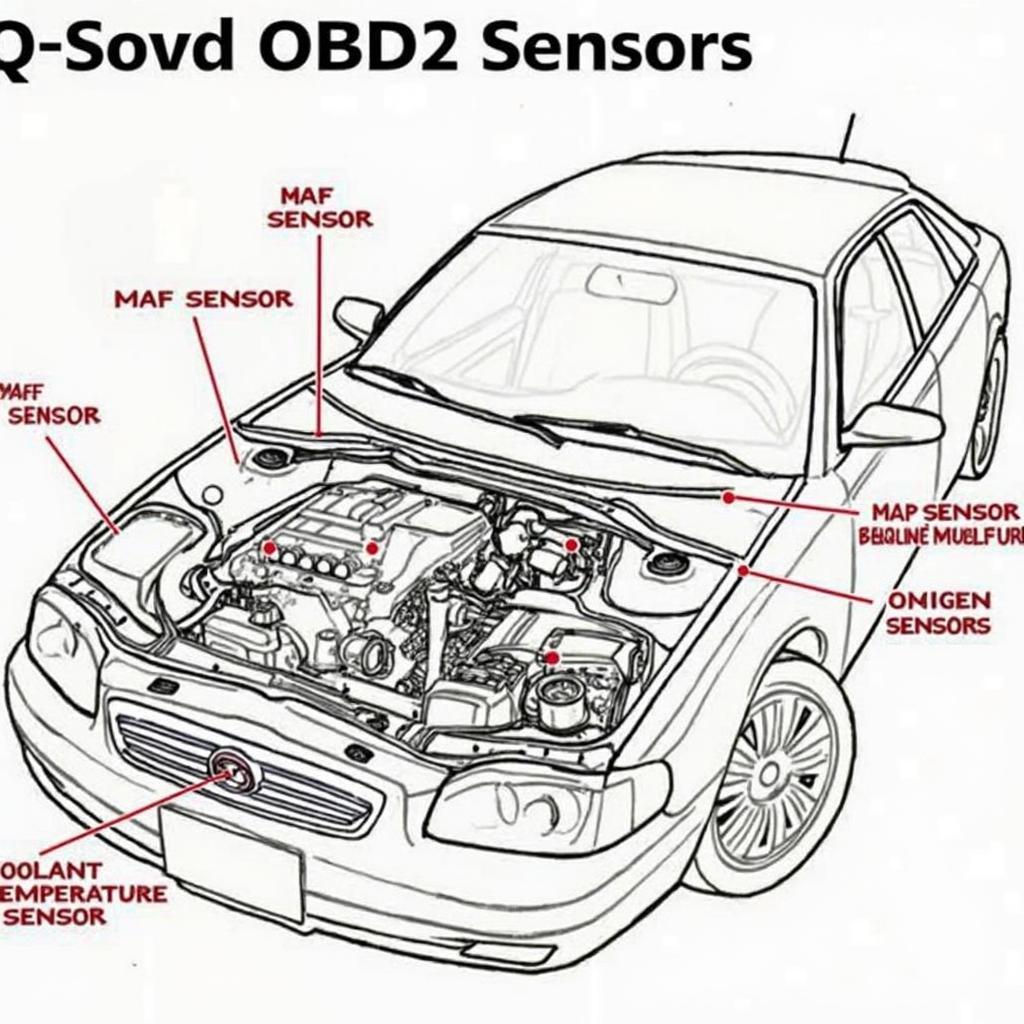 Common OBD2 Sensor Locations in a Car Engine Bay
Common OBD2 Sensor Locations in a Car Engine Bay
Conclusion
OBD2 sensor data is an invaluable tool for understanding and maintaining your vehicle. By learning to interpret this data, you can gain valuable insights into your car’s performance, diagnose problems effectively, and ensure it stays running smoothly for years to come. Understanding OBD2 sensor data empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s health and performance.
FAQ
- What is OBD2? On-Board Diagnostics II, a standardized system for vehicle diagnostics.
- What does an OBD2 scanner do? Reads data from the vehicle’s sensors and displays DTCs.
- What is a DTC? Diagnostic Trouble Code, indicating a specific problem.
- How can I use OBD2 sensor data? To diagnose problems, perform maintenance, and improve fuel efficiency.
- Where can I find more information about specific sensors? Refer to your vehicle’s service manual or online resources.
- How often should I check my OBD2 data? Periodically, or when you suspect a problem.
- Are all OBD2 scanners the same? No, they vary in features and capabilities.
Need help with your car diagnostics? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We have a 24/7 customer support team.

Leave a Reply