The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor plays a crucial role in your vehicle’s performance and efficiency. Understanding its meaning within the context of OBD2 diagnostics is key to maintaining your car’s health. This article will delve into the ECT meaning obd2, its function, common problems, and how to troubleshoot them.
The ECT sensor measures the temperature of the engine coolant and sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU). This data is vital for the ECU to adjust the fuel injection, ignition timing, and other engine parameters to optimize performance and emissions. A faulty ECT sensor can lead to a variety of issues, impacting fuel economy, drivability, and even causing damage to the engine.
What Does the ECT Sensor Do?
The ECT sensor is a small device, usually located near the thermostat housing or in the coolant passage. It works by measuring the resistance of a thermistor, which changes with temperature. As the engine warms up, the resistance decreases, and the ECU interprets this change as an increase in coolant temperature. This information allows the ECU to make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal engine operation. For instance, when the engine is cold, the ECU enriches the fuel mixture to aid in starting and warm-up. As the engine reaches operating temperature, the ECU leans out the fuel mixture for better fuel economy. Understanding the ECT meaning obd2 allows you to better comprehend how a malfunctioning sensor can impact these critical processes. You can learn more about specific car makes and models, like their OBD2 codes, by checking out resources like Hyundai Accent OBD2 codes.
After this complete paragraph, insert the following shortcode: 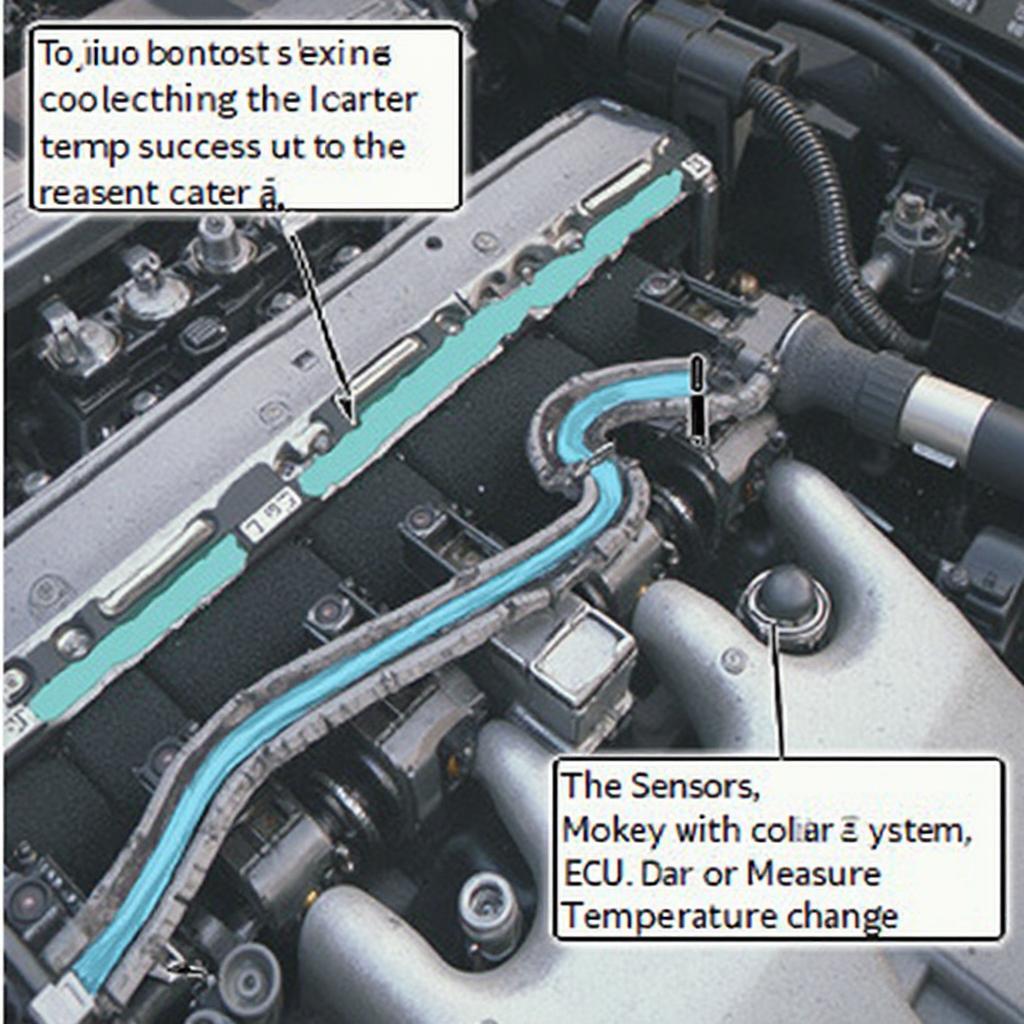{width=1024 height=1024}
Common ECT Sensor Problems and Their OBD2 Codes
Several problems can arise with the ECT sensor, often indicated by specific OBD2 codes. One common issue is a faulty sensor reading, which can trigger codes such as P0117 (ECT sensor circuit low input) or P0118 (ECT sensor circuit high input). These codes suggest that the sensor is sending incorrect data to the ECU. Another common problem is a stuck open or closed thermostat, which can also indirectly affect the ECT sensor readings. This might be indicated by the engine taking too long to warm up or overheating. You can delve deeper into specific OBD2 code combinations, like P0420 and P0172, by visiting resources dedicated to OBD2 codes P0420 P0172.
Other issues can include wiring problems, a damaged connector, or even a malfunctioning ECU. Understanding Cadillac OBD2 codes can provide a more specific insight if you own a Cadillac vehicle. Diagnosing these problems often requires using an OBD2 scanner to read the codes and perform further tests.
After this complete paragraph, insert the following shortcode: “
How to Troubleshoot ECT Sensor Problems
If you suspect a problem with your ECT sensor, the first step is to retrieve the OBD2 codes using a scanner. Auto code reader OBD2 codes resources can help you understand the codes and their potential causes. Once you have the codes, you can begin troubleshooting. Start by visually inspecting the sensor and its wiring for any damage or loose connections. You might find resources about specific car models’ pinouts helpful, such as BMW 95 S600 pin to OBD2 pinout.
Next, you can use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance. Compare your readings with the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the sensor is functioning correctly. If the sensor is faulty, replacing it is a relatively simple procedure. If the problem lies elsewhere, such as a wiring issue or a faulty ECU, further diagnostics will be required.
After this complete paragraph, insert the following shortcode: “
Conclusion
The ECT sensor is a small but critical component of your car’s engine management system. Understanding the ect meaning obd2 and its function is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, and overall health. By being aware of the common problems associated with the ECT sensor and how to troubleshoot them, you can save yourself time and money in the long run.
FAQs
- What does ECT stand for in OBD2? ECT stands for Engine Coolant Temperature.
- What happens if the ECT sensor fails? A failing ECT sensor can lead to poor fuel economy, rough idling, difficulty starting, and even engine damage.
- How do I test an ECT sensor? You can test an ECT sensor using a multimeter to measure its resistance.
- Where is the ECT sensor located? The ECT sensor is typically located near the thermostat housing or in the coolant passage.
- What are some common OBD2 codes related to the ECT sensor? P0117 (ECT sensor circuit low input) and P0118 (ECT sensor circuit high input) are common codes.
- Can I drive my car with a bad ECT sensor? While you can sometimes drive with a bad ECT sensor, it’s not recommended as it can lead to further problems.
- How much does it cost to replace an ECT sensor? The cost to replace an ECT sensor is relatively inexpensive, typically between $20 and $50 for the part.
For further assistance, contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.


