The OBD2 connector, a vital gateway to your vehicle’s diagnostics, relies on a specific pinout configuration. This article delves into the intricacies of the pinout for obd2 connector, exploring its function, variations, and how it empowers you to understand your vehicle’s health. Let’s dive in.
Decoding the OBD2 Connector Pinout
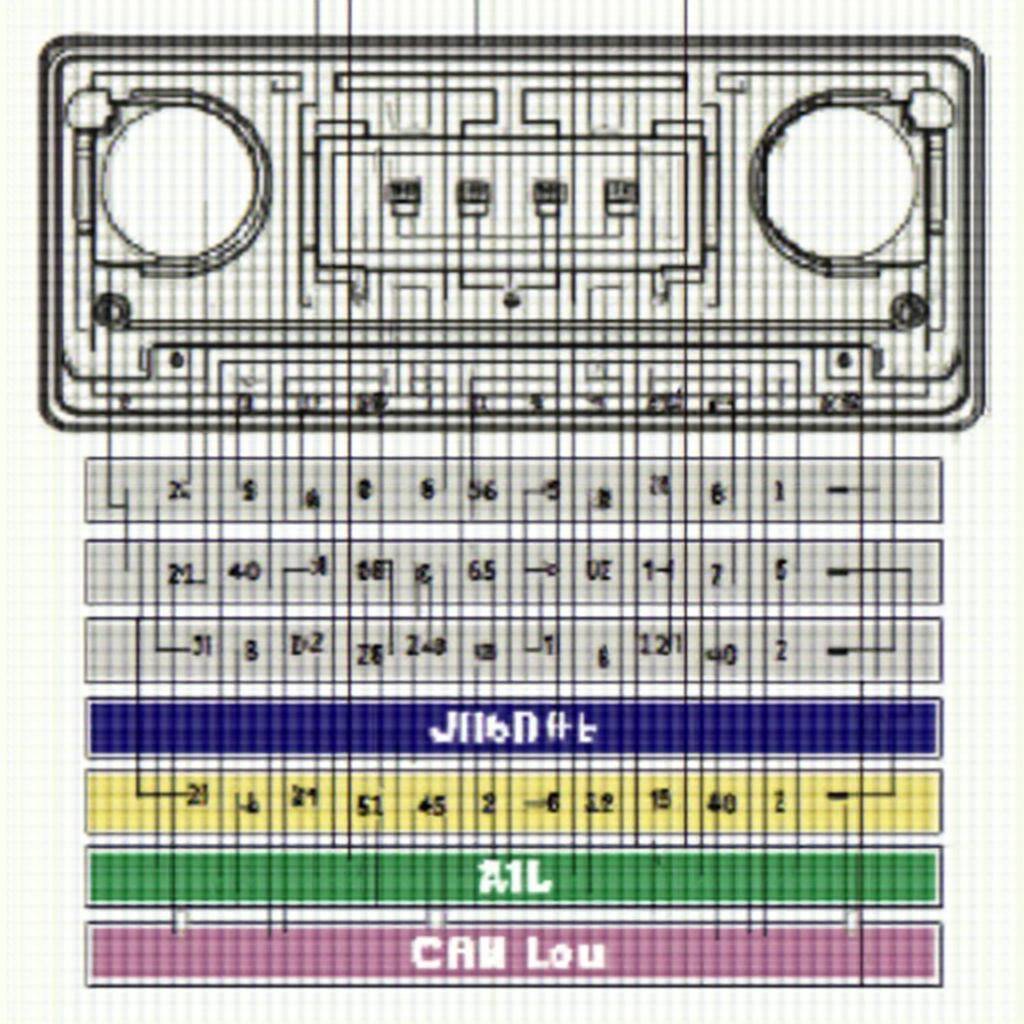
The standard OBD2 connector, also known as the Data Link Connector (DLC), features 16 pins, each serving a specific purpose. While some pins are universally designated, others can vary depending on the vehicle’s make, model, and year. Understanding the obd2 connector pinoujt is crucial for troubleshooting, diagnostics, and even customizing your vehicle’s performance.
Common Pin Functions
Several pins within the OBD2 connector maintain consistent functions across different vehicle makes and models:
- Pin 4 (Chassis Ground): Provides a ground connection for the circuit.
- Pin 5 (Signal Ground): Serves as a ground for the sensor signals.
- Pin 16 (Battery Power): Supplies power directly from the vehicle’s battery.
Manufacturer-Specific Pins
While some pins offer standardized functionality, others are left to the discretion of the manufacturer. This allows for flexibility in incorporating vehicle-specific diagnostic features. For example, obd2 connector pinout toyota might have specific designations on certain pins not found in other vehicle makes.
Communication Protocols
The OBD2 standard utilizes various communication protocols to transmit data between the vehicle’s Electronic Control Unit (ECU) and the diagnostic scanner. These include:
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Primarily used in Ford vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Common in GM vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Frequently found in European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Another protocol common in European and Asian makes.
- ISO 15765-4 (CAN): Controller Area Network, the most modern and widely adopted protocol.
Knowing which protocol your vehicle uses is essential for selecting the correct OBD2 scanner and interpreting the diagnostic data. You can find more information about pinout connector obd2 variations and protocols on dedicated automotive forums and websites.
Why is Understanding the OBD2 Pinout Important?
“Knowing the pinout allows for more targeted diagnostics and even DIY repairs,” explains automotive expert, David Miller, ASE certified Master Technician. Having a firm grasp of the obd2 dlc connector pinout allows you to:
- Diagnose Problems: Identify the source of trouble codes and malfunctions more accurately.
- Customize Performance: Access and modify certain vehicle parameters for enhanced performance.
- Troubleshoot Wiring Issues: Identify and resolve wiring problems within the diagnostic system.
- Use Advanced Scan Tools: Utilize specialized tools that require specific pin connections.
Using Jumper Wires with the OBD2 Connector
jumper wire male to male obd2 connector pinout can be helpful for specific diagnostic tests or for bypassing certain sensors. However, caution should be exercised when using jumper wires, as incorrect connections can damage the vehicle’s electrical system.
Conclusion
Understanding the pinout for obd2 connector is essential for anyone working with vehicle diagnostics. This knowledge empowers you to interpret diagnostic data effectively, troubleshoot issues, and even customize your vehicle’s performance. By taking the time to learn the function of each pin, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of your vehicle’s inner workings.
FAQ
-
What is the OBD2 connector? The OBD2 connector is a standardized 16-pin port used for vehicle diagnostics.
-
Are all OBD2 pins the same? No, some pins are standardized, while others are manufacturer-specific.
-
How can I find my vehicle’s specific pinout? Consult your vehicle’s service manual or online resources.
-
What are the main communication protocols used by OBD2? J1850 PWM, J1850 VPW, ISO 9141-2, KWP2000, and CAN.
-
Why is pin 16 important? Pin 16 provides constant battery power to the OBD2 connector.
-
Can I damage my car by misusing the OBD2 port? Yes, incorrect connections can potentially damage your vehicle’s electrical system.
-
Where can I find more information about OBD2? Reputable automotive websites, forums, and service manuals are excellent resources.
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: cardiagtechworkshop@gmail.com or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.