Your cart is currently empty!
What Does OBD2 Code ATHR2 Mean?
The OBD2 code ATHR2 can be a head-scratcher for car owners. It signals a potential issue within your vehicle’s throttle actuator system, but what exactly does that mean, and should you be concerned? This article dives deep into the ATHR2 code, explaining its causes, symptoms, and how to address it effectively.
Understanding the OBD2 Code ATHR2
The code “ATHR2” itself isn’t a standard OBD2 diagnostic trouble code. OBD2 codes typically consist of a letter (P, B, C, or U) followed by four digits. It’s possible that “ATHR2” is a manufacturer-specific code or a shortened or informal term used in certain contexts.
However, since the term refers to the throttle actuator, it likely points to a problem within the electronic throttle control system, a common component in modern vehicles. This system replaces the traditional mechanical linkage between the accelerator pedal and the throttle plate with electronic sensors and actuators. When you press the gas pedal, a sensor sends a signal to the engine control unit (ECU), which then commands the throttle actuator to open or close the throttle plate, regulating air intake and engine speed.
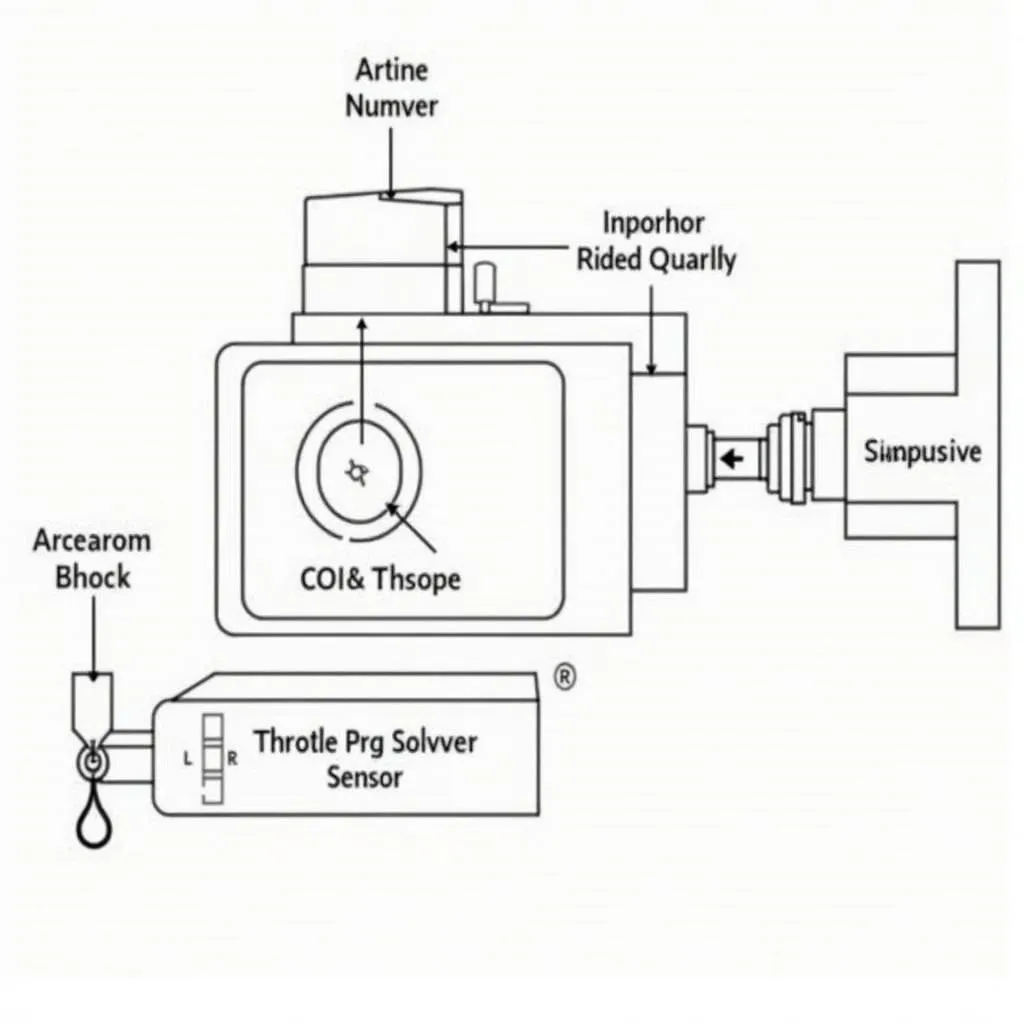
 Electronic Throttle Control System Components
Electronic Throttle Control System Components
Common Causes of Throttle Actuator Problems
While the exact meaning of “ATHR2” might be unclear without more context, several common issues can trigger throttle actuator-related codes:
- Faulty Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): The TPS monitors the throttle plate’s position and reports it to the ECU. A malfunctioning TPS can send incorrect data, leading to issues with throttle control.
- Malfunctioning Throttle Actuator: The throttle actuator itself can wear out or fail due to electrical or mechanical problems, causing the throttle plate to stick or move erratically.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring within the throttle actuator system can disrupt communication between components, triggering error codes.
- ECU Problems: In some cases, the issue might originate from the ECU itself. Software glitches or faulty processing can disrupt the signals sent to the throttle actuator.
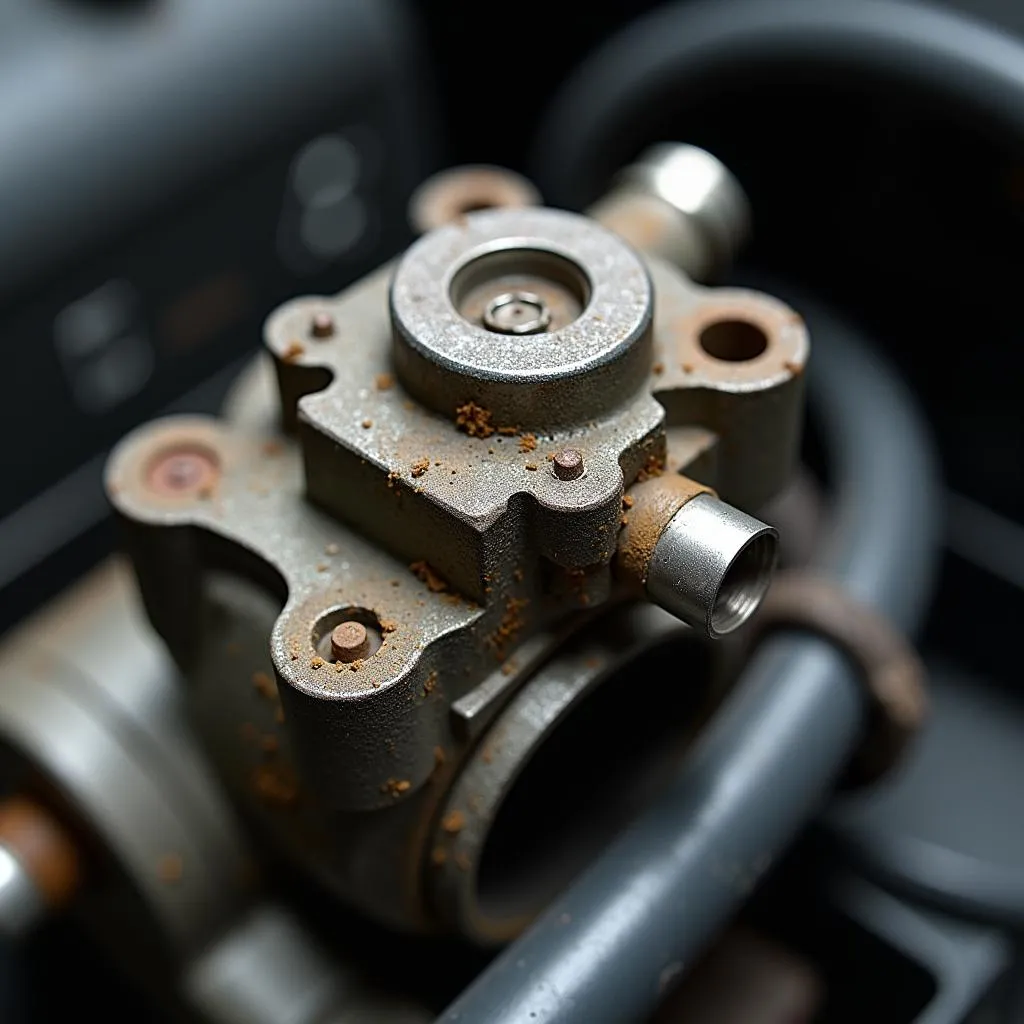 Worn Out Throttle Actuator
Worn Out Throttle Actuator
Recognizing the Symptoms
Problems with the throttle actuator system can manifest in various ways, often affecting your vehicle’s performance and drivability:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light: One of the first indicators is usually the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard.
- Reduced Engine Power: You might experience a noticeable decrease in engine power and acceleration, making it difficult to reach or maintain desired speeds.
- Limp Mode: In severe cases, the ECU might put the vehicle into “limp mode” as a safety precaution. This mode severely limits engine power to prevent potential damage.
- Rough Idling: The engine might idle erratically, with fluctuations in RPM, or even stall at stoplights.
- Sudden Acceleration or Deceleration: In some instances, the throttle might stick open or closed, leading to unintended acceleration or deceleration.
Diagnosing and Addressing the ATHR2 Code
If you suspect a problem with your throttle actuator system, it’s crucial to have it diagnosed properly:
- Read the Code: While “ATHR2” might not be a standard OBD2 code, using an OBD2 scanner can retrieve the specific code stored in your vehicle’s ECU.
- Consult a Mechanic: It’s best to consult a qualified mechanic experienced in diagnosing and repairing electronic throttle control systems. They can accurately interpret the code and pinpoint the root cause.
- Thorough Inspection: A mechanic will likely perform a visual inspection of the throttle actuator, wiring, and related components, checking for obvious damage or loose connections.
- Testing Procedures: They might also use specialized equipment to test the throttle position sensor, actuator, and wiring harness for proper function.
- Component Replacement: Depending on the diagnosis, the mechanic might recommend replacing the faulty component, such as the TPS, throttle actuator, or a section of the wiring harness.
- ECU Update or Repair: If the issue stems from the ECU, it might require a software update or, in rare cases, repair or replacement.
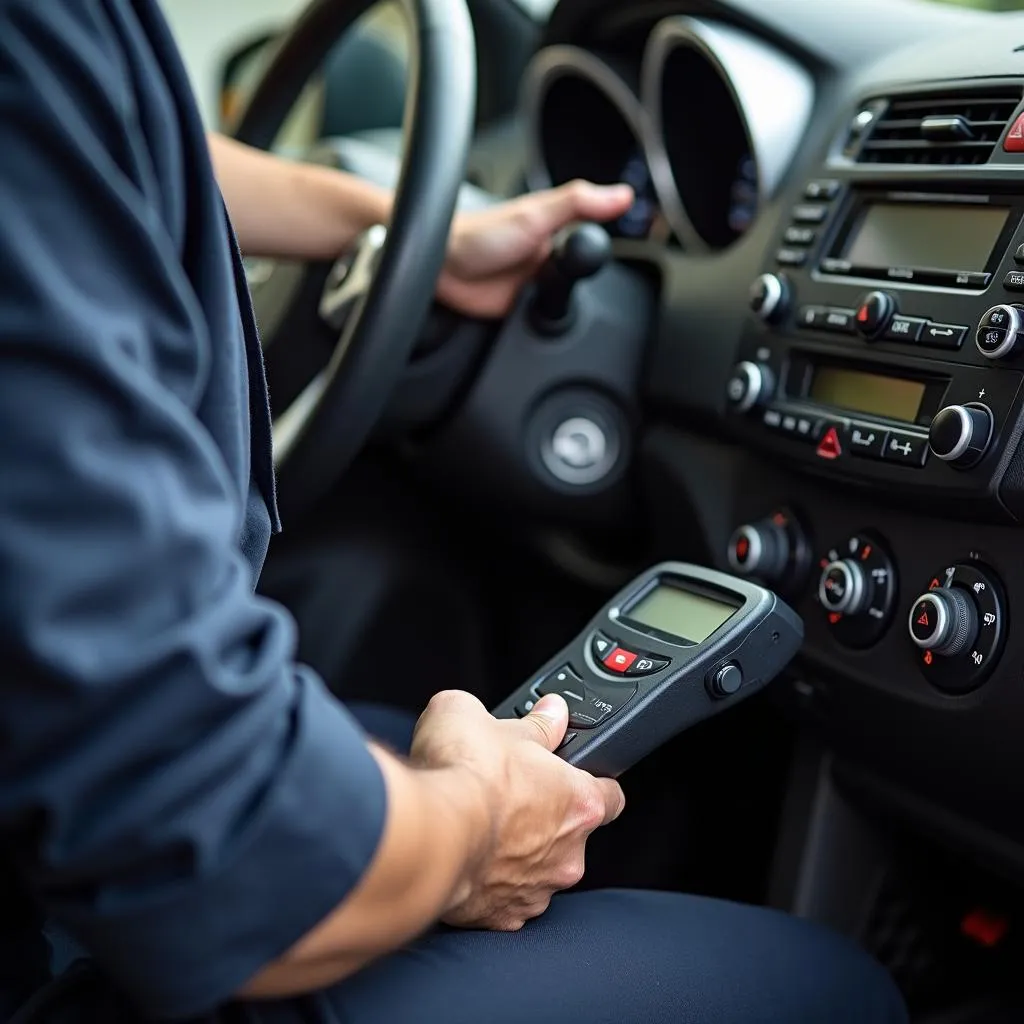 Mechanic Diagnosing Car with OBD2 Scanner
Mechanic Diagnosing Car with OBD2 Scanner
Conclusion
While the specific meaning of the code “ATHR2” remains unclear without more context, it strongly suggests a potential problem within the electronic throttle control system. Addressing throttle actuator-related issues promptly is essential to maintain your vehicle’s performance, reliability, and safety. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures, you can ensure your car receives the necessary attention from a qualified mechanic, getting you back on the road with confidence.

Leave a Reply