Your cart is currently empty!
Understanding o2sloc obd2: A Comprehensive Guide
The O2sloc Obd2 code can be a frustrating mystery for car owners. This guide dives deep into the meaning, causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and solutions related to the o2sloc obd2 trouble code, empowering you to understand and address this issue effectively.
What is o2sloc obd2?
The o2sloc obd2 code refers to a problem with the oxygen sensor location. More specifically, it indicates that the oxygen sensor downstream of the catalytic converter is not reading correctly. While “o2sloc” itself isn’t a standardized OBD-II code, it likely points to a P0136, P0140, P0156, or P0160 code, all of which relate to oxygen sensor circuit malfunctions. Understanding the specific code your vehicle is throwing is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair.
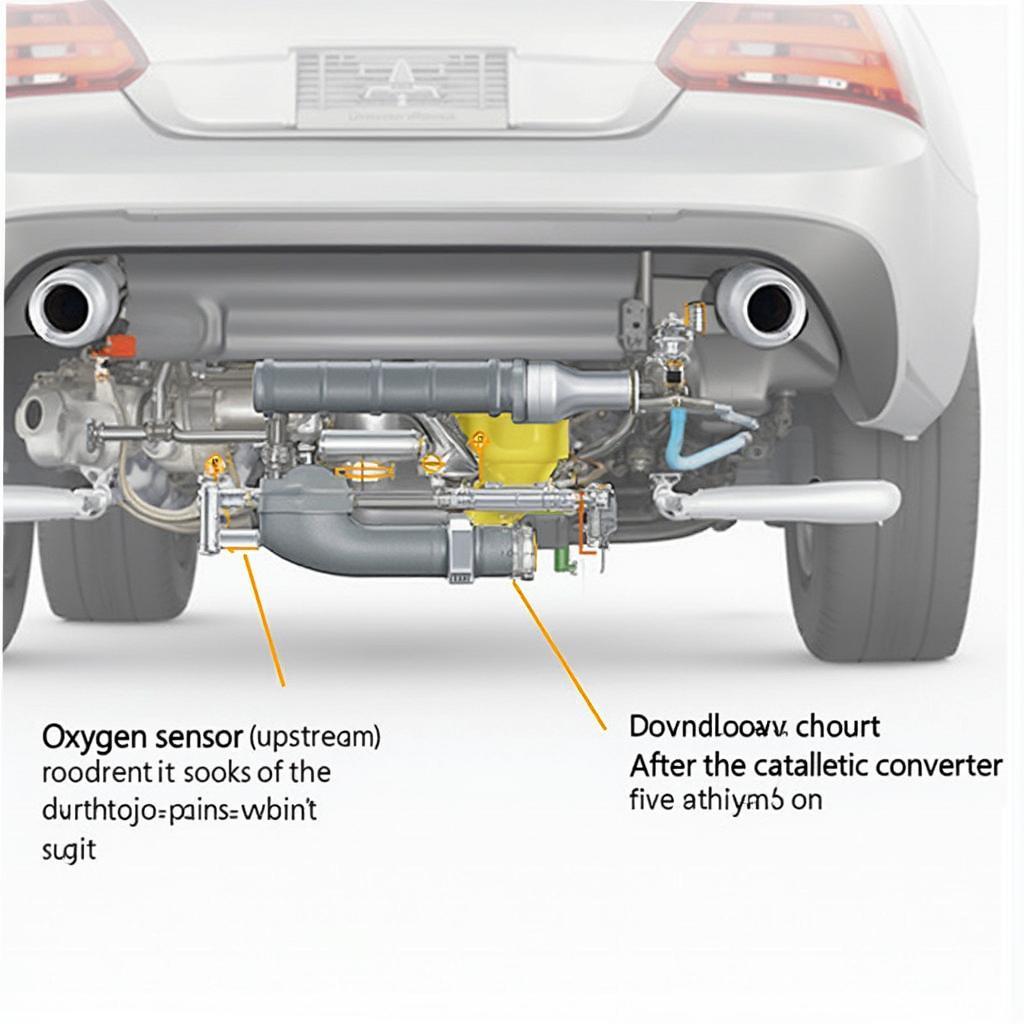
 Oxygen Sensor Location in a Vehicle Exhaust System
Oxygen Sensor Location in a Vehicle Exhaust System
Why is the o2sloc obd2 Code Important?
A functioning oxygen sensor is critical for optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. The downstream oxygen sensor, indicated by the o2sloc-related codes, monitors the efficiency of the catalytic converter. A faulty reading can lead to decreased fuel economy, increased emissions, and potential damage to the catalytic converter.
Common Causes of o2sloc obd2 Codes
Several factors can trigger an o2sloc obd2 code. These include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: This is the most common culprit. Over time, oxygen sensors can degrade and fail to provide accurate readings.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system, especially before the downstream sensor, can introduce fresh air and skew the sensor’s readings.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring to the oxygen sensor can disrupt the signal transmission.
- Faulty Catalytic Converter: While less common, a failing catalytic converter can also trigger these codes.
- Vacuum Leaks: Unmetered air entering the engine can affect the air/fuel mixture and indirectly impact oxygen sensor readings.
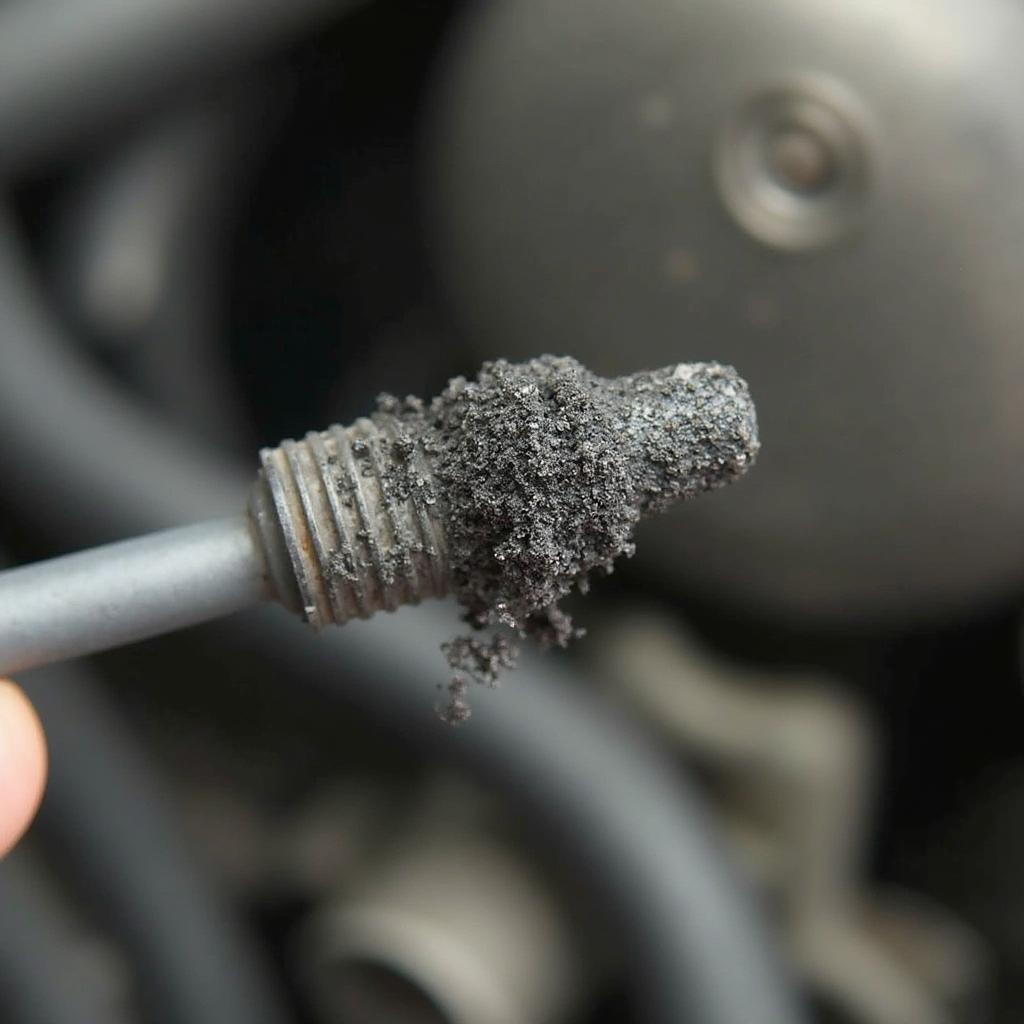 Damaged Oxygen Sensor
Damaged Oxygen Sensor
Symptoms of an o2sloc obd2 Problem
Recognizing the symptoms associated with an o2sloc obd2 code can help you identify the problem early on. Common symptoms include:
- Check Engine Light: The most obvious sign.
- Decreased Fuel Economy: Noticeably lower miles per gallon.
- Rough Idling: The engine might idle unevenly or stumble.
- Failed Emissions Test: High levels of pollutants in the exhaust.
Diagnosing o2sloc obd2 Codes
Proper diagnosis is essential before replacing any parts. Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the specific code. Then follow these steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any visible damage to the oxygen sensor wiring or exhaust leaks.
- Check Wiring: Use a multimeter to test the voltage and resistance of the oxygen sensor circuit.
- Monitor Sensor Data: Use a scan tool to monitor the oxygen sensor readings in real time. This can help pinpoint whether the sensor is responding correctly to changes in exhaust gas composition.
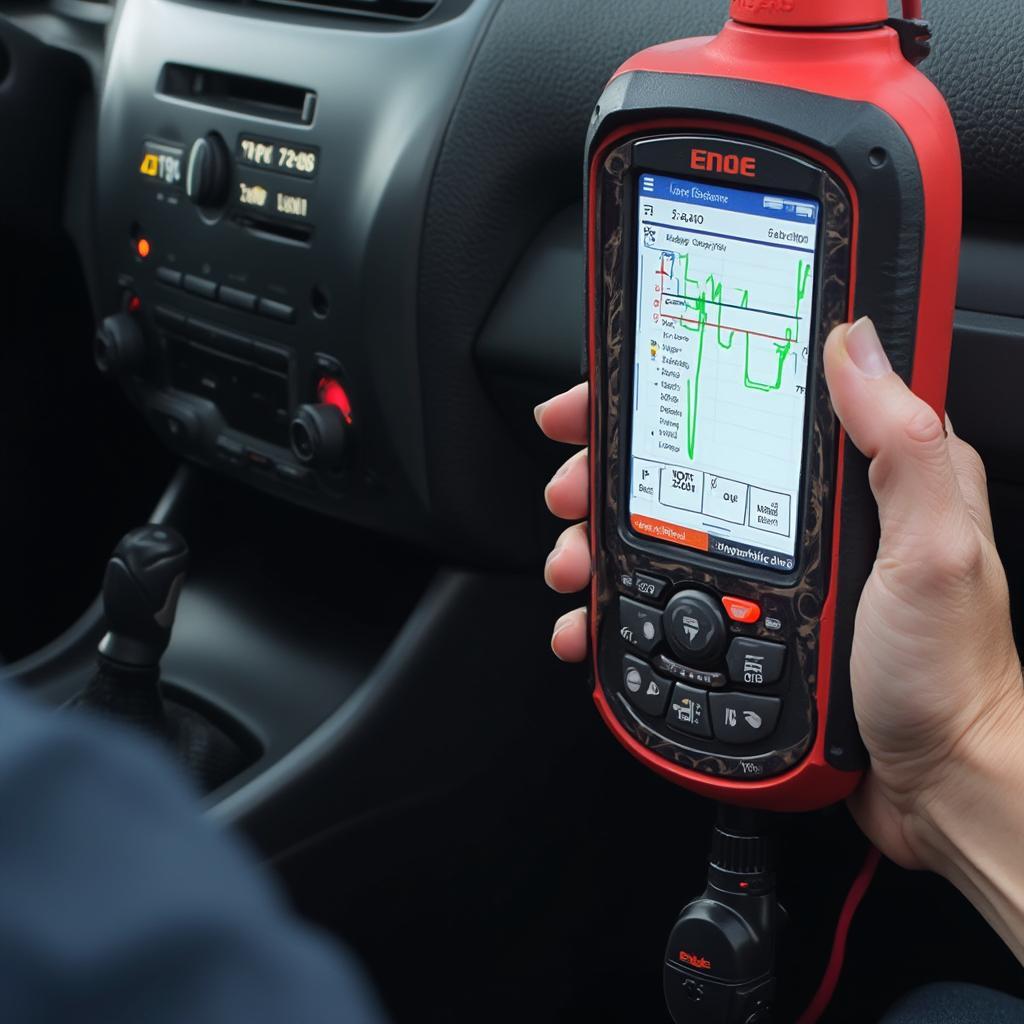 Using an OBD2 Scanner to Diagnose Car Problems
Using an OBD2 Scanner to Diagnose Car Problems
Fixing o2sloc obd2 Codes
Once you’ve identified the cause, you can address the problem. Solutions might include:
- Replacing the Oxygen Sensor: A straightforward fix if the sensor is faulty.
- Repairing Exhaust Leaks: Patching or replacing damaged exhaust components.
- Repairing Wiring: Replacing damaged or corroded wires.
- Replacing the Catalytic Converter: A more expensive repair, but necessary if the converter is failing.
Conclusion
Understanding the o2sloc obd2 code and its implications is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s health and performance. By using this guide, you can diagnose and address the issue effectively, saving you time and money. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can prevent future problems related to oxygen sensors and ensure optimal engine performance.
FAQs
-
What does o2sloc stand for? While not a standardized code, it relates to oxygen sensor location, usually downstream of the catalytic converter.
-
Can I drive with an o2sloc code? While you might be able to drive, it’s recommended to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage.
-
How much does it cost to replace an oxygen sensor? The cost varies depending on the vehicle and sensor type, but generally ranges from $100 to $300.
-
How often should oxygen sensors be replaced? Generally, every 60,000 to 90,000 miles.
-
Can I replace an oxygen sensor myself? Yes, with basic mechanical skills and the right tools.
-
What is a catalytic converter? A device that reduces harmful pollutants in exhaust gases.
-
How can I prevent o2sloc codes in the future? Regular maintenance, including timely replacement of oxygen sensors, can help prevent these codes.
Common Scenarios and Questions
-
My car is running rough and the check engine light is on. Could it be an o2sloc issue? Yes, a faulty oxygen sensor can cause rough running and trigger the check engine light.
-
I just failed my emissions test. Could an o2sloc code be the reason? A faulty downstream oxygen sensor can cause increased emissions and lead to a failed emissions test.
-
My fuel economy has suddenly dropped. Could this be related to o2sloc? Yes, a malfunctioning oxygen sensor can impact fuel economy.
Related Articles and Resources
- OBD2 Code P0136: Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
- OBD2 Code P0140: Oxygen Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
- How to Use an OBD2 Scanner
- Catalytic Converter: Function and Importance
Need further assistance? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.

Leave a Reply