The OBD2 code P1140 can be a real headache for car owners. This article provides a detailed explanation of the P1140 code, its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions. We’ll cover everything you need to know to understand and address this frustrating trouble code.
Decoding the Mystery of OBD2 Code P1140
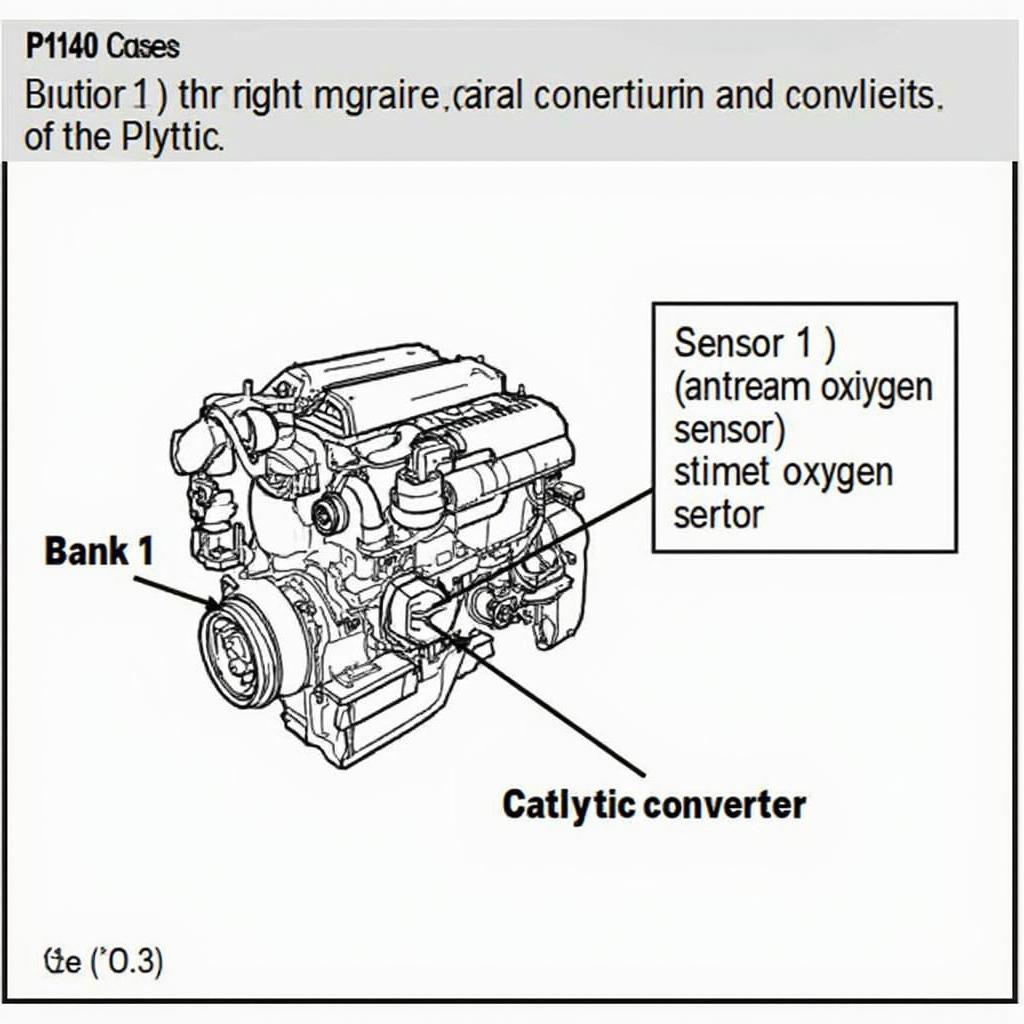
The OBD2 code P1140 typically signifies a problem with the air/fuel ratio sensor circuit, specifically relating to a malfunction in the sensor heater circuit for Bank 1 Sensor 1. Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine containing cylinder number 1, and Sensor 1 is the upstream oxygen sensor, located before the catalytic converter. The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) plays a vital role in optimizing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. A malfunctioning heater can significantly impact engine performance and fuel economy.
Common Causes of P1140
Several factors can contribute to the P1140 code. These include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The most common culprit is a damaged or worn-out oxygen sensor. Over time, the sensor can become contaminated or fail due to exposure to high temperatures and exhaust gases.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring in the sensor circuit can disrupt the heater’s operation, triggering the P1140 code.
- Blown Fuse: A blown fuse in the oxygen sensor heater circuit can prevent power from reaching the heater.
- Faulty Engine Control Module (ECM): While less common, a malfunctioning ECM can sometimes misinterpret signals or fail to provide the necessary power to the sensor heater.
Symptoms of a P1140 Code
The symptoms associated with a P1140 code can vary depending on the severity of the problem. Common symptoms include:
- Check Engine Light: The most obvious sign is the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard.
- Reduced Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to inefficient fuel consumption.
- Rough Idle: The engine might idle erratically or stumble.
- Hesitation on Acceleration: You might experience hesitation or sluggishness when accelerating.
- Failed Emissions Test: The P1140 code can often cause your vehicle to fail an emissions test.
Diagnosing the P1140 Code
Diagnosing the P1140 code typically involves the following steps:
- Retrieve the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the trouble code.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the wiring and connectors associated with the oxygen sensor for any visible damage or corrosion.
- Check the Fuse: Verify that the fuse for the oxygen sensor heater circuit is intact.
- Test the Sensor Heater Circuit: Use a multimeter to test the voltage and resistance of the sensor heater circuit.
- Test the Oxygen Sensor: Test the oxygen sensor’s output voltage using a multimeter.
Fixing the P1140 Code
The solution to the P1140 code depends on the underlying cause. Common solutions include:
- Replacing the Oxygen Sensor: If the oxygen sensor is faulty, replacement is usually necessary.
- Repairing Wiring: Repair any damaged or corroded wiring in the sensor circuit.
- Replacing the Fuse: Replace a blown fuse with a new one of the correct amperage.
- Addressing ECM Issues: If the ECM is malfunctioning, it might require reprogramming or replacement.
What is the P1140 code?
The P1140 code indicates a problem with the oxygen sensor heater circuit for Bank 1 Sensor 1.
What causes the P1140 code?
Common causes include a faulty oxygen sensor, wiring problems, a blown fuse, or a faulty ECM.
What are the symptoms of a P1140 code?
Symptoms may include the check engine light, reduced fuel economy, rough idle, hesitation on acceleration, and failed emissions tests.
Conclusion: Taking Control of the P1140 Code
Understanding the OBD2 code P1140 empowers you to address this common issue effectively. By following the diagnostic and repair procedures outlined in this guide, you can restore your vehicle’s performance, improve fuel efficiency, and ensure compliance with emissions standards. Don’t let the P1140 code leave you stranded – take control and get back on the road with confidence.
FAQs
-
Can I drive with a P1140 code? While you can technically drive with a P1140 code, it’s not recommended. Driving with a faulty oxygen sensor can lead to further damage and reduced fuel economy.
-
How much does it cost to fix a P1140 code? The cost of repair depends on the underlying cause. Replacing an oxygen sensor can cost anywhere from $100 to $300, while more complex repairs involving the ECM can be significantly more expensive.
-
How can I prevent a P1140 code? Regular maintenance, including timely replacement of the oxygen sensor, can help prevent the P1140 code from occurring.
-
Is it safe to ignore the P1140 code? Ignoring the code could lead to further engine damage and reduced fuel efficiency. It is not recommended to ignore this code.
-
Can I fix the P1140 code myself? Depending on your mechanical skills, you might be able to replace a faulty oxygen sensor yourself. However, diagnosing and repairing wiring issues or ECM problems often requires the expertise of a qualified mechanic.
Need further assistance? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our 24/7 customer support team is ready to help.