An OBD2 knock monitor, also known as a knock sensor, is a critical component in modern vehicles that helps protect your engine from the damaging effects of engine knock. This article delves into the world of OBD2 knock monitors, explaining what they are, how they work, and why they are essential for maintaining your vehicle’s health and performance.
What is Engine Knock?
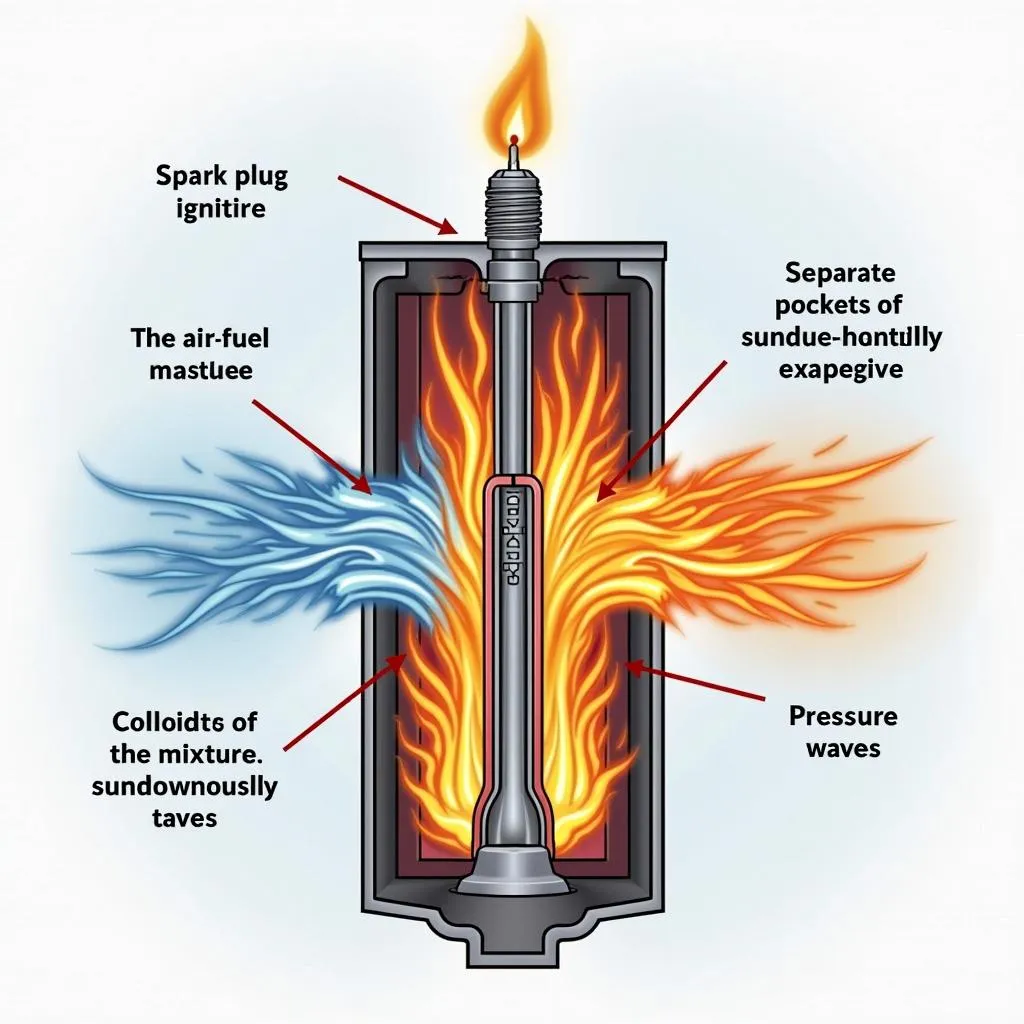
Before we explore knock monitors, it’s essential to understand what engine knock is and why it’s a problem. Engine knock, also known as detonation or spark knock, is the unpleasant rattling or pinging sound you might hear coming from your engine, especially under heavy load or acceleration. This noise signifies an uncontrolled combustion of the air-fuel mixture inside your engine’s cylinders.
Instead of the air-fuel mixture burning smoothly from the spark plug’s ignition, engine knock occurs when pockets of this mixture spontaneously ignite, creating multiple flame fronts that collide. These collisions generate pressure waves that can damage engine components like pistons, valves, and spark plugs.
The Role of an OBD2 Knock Monitor
An OBD2 knock monitor is a small, sensitive piezoelectric sensor typically located on the engine block or cylinder head. This strategic placement allows it to detect the high-frequency vibrations produced by engine knock. The sensor converts these vibrations into electrical signals, which are then sent to the Engine Control Unit (ECU).
The ECU acts as your vehicle’s brain, constantly analyzing data from various sensors, including the knock monitor. When the ECU receives signals indicating engine knock, it takes immediate action to protect your engine.
How a Knock Monitor Protects Your Engine
Upon detecting engine knock, the ECU will adjust the engine’s timing by retarding the ignition spark. This adjustment delays the combustion process, allowing the air-fuel mixture to burn more smoothly and eliminate the knock. In modern vehicles, this process happens continuously and seamlessly, often without the driver even noticing.
The knock monitor and ECU work in tandem to prevent engine damage and ensure optimal performance. While the ECU adjusts the timing, the knock monitor continuously monitors the engine for any signs of knock. This continuous feedback loop allows the ECU to fine-tune the timing and maintain a delicate balance between performance and engine safety.
Symptoms of a Failing Knock Sensor
A failing or faulty knock sensor can have detrimental effects on your engine. Here are some common symptoms that might indicate a problem with your knock sensor:
- Increased engine noise: A noticeable increase in engine knocking or pinging sounds, especially under acceleration or load.
- Decreased fuel efficiency: As the ECU compensates for potential knock by retarding timing, your engine might experience a drop in fuel economy.
- Loss of power: Retarded timing can also lead to a decrease in engine power and acceleration.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning knock sensor will often trigger the check engine light on your dashboard.
Diagnosing Knock Sensor Problems
If you suspect a problem with your knock sensor, it’s crucial to diagnose and address the issue promptly. Here’s how you can do it:
- Read the OBD2 Codes: Connect an OBD2 scanner to your vehicle’s diagnostic port and read any stored trouble codes. Codes related to the knock sensor will pinpoint the problem.
- Inspect the Knock Sensor: Visually inspect the knock sensor for any signs of damage, such as cracks, loose connections, or corrosion.
- Test the Sensor: You can use a multimeter to test the knock sensor’s resistance and voltage output.
Maintaining Your Knock Sensor
While knock sensors are generally durable, proper maintenance can extend their lifespan and prevent premature failure.
- Regular Engine Tune-Ups: Ensure your engine is properly tuned, including spark plug replacements at recommended intervals.
- Use Quality Fuel: Using the recommended octane rating fuel for your vehicle can help prevent engine knock and reduce stress on the knock sensor.
Conclusion
An OBD2 knock monitor plays a vital role in protecting your engine from the harmful effects of engine knock. This small sensor works tirelessly to ensure your engine operates smoothly, efficiently, and safely. By understanding how it works and recognizing the signs of a failing sensor, you can help keep your engine running strong for miles to come. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are essential for maximizing the lifespan of your knock sensor and ensuring optimal engine performance.
Remember, when it comes to engine health, early detection and proactive maintenance are always the best strategies.