Connecting an OBD1 harness to an OBD2 distributor can be a tricky process, often required for engine swaps or performance upgrades. This guide provides a detailed understanding of the differences between OBD1 and OBD2 systems, the challenges involved in this conversion, and the steps to successfully integrate these two technologies.
Understanding OBD1 and OBD2 Systems
OBD, or On-Board Diagnostics, is a standardized system that allows you to access your vehicle’s diagnostic data. OBD1, used in cars pre-1996, is less sophisticated than its successor, OBD2, which became mandatory in 1996 for all vehicles sold in the United States. OBD1 uses a variety of manufacturer-specific connectors and communication protocols, while OBD2 standardizes these aspects, making diagnostics and troubleshooting much easier. The differences extend beyond the diagnostic port itself. The systems controlling fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions are significantly different. This is why connecting an obd1 harness to obd2 distributor requires careful planning and execution.
Challenges of Connecting OBD1 Harness to OBD2 Distributor
The primary challenge lies in the incompatibility of the wiring and signaling between the two systems. OBD2 distributors often incorporate crankshaft position sensors and camshaft position sensors, which provide more precise engine timing information to the ECU (Engine Control Unit). OBD1 systems typically lack these sensors, relying on the distributor for timing signals. This difference necessitates modifications to the wiring harness and potentially the ECU itself. Another key difference lies in the communication protocols. obd2 distributor to obd1 harness conversions often require specialized adapters or custom wiring to bridge the communication gap between the two systems.
Common Issues Encountered
- Incorrect Timing Signals: Leading to poor engine performance, misfires, or even engine damage.
- Check Engine Light (CEL) Illumination: Due to the ECU detecting inconsistencies in the sensor data.
- Compatibility Issues: Between the ECU and the distributor, resulting in improper engine operation.
- Wiring Complications: Requiring a thorough understanding of both systems to avoid errors.
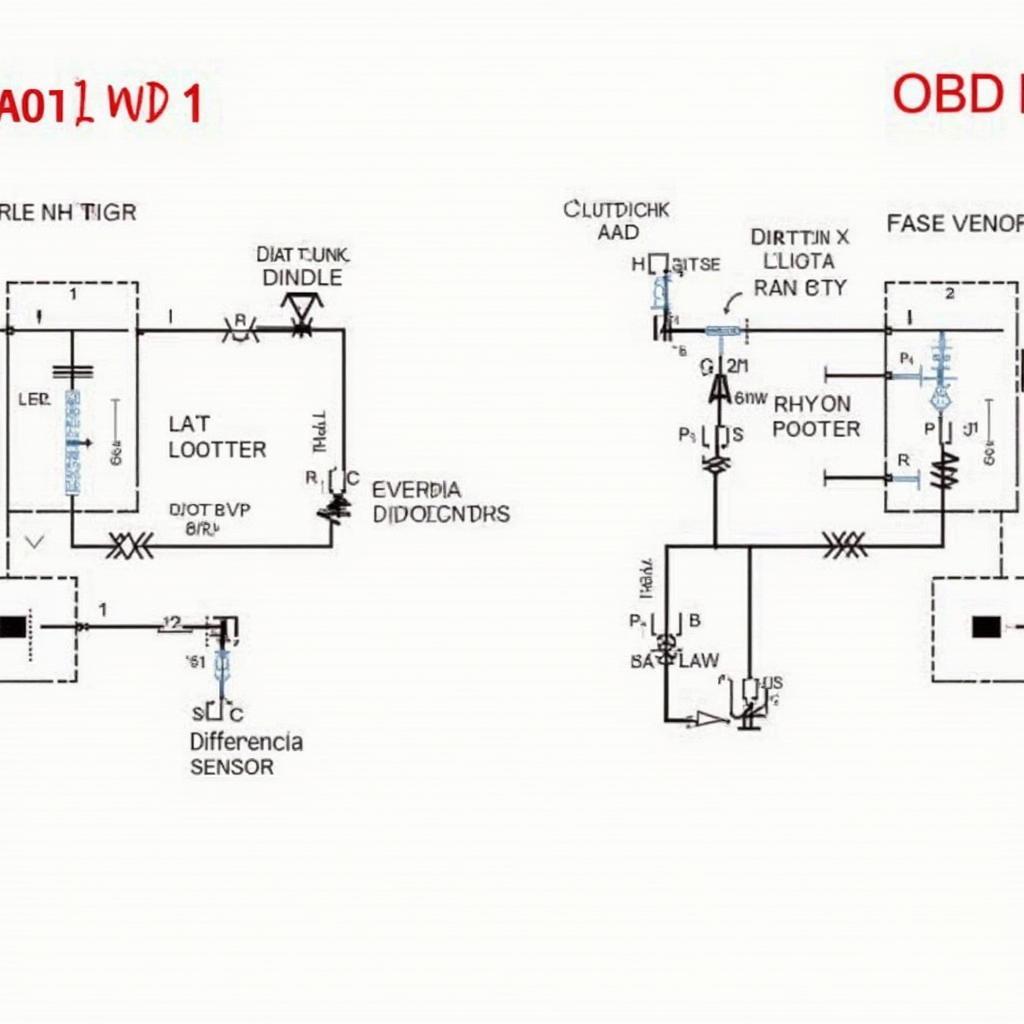 OBD1 and OBD2 Wiring Diagram
OBD1 and OBD2 Wiring Diagram
Steps to Connect an OBD1 Harness to an OBD2 Distributor
Converting from convert obd2 to obd1 often requires adapting the wiring harness. Before starting this process, disconnect the battery negative terminal. Consult the wiring diagrams for both your OBD1 harness and the OBD2 distributor.
- Identify Corresponding Wires: Determine which wires on the OBD1 harness correspond to the necessary signals for the OBD2 distributor.
- Adapt the Wiring: This may involve splicing, soldering, and using appropriate connectors to create a bridge between the two systems. You may need an obd1 to obd2 distributor jumper harness.
- ECU Modifications: In some cases, you may need to modify or replace the ECU to ensure compatibility with the OBD2 distributor’s signals. This process might require specialized tools and expertise. Understanding the difference between obd1 and obd2 harness is crucial for this step.
- Testing: After completing the wiring modifications, thoroughly test the connection to ensure proper functionality.
Conclusion
Connecting an obd1 harness to obd2 distributor requires careful planning and execution. By understanding the key differences between OBD1 and OBD2 systems and following the appropriate steps, you can successfully integrate these two technologies. However, this process can be complex and may require specialized knowledge.
FAQs
- Why would I want to connect an OBD1 harness to an OBD2 distributor? This is often done for engine swaps or performance upgrades.
- Is this conversion possible for all vehicles? Compatibility varies depending on the specific make and model of the vehicle and the components involved.
- What tools do I need for this conversion? Basic tools like wire strippers, crimpers, soldering iron, and multimeter are essential.
- What are the risks involved if the conversion is not done correctly? Incorrect wiring can lead to engine damage or malfunction.
- Where can I find more information about OBD systems? Online forums and automotive communities can provide additional guidance.
- Is there a specific guide for converting a honda prelude obd1 to obd2? Consult specific forums and resources related to Honda Preludes.
- What are the long-term implications of this conversion? Properly executed, the conversion can enhance performance or enable the use of a more modern engine.
Need support? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We have a 24/7 customer support team.

