The dreaded check engine light can strike fear into the heart of any car owner. While it could signal a minor issue, it can also be a harbinger of a costly repair. One common culprit behind this automotive warning is the OBD2 fault code P0137. This code indicates a problem with the oxygen sensor circuit, specifically low voltage detected in Bank 1, Sensor 2. But what does that mean, and how concerned should you be? This comprehensive guide delves deep into the intricacies of the P0137 code, equipping you with the knowledge to diagnose and address this issue effectively.
Deciphering the P0137 Code
Before diving into the specifics of the P0137 code, let’s break down the terminology:
- OBD2: On-Board Diagnostics II, a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and report engine and emission system performance.
- Fault Code: A specific alphanumeric code that represents a particular malfunction detected by the OBD2 system.
- P0137: A specific fault code indicating low voltage detected in the oxygen sensor circuit for Bank 1, Sensor 2.
- Bank 1: Refers to the side of the engine where cylinder #1 is located.
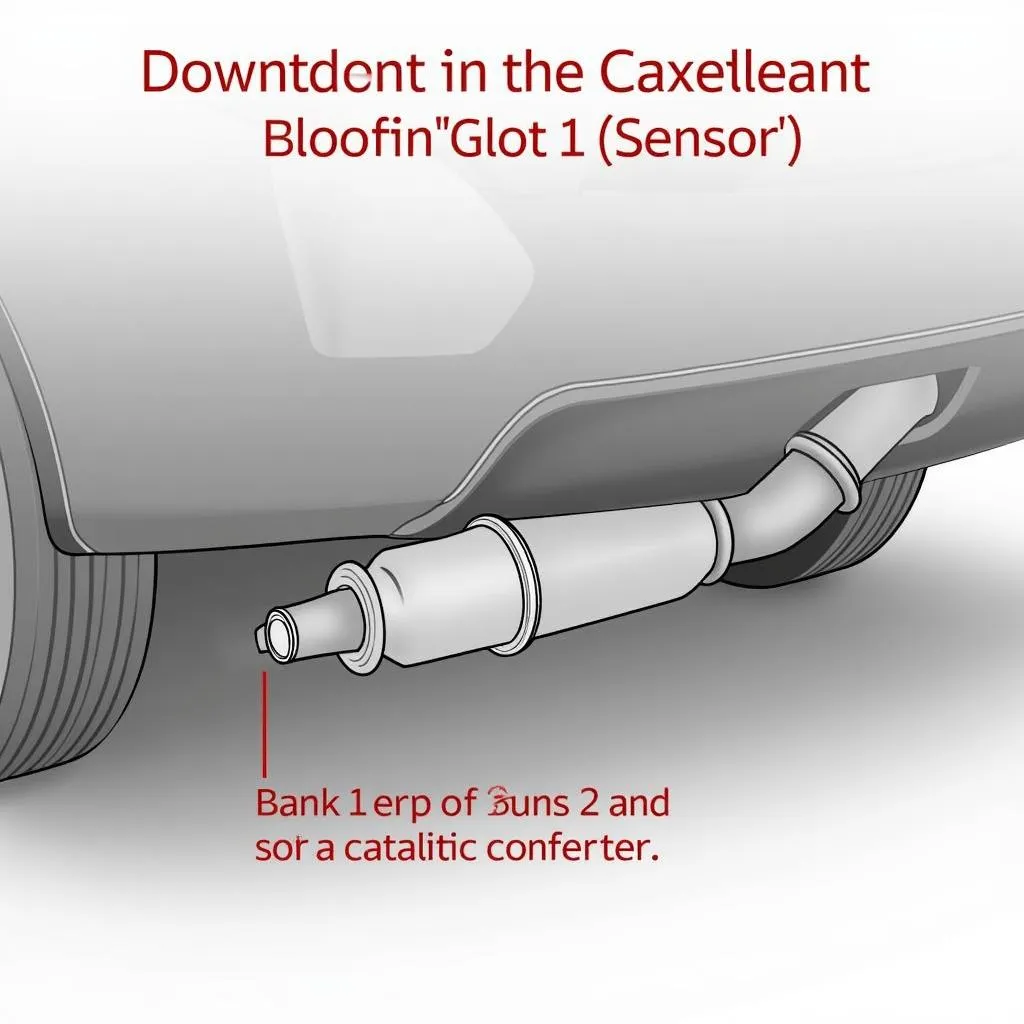
- Sensor 2: Denotes the downstream oxygen sensor, positioned after the catalytic converter.
In essence, the P0137 code signals that the engine control module (ECM) is receiving an abnormally low voltage signal from the downstream oxygen sensor on the side of the engine with cylinder #1. This sensor plays a critical role in monitoring the exhaust gases after they pass through the catalytic converter, ensuring efficient operation and minimal emissions.
Common Causes of OBD2 Code P0137
Several factors can contribute to a low voltage signal from the downstream oxygen sensor, triggering the P0137 code:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The sensor itself may be worn out, contaminated, or damaged, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring between the sensor and the ECM can disrupt the voltage signal.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust manifold, pipes, or catalytic converter can introduce excess oxygen into the exhaust stream, affecting sensor readings.
- Faulty Catalytic Converter: An inefficient or clogged catalytic converter can alter the exhaust gas composition, impacting the downstream sensor’s voltage output.
- ECM Malfunction: While less common, a problem with the engine control module itself can disrupt sensor communication and trigger the P0137 code.
Symptoms of a P0137 Code
Apart from the illuminated check engine light, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Decreased Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to reduced fuel efficiency.
- Engine Performance Issues: You might notice sluggish acceleration, rough idling, or hesitation during acceleration.
- Failed Emissions Test: A faulty downstream oxygen sensor can indicate an issue with the catalytic converter, potentially causing your vehicle to fail an emissions test.
Diagnosing the P0137 Code
While the P0137 code pinpoints the downstream oxygen sensor circuit, proper diagnosis is crucial to identify the root cause. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Read the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the stored fault code(s).
- Inspect the Wiring: Visually examine the wiring harness connected to the oxygen sensor for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Listen for any hissing sounds coming from the exhaust system, which could indicate a leak.
- Test the Sensor Voltage: Using a multimeter, check the voltage signal from the sensor. A healthy sensor should fluctuate between 0.1 and 0.9 volts.
- Inspect the Catalytic Converter: Assess the catalytic converter for any signs of physical damage or blockage.
Fixing the P0137 Code
Once you’ve identified the underlying cause of the P0137 code, take the necessary steps to rectify the issue:
- Replace the Oxygen Sensor: If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one that meets the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Repair Wiring Issues: Repair or replace any damaged, corroded, or loose wiring in the sensor circuit.
- Fix Exhaust Leaks: Address any leaks in the exhaust system by tightening connections, replacing gaskets, or repairing damaged components.
- Replace the Catalytic Converter: If the catalytic converter is faulty, replacement is typically the only solution.
Preventive Measures
While not all causes of the P0137 code are preventable, some measures can help minimize the risk:
- Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, including regular inspections of the exhaust system and oxygen sensors.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Using high-quality fuel with the correct octane rating can help prevent premature sensor contamination and catalytic converter damage.
- Address Engine Issues Promptly: Resolve any engine-related issues promptly, as they can impact the exhaust gas composition and affect sensor readings.
OBD2 Fault Code P0137 FAQs
1. Can I drive with a P0137 code?
While driving with a P0137 code might be possible in the short term, it’s not advisable. Ignoring the issue can lead to further damage to your vehicle’s engine and emissions system, potentially resulting in costly repairs down the line.
2. How much does it cost to fix a P0137 code?
The repair cost can vary widely depending on the underlying cause. A simple sensor replacement might cost a few hundred dollars, while a catalytic converter replacement could be significantly more expensive.
3. Can a bad oxygen sensor damage my catalytic converter?
Yes, a malfunctioning oxygen sensor can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, potentially leading to an overly rich mixture. This can cause excessive heat in the catalytic converter, eventually damaging it.
Need More Help with Your bmw r1200gs obd2?
Understanding and addressing OBD2 fault codes, like the P0137, can be daunting. If you’re unsure about any aspect of diagnosing or repairing your vehicle, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Our team of expert mechanics is here to provide guidance and support.
Contact us today for all your car diagnostic needs!
WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880
Email: [email protected]
We offer 24/7 customer support to help you get back on the road as quickly as possible.