Your cart is currently empty!
Difference Between OBD1 and OBD2: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the difference between OBD1 and OBD2 is crucial for any car owner or automotive professional. This article dives deep into the distinctions between these two diagnostic systems, covering their history, functionality, and impact on the automotive world.
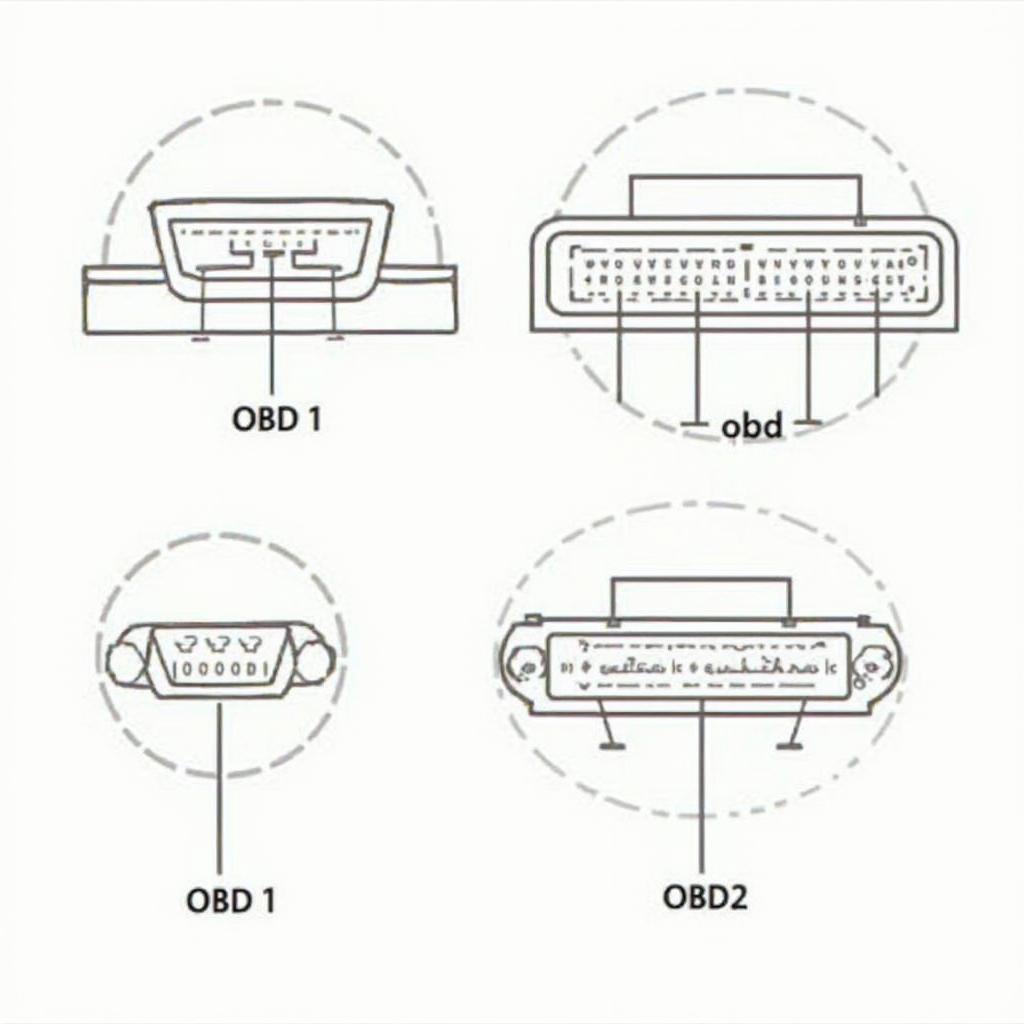
 Comparison of OBD1 and OBD2 Connectors
Comparison of OBD1 and OBD2 Connectors
OBD1, or On-Board Diagnostics generation one, was introduced in the early 1980s as a rudimentary system for monitoring vehicle emissions. Unlike its successor, OBD1 lacked standardization. Each manufacturer implemented its own proprietary system, leading to a confusing array of connectors, diagnostic procedures, and trouble codes. Imagine trying to troubleshoot a problem with your car and needing a different tool for every make and model! This lack of uniformity made diagnostics challenging and often required specialized equipment for each vehicle. OBD2 monitors explained can help you understand how these systems work.
Understanding OBD1: The Precursor to Modern Diagnostics
OBD1 primarily focused on monitoring components related to emissions, such as the catalytic converter and oxygen sensor. It offered limited diagnostic capabilities and often provided only basic information about the nature of the problem. Accessing the diagnostic information typically involved using manufacturer-specific scan tools or interpreting blinking check engine lights. Think of it like trying to decipher a secret code!
Limitations of OBD1
- Lack of Standardization: The biggest drawback of OBD1 was the absence of a universal standard. This made diagnostics complex and time-consuming.
- Limited Diagnostic Capabilities: OBD1 provided limited information about the root cause of problems.
- Manufacturer-Specific Tools: Diagnosing OBD1 systems required specialized tools, increasing the cost and complexity of repairs.
OBD2: The Standardized Diagnostic Revolution
In 1996, OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics generation two, became mandatory for all vehicles sold in the United States. This marked a significant shift in automotive diagnostics, introducing a standardized system that revolutionized how we troubleshoot and repair vehicles. OBD2 expanded the scope of monitoring to include a wider range of systems beyond emissions, such as the transmission, ABS, and airbags. It also introduced a standardized 16-pin connector, simplifying the diagnostic process.
Advantages of OBD2
- Standardization: OBD2 introduced a universal standard, making diagnostics simpler and more efficient.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities: OBD2 provides detailed information about a wider range of vehicle systems.
- Generic Scan Tools: The standardized connector allows the use of generic scan tools, making diagnostics more accessible and affordable.
“The introduction of OBD2 was a game-changer for the automotive industry,” says John Smith, a veteran automotive technician. “It streamlined diagnostics, making repairs faster and more accurate.”
Key Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2
| Feature | OBD1 | OBD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | No universal standard | Standardized 16-pin connector |
| Diagnostic Scope | Limited to emissions-related systems | Expanded to various vehicle systems |
| Connectors | Manufacturer-specific | Standardized |
| Data Access | Manufacturer-specific tools | Generic scan tools |
“OBD2 empowers car owners with more control over their vehicle’s maintenance,” adds Jane Doe, an automotive engineer. “The ability to easily access diagnostic information can help prevent costly repairs down the road.” You might be interested in finding an owl cam for car with no obd2.
Conclusion: OBD2: The Modern Standard
The difference between OBD1 and OBD2 is significant. OBD2 represents a major advancement in automotive diagnostics. Its standardized approach has simplified troubleshooting, improved repair efficiency, and empowered car owners with greater control over their vehicle’s maintenance. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in the automotive world.
FAQs
- What does OBD stand for? OBD stands for On-Board Diagnostics.
- When did OBD2 become mandatory? OBD2 became mandatory in 1996 for all vehicles sold in the United States.
- What is the main advantage of OBD2 over OBD1? The main advantage of OBD2 is its standardization.
- Can I use a generic scan tool on an OBD1 vehicle? No, you typically need a manufacturer-specific tool for OBD1 vehicles.
- What systems does OBD2 monitor? OBD2 monitors various vehicle systems, including emissions, transmission, ABS, and airbags.
- How can I find out if my car is OBD1 or OBD2? Check the connector under your dashboard or consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
- Where can I learn more about OBD2 monitors? You can find more information at obd2 monitors explained.
Need support? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.

Leave a Reply