The OBD2 code P1131 is a common issue that can cause frustration for car owners. This guide dives deep into the P1131 code, explaining its meaning, symptoms, causes, diagnostic procedures, and solutions. We’ll equip you with the knowledge to understand and address this trouble code effectively.
What Does the OBD2 Code P1131 Mean?
The P1131 code typically signifies a problem with the air/fuel ratio sensor’s operation, specifically indicating a “lack of HO2S-11 switches, sensor indicates lean.” HO2S-11 refers to the heated oxygen sensor (bank 1, sensor 1), located before the catalytic converter. Essentially, the sensor is reporting a lean condition, meaning there’s too much air and not enough fuel in the air/fuel mixture. This can lead to decreased performance, reduced fuel efficiency, and potential damage to the catalytic converter.
Symptoms of OBD2 Code P1131
Recognizing the symptoms of P1131 can help you diagnose the issue early. These symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the problem and the specific vehicle, but common signs include:
- Check Engine Light illuminated
- Reduced fuel economy
- Rough idling or engine misfires
- Hesitation or stumbling during acceleration
- Increased exhaust emissions
Common Causes of OBD2 Code P1131
Several factors can trigger the P1131 code. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective troubleshooting:
- Faulty HO2S-11 sensor: This is the most common culprit. Over time, oxygen sensors can degrade, providing inaccurate readings.
- Vacuum leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold or vacuum hoses can introduce excess air into the engine, leading to a lean condition.
- Fuel pressure issues: Low fuel pressure can prevent sufficient fuel delivery, causing a lean mixture. This can be due to a failing fuel pump, clogged fuel filter, or faulty fuel pressure regulator.
- Exhaust leaks: Leaks before the oxygen sensor can allow unmetered air into the exhaust stream, affecting the sensor’s readings.
- Wiring problems: Damaged or corroded wiring to the oxygen sensor can disrupt its signal.
- PCM (Powertrain Control Module) issues: In rare cases, a faulty PCM can incorrectly interpret data from the sensor.
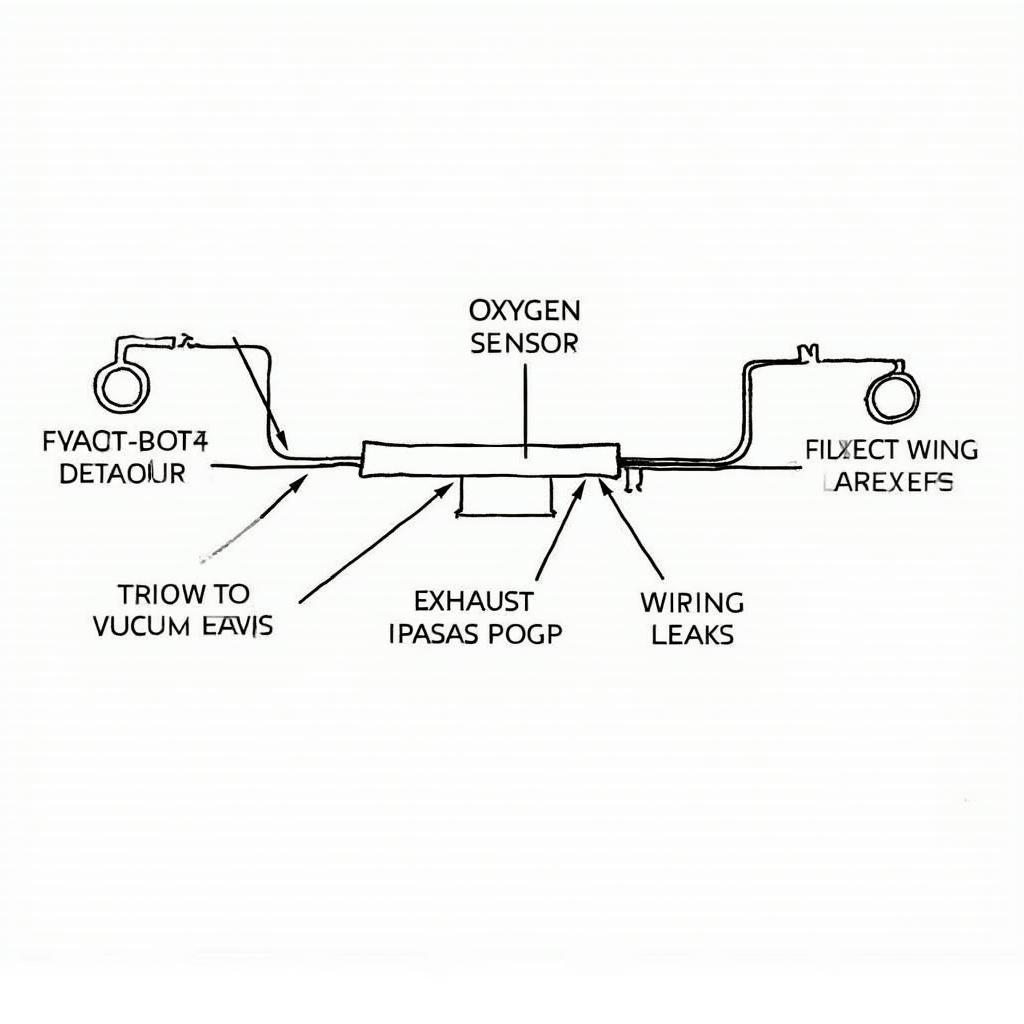 P1131 Trouble Code Causes
P1131 Trouble Code Causes
Diagnosing OBD2 Code P1131
Diagnosing P1131 involves a systematic approach to identify the root cause:
- Retrieve the code: Use an OBD2 scanner to confirm the P1131 code and check for other related codes.
- Inspect the vacuum system: Check for leaks in hoses, connections, and the intake manifold.
- Check fuel pressure: Test fuel pressure with a gauge to ensure it’s within the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Inspect the exhaust system: Look for leaks or damage before the oxygen sensor.
- Check the HO2S-11 sensor: Visually inspect the sensor for damage and test its voltage output using a multimeter.
- Check wiring and connectors: Inspect the wiring harness for damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
Fixing OBD2 Code P1131
The solution to the P1131 code depends on the diagnosed cause:
- Replace the HO2S-11 sensor: This is the most common fix.
- Repair vacuum leaks: Replace damaged hoses or repair leaks in the intake manifold.
- Address fuel pressure issues: Replace the fuel pump, fuel filter, or fuel pressure regulator as needed.
- Repair exhaust leaks: Seal or replace damaged components in the exhaust system.
- Repair wiring problems: Repair or replace damaged wiring and connectors.
- Address PCM issues: In rare cases, the PCM may need to be reprogrammed or replaced.
Conclusion: Tackling OBD2 Code P1131 Effectively
Understanding the OBD2 code P1131 is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and efficiency. By following the diagnostic procedures and solutions outlined in this guide, you can effectively address the issue and prevent further complications. Don’t hesitate to consult a qualified mechanic if you encounter difficulties diagnosing or repairing the P1131 code.
FAQ about OBD2 Code P1131
-
What does P1131 mean? It signifies a lean air/fuel mixture detected by the upstream oxygen sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1).
-
Can I drive with a P1131 code? While you might be able to drive, it’s recommended to address the issue promptly to prevent potential damage to the catalytic converter and other components.
-
How much does it cost to fix P1131? The cost varies depending on the cause and required repairs, ranging from a relatively inexpensive oxygen sensor replacement to more complex repairs.
-
How do I diagnose P1131? Use an OBD2 scanner, inspect the vacuum and exhaust systems, check fuel pressure, and test the oxygen sensor.
-
Is P1131 serious? While not immediately critical, ignoring it can lead to more significant problems down the line.
Need further assistance with your car’s diagnostic trouble codes? Contact our expert team via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected], or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We offer 24/7 customer support to help you get back on the road.
