The OBD2 code P0138 indicates a problem with the oxygen sensor circuit, specifically high voltage detected in Bank 1, Sensor 2. This code can be frustrating, but understanding its meaning and potential causes can help you address the issue effectively. p0138 obd2 This article dives deep into everything you need to know about the P0138 code, from its causes and symptoms to diagnostic and repair strategies.
What Does the P0138 Code Mean?
The P0138 code specifically refers to the downstream oxygen sensor, also known as the post-catalytic converter sensor, on Bank 1. “Bank 1” refers to the side of the engine that contains cylinder #1. Sensor 2 is the downstream sensor. This sensor’s primary function is to monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter. A high voltage reading suggests that the sensor is sending a signal outside the normal operating range, indicating a potential problem.
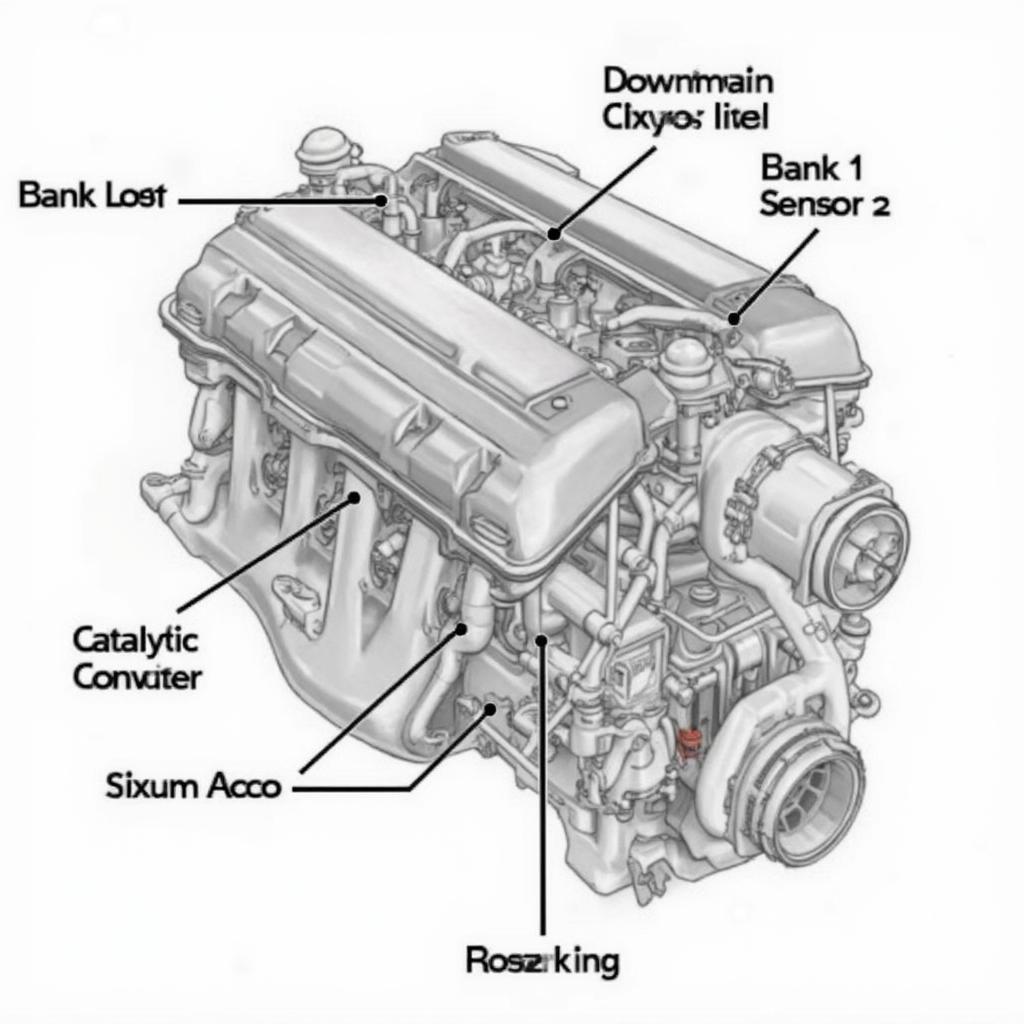 OBD2 Code P0138 Location
OBD2 Code P0138 Location
Common Causes of the P0138 Code
Several issues can trigger the P0138 code. Some of the most common culprits include:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor is the most likely cause. Over time, sensors can degrade and provide inaccurate readings.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring in the sensor circuit can disrupt the signal and cause a high voltage reading.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system, particularly before the downstream sensor, can introduce excess oxygen and affect sensor readings.
- Vacuum Leaks: Unmetered air entering the engine through vacuum leaks can disrupt the air/fuel mixture and impact oxygen sensor readings.
- Fuel System Problems: Issues like a faulty fuel injector or fuel pressure regulator can lead to a rich or lean air/fuel mixture, affecting sensor readings.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a P0138 Code
While the check engine light illuminating is the most obvious symptom, other signs may indicate a P0138 code:
- Decreased Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can cause the engine to run less efficiently, resulting in lower fuel mileage.
- Rough Idle or Misfires: While not always directly related, the underlying issues causing the P0138 code can sometimes lead to rough idling or misfires.
- Failed Emissions Test: A P0138 code almost certainly means your vehicle will fail an emissions test.
Diagnosing and Fixing the P0138 Code
Diagnosing a P0138 code requires a systematic approach:
- Retrieve the Code: Use an obd2 138 scanner to confirm the P0138 code and check for other related codes.
- Inspect the Wiring: Visually inspect the wiring and connector for the oxygen sensor, looking for damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Inspect the exhaust system for leaks, particularly before the downstream sensor.
- Test the Oxygen Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the oxygen sensor’s voltage output and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Replace the Oxygen Sensor: If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one.
“Always start with the simplest and most likely causes,” advises John Smith, a certified ASE Master Technician. “Checking the wiring and sensor itself is often the quickest way to identify the problem.”
Conclusion
The OBD2 code P0138, indicating a high voltage in the downstream oxygen sensor circuit, can be addressed with a methodical diagnostic approach. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic steps, you can effectively resolve this issue and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. Don’t ignore this code, as it can lead to further problems and decreased fuel economy. Addressing the P0138 code promptly will help maintain your vehicle’s performance and pass emissions tests.
FAQ
- Can I drive with a P0138 code? While you can technically drive with a P0138 code, it’s not recommended. It can impact fuel economy and potentially lead to further issues.
- How much does it cost to fix a P0138 code? The cost varies depending on the cause and whether you do the repair yourself or hire a mechanic. A new oxygen sensor typically costs between $50 and $200.
- How long does it take to fix a P0138 code? Replacing an oxygen sensor is a relatively quick job, usually taking less than an hour.
- Can a bad catalytic converter cause a P0138 code? While less common, a failing catalytic converter can sometimes contribute to a P0138 code.
- Will clearing the code fix the problem? Clearing the code will temporarily turn off the check engine light, but the underlying problem will remain and the code will likely return.
- How can I prevent a P0138 code in the future? Regular maintenance, including checking for exhaust leaks and ensuring the fuel system is functioning correctly, can help prevent oxygen sensor issues.
- What other codes are related to the P0138 code? Related codes might include P0137 (low voltage), P0139 (slow response), and P0140 (no activity).
Common Scenarios with P0138
- Scenario 1: A driver notices their check engine light is on and experiences reduced fuel economy. Scanning reveals a P0138 code. Inspection shows corroded wiring to the oxygen sensor.
- Scenario 2: A vehicle fails an emissions test. A scan reveals a P0138 code. Further diagnosis reveals a faulty oxygen sensor.
- Scenario 3: A driver notices a fluctuating idle and a check engine light. A scan reveals a P0138 code, along with a misfire code. Further investigation reveals a vacuum leak contributing to both issues.
Related Articles and Questions
- What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- Understanding Oxygen Sensors
- Troubleshooting Catalytic Converter Problems
Contact us for assistance via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We offer 24/7 customer support.
