The OBD2 codes P1150 and P1151 are common issues that can plague vehicle owners. These codes indicate problems with the air/fuel ratio sensor, specifically relating to the oxygen sensor’s performance and its ability to regulate the engine’s air and fuel mixture. Understanding these codes is crucial for effective troubleshooting and repair.
Decoding P1150 and P1151: What Do They Mean?
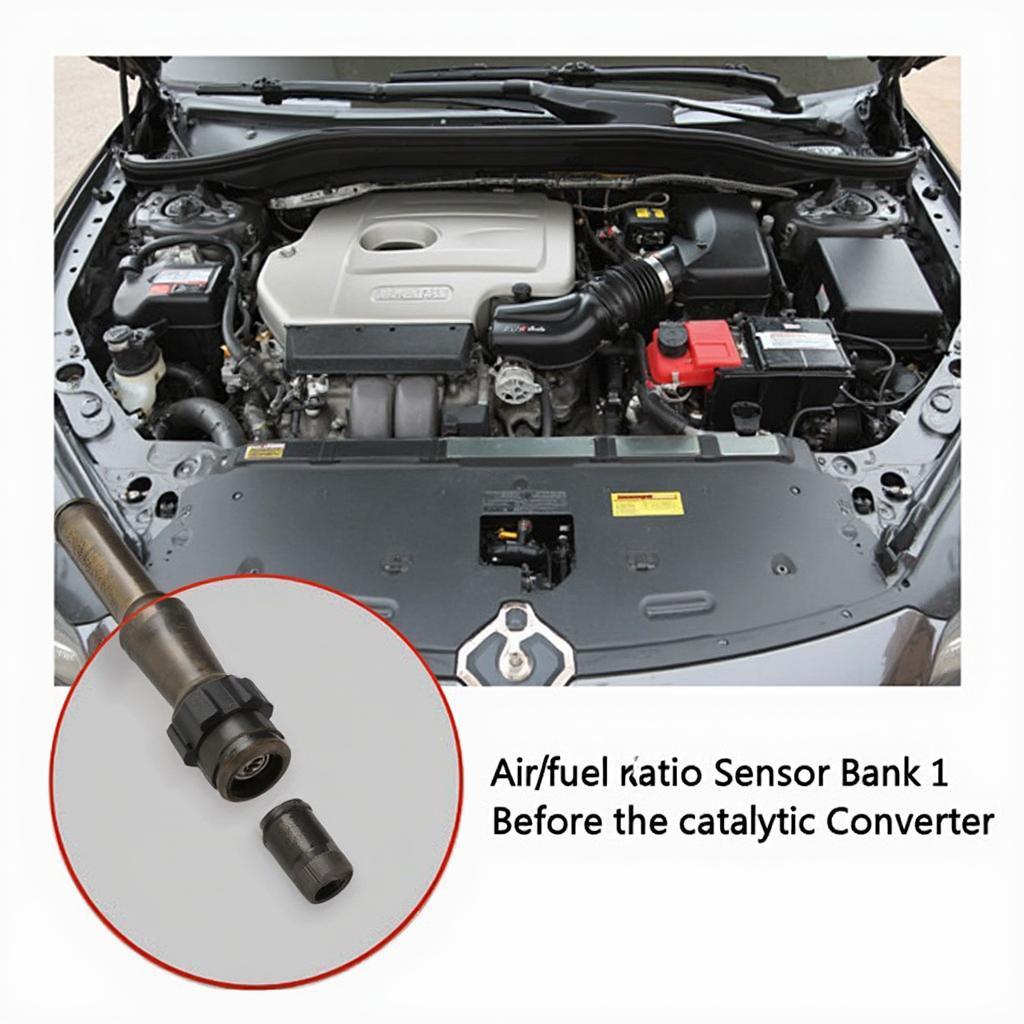
P1150 and P1151 often appear together and signal a problem with the air/fuel ratio sensor, usually in Bank 1 Sensor 1. This sensor is located before the catalytic converter and plays a vital role in optimizing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
- P1150: Indicates a lack of switching detected in the air/fuel ratio sensor circuit. This often points to a sensor that’s stuck in a lean or rich condition.
- P1151: Signifies that the air/fuel ratio sensor voltage is stuck lean. The engine control unit (ECU) detects a consistently low voltage from the sensor, indicating a lean air/fuel mixture.
Common Causes of P1150 and P1151
Several factors can trigger these trouble codes. Identifying the root cause is critical to avoid unnecessary repairs. Some common culprits include:
- Faulty Air/Fuel Ratio Sensor: The sensor itself might be malfunctioning due to wear and tear, contamination, or damage.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold or vacuum hoses can disrupt the air/fuel mixture and trigger the codes.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system before the sensor can also influence its readings.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring connections to the sensor can cause communication problems.
- Fuel Pressure Problems: Low or fluctuating fuel pressure can affect the air/fuel mixture and trigger the codes.
- Faulty ECU: In rare cases, a malfunctioning ECU can misinterpret sensor readings and set these codes.
Diagnosing P1150 and P1151 OBD2 Codes: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Read the Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the exact trouble codes stored in the ECU.
- Inspect the Wiring: Carefully check the wiring harness and connectors for any damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect vacuum hoses and the intake manifold for leaks.
- Inspect the Exhaust System: Look for leaks in the exhaust system, especially before the sensor.
- Test the Air/Fuel Ratio Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s voltage output and resistance.
- Check Fuel Pressure: Verify that the fuel pressure is within the manufacturer’s specifications.
How to Fix P1150 and P1151
The solution depends on the underlying cause. Here’s a breakdown:
- Replace the Sensor: If the sensor is faulty, replacement is the most common solution.
- Repair Vacuum Leaks: Seal any leaks found in the intake manifold or vacuum hoses.
- Repair Exhaust Leaks: Fix any leaks in the exhaust system.
- Repair Wiring Issues: Repair or replace damaged wiring or connectors.
- Address Fuel Pressure Problems: Repair the fuel pump or regulator if necessary.
“Addressing these codes promptly can prevent further damage and improve fuel efficiency,” says Michael Sanchez, Lead Automotive Diagnostic Technician at AutoTech Solutions.
Conclusion: Tackling P1150 and P1151
Understanding and addressing the P1150 and P1151 OBD2 codes are essential for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and efficiency. By following the diagnostic steps outlined above, you can pinpoint the root cause and implement the necessary repairs. Ignoring these codes can lead to more significant problems down the road.
FAQ
- Can I drive with P1150 and P1151? While driving is possible, it’s recommended to address the issue promptly to avoid further damage and reduced fuel economy.
- How much does it cost to fix P1150 and P1151? The cost varies depending on the cause and the specific vehicle.
- Are P1150 and P1151 serious? While not immediately critical, they can lead to more significant issues if left unaddressed.
- How can I prevent these codes? Regular maintenance, including checking for leaks and inspecting wiring, can help prevent these codes.
- Can I fix P1150 and P1151 myself? With some mechanical knowledge and the right tools, some repairs can be done DIY.
- What tools do I need to diagnose P1150 and P1151? An OBD2 scanner and a multimeter are essential for diagnosis.
- Where can I find more information about OBD2 codes? OBDFree.com offers extensive resources and information on various OBD2 codes.
Need support? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.