The OBD2 DLC (Data Link Connector), also known as the OBD2 port, is the gateway to your vehicle’s diagnostic system. Understanding obd2 dlc wiring is crucial for anyone who wants to delve deeper into their car’s performance, troubleshoot issues, or simply monitor its vital signs. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to OBD2 DLC wiring, covering everything from the basic pinout to advanced diagnostic techniques.
Decoding the OBD2 DLC Pinout
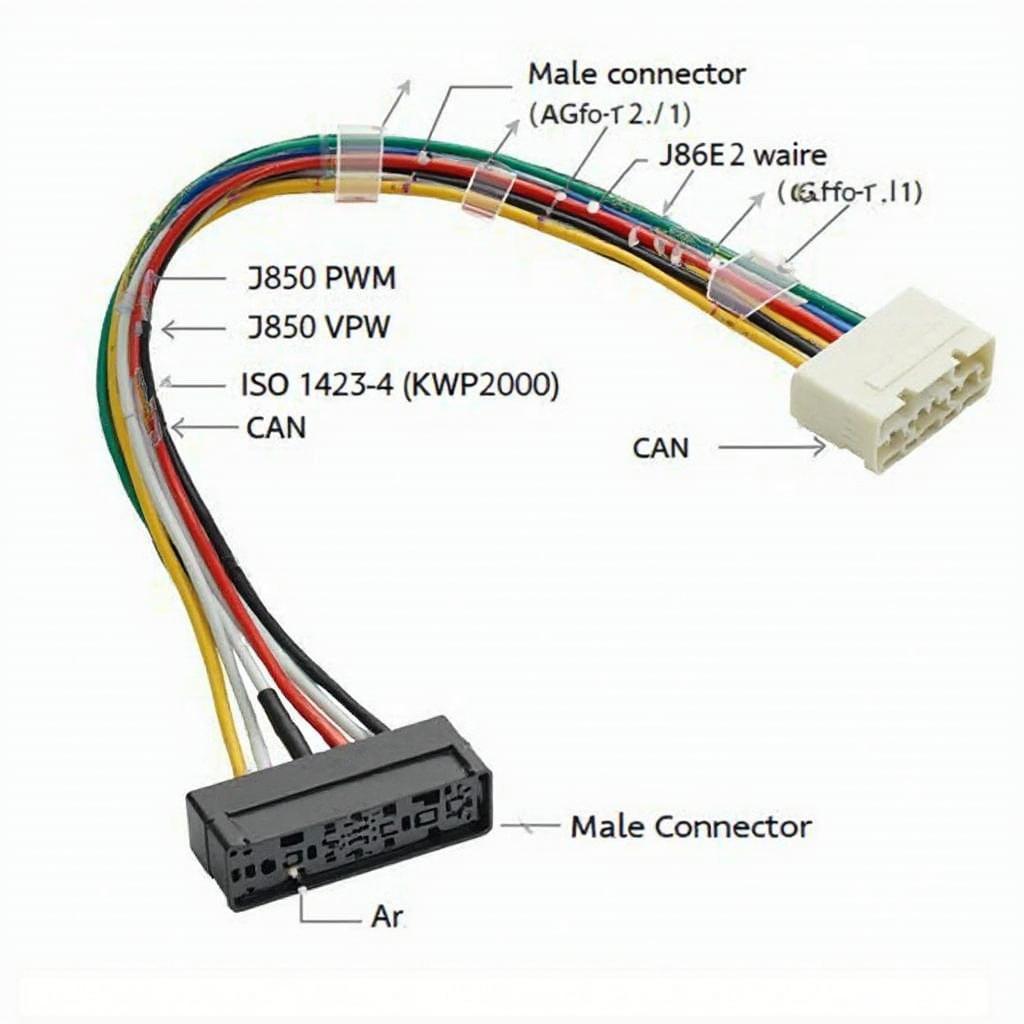
The OBD2 DLC is a standardized 16-pin connector. Each pin has a specific function, ranging from power supply to communication lines for various diagnostic protocols. While not all pins are used in every vehicle, understanding the standard pinout is essential for effective troubleshooting. For instance, pin 16 is your battery positive, essential for powering your obd2 scanner port.
Key Pins and Their Functions
- Pin 2 (J1850 Bus+): Used for the J1850 PWM communication protocol, primarily found in Ford vehicles.
- Pin 4 (Chassis Ground): Provides a ground connection for the diagnostic system.
- Pin 5 (Signal Ground): Another ground connection, specifically for signal circuits.
- Pin 6 (CAN High): Used for the Controller Area Network (CAN) communication protocol, a high-speed data bus commonly found in modern vehicles.
- Pin 7 (ISO 9141-2 K-Line): Used for the ISO 9141-2 communication protocol, often found in European and Asian vehicles.
- Pin 10 (J1850 Bus-): Complements Pin 2 for the J1850 PWM protocol.
- Pin 14 (CAN Low): Complements Pin 6 for the CAN communication protocol.
- Pin 15 (ISO 9141-2 L-Line): Used for the ISO 9141-2 protocol, often for bidirectional communication.
- Pin 16 (Battery Positive): Supplies power to the connected scan tool.
“Knowing the function of each pin is like having a roadmap to your vehicle’s internal systems,” says John Miller, Senior Automotive Diagnostic Technician at Miller’s Auto Repair. “It allows you to pinpoint communication issues and quickly diagnose problems.”
Common OBD2 DLC Wiring Issues
Several issues can arise with the obd2 dlc wiring, preventing proper communication between the scan tool and the vehicle’s ECU. These can include:
- Loose or Damaged Wires: Physical damage or loose connections can interrupt communication.
- Blown Fuses: A blown fuse related to the OBD2 system can cut off power to the port. If you suspect a fuse issue, checking your 2005 chevy trailblazer obd2 fuse is a good starting point. Similarly, for a 2006 Silverado, understanding the 2006 chevy silverado obd2 fuse location is critical.
- Corroded Connectors: Corrosion can build up on the pins, hindering electrical contact.
- Short Circuits: A short circuit can damage the OBD2 port or related components.
Troubleshooting OBD2 DLC Wiring Problems
If you’re experiencing issues with your OBD2 DLC, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you troubleshoot:
- Check the Fuse: Locate the OBD2 fuse in your vehicle’s fuse box (refer to your owner’s manual) and check if it’s blown. A quick check of your 2014 ford mustang v6 obd2 fuse location can save you a lot of hassle.
- Inspect the Connector: Visually examine the OBD2 DLC for any signs of damage, loose wires, or corrosion.
- Test for Power: Use a multimeter to check for power at pin 16 (Battery Positive) and ground at pin 4 (Chassis Ground).
- Check for Communication: If power and ground are present, use a scan tool to check for communication with the vehicle’s ECU. If the 98 nissan pathfinder obd2 port wont read, there could be a wiring issue.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re unable to identify the problem, it’s best to consult a qualified automotive technician.
“Remember, safety first! Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components in your vehicle,” advises Maria Sanchez, Lead Electrical Systems Engineer at Apex Automotive.
In conclusion, understanding obd2 dlc wiring is essential for effective vehicle diagnostics. By familiarizing yourself with the pinout, common issues, and troubleshooting steps, you can confidently diagnose and resolve problems related to your vehicle’s OBD2 system.
FAQ
- What is the OBD2 DLC? The OBD2 DLC is the standardized 16-pin connector used to access a vehicle’s diagnostic system.
- How many wires are in an OBD2 DLC? While the connector has 16 pins, not all of them are necessarily wired in every vehicle.
- What is the purpose of pin 16? Pin 16 provides battery positive voltage to power the connected scan tool.
- Can I damage my car by messing with the OBD2 DLC wiring? Yes, if you’re not careful, you could cause damage. Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components.
- What if my scan tool won’t connect to my car? There could be a number of reasons, including a blown fuse, damaged wiring, or a faulty scan tool.
For support contact WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or address 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We have a 24/7 customer support team.