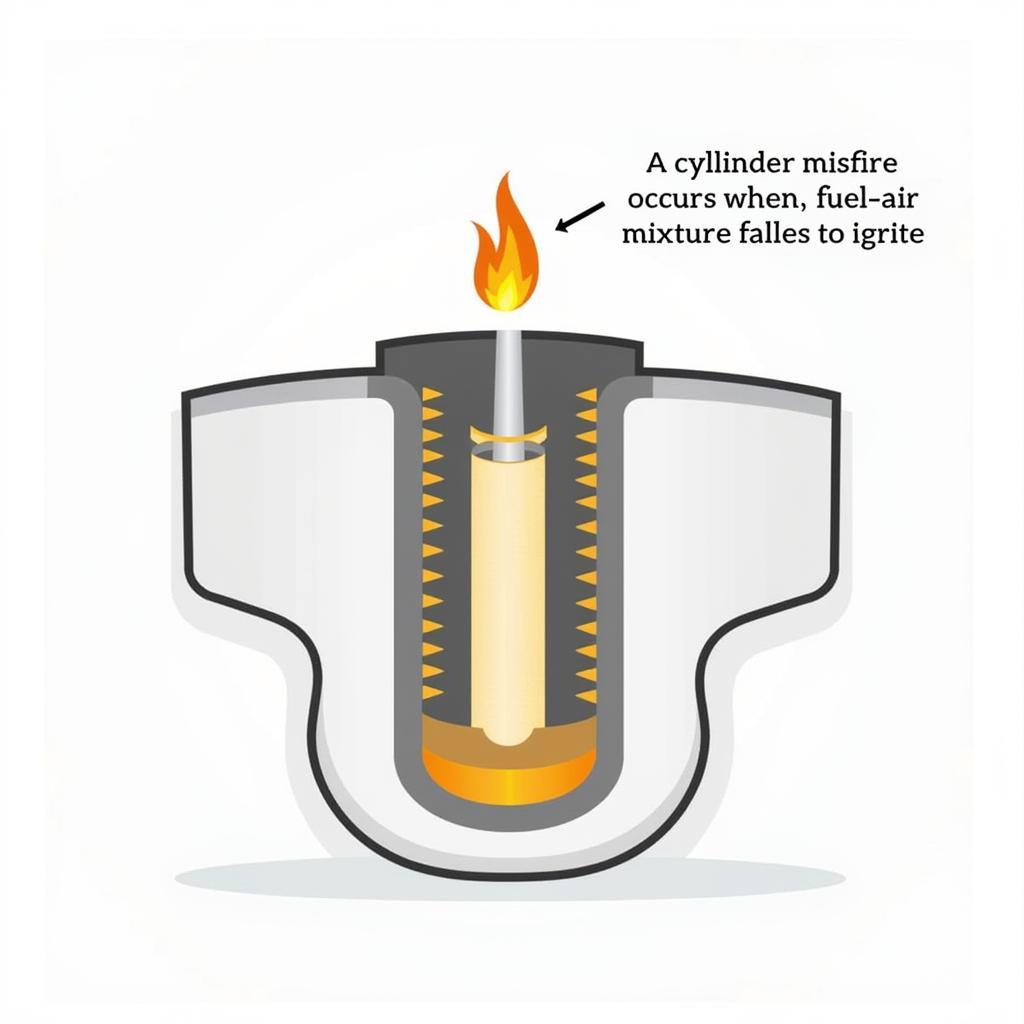
The dreaded check engine light is on, and your OBD2 scanner throws out the code P0306. What does it mean? In short, P0306 indicates a cylinder 6 misfire, a common yet potentially serious engine problem. This article dives deep into understanding OBD2 code P0306, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnostic steps, and possible solutions.
Understanding OBD2 Code P0306
A P0306 code specifically points to a misfire in cylinder 6. A misfire occurs when the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder fails to ignite properly or burns inefficiently. This disrupts the engine’s combustion cycle, leading to various performance issues and potentially damaging your vehicle’s catalytic converter.
Common Causes of P0306
Several factors can contribute to a P0306 code. Here’s a breakdown of the most common culprits:
- Faulty Spark Plugs or Wires: Worn-out spark plugs or damaged spark plug wires can prevent the electrical spark needed for ignition, causing a misfire.
- Fuel Injector Problems: A clogged or malfunctioning fuel injector may not deliver the right amount of fuel to cylinder 6, resulting in an improper air-fuel mixture.
- Vacuum Leaks: Any leaks in the intake manifold or vacuum hoses can disrupt the engine’s air intake, affecting the air-fuel ratio and leading to misfires.
- Compression Issues: Low compression in cylinder 6, often caused by worn piston rings or a damaged valve, can prevent efficient combustion.
- Ignition Coil Failure: A failing ignition coil responsible for cylinder 6 will fail to provide adequate spark for ignition.
- Timing Chain or Belt Issues: A stretched or slipped timing chain/belt can disrupt the engine’s timing, causing the valves to open and close at the wrong time, resulting in misfires.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor): While not a direct cause, a faulty O2 sensor can send incorrect data to the engine control unit (ECU), leading to an improper air-fuel mixture and potential misfires.
Symptoms of a P0306 Code
Along with the illuminated check engine light, you might experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Engine Hesitation or Stuttering: The engine might hesitate or stumble during acceleration or when under load.
- Rough Idle: Your vehicle might vibrate excessively while idling, indicating a misfire.
- Reduced Engine Power: A noticeable decrease in engine power and acceleration can occur.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: Misfires can lead to inefficient fuel burning, lowering your gas mileage.
- Strong Gasoline Odor: A strong smell of unburnt fuel from the exhaust can indicate a misfire.
Diagnosing OBD2 Code P0306
Accurately diagnosing the root cause of a P0306 code is crucial for effective repair. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Read the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner e46 to confirm the P0306 code and check for any other codes that might provide additional clues.
- Inspect Spark Plugs and Wires: Start by visually inspecting the spark plugs for wear, damage, or fouling. Check the spark plug wires for cracks, burns, or loose connections.
- Check Fuel Injectors: Inspect the fuel injector for cylinder 6. You can use a multimeter to test its resistance or perform a fuel injector balance test to ensure it’s working correctly.
- Inspect for Vacuum Leaks: Listen for hissing sounds around the intake manifold and vacuum hoses. Use a carburetor cleaner or a smoke machine to detect leaks.
- Compression Test: Perform a compression test on all cylinders, paying close attention to cylinder 6. This will help determine if there’s a compression issue.
- Test Ignition Components: Test the ignition coil responsible for cylinder 6 using a multimeter. Check the ignition system wiring for any damage or loose connections.
- Inspect Timing Components: Inspect the timing belt or chain for any signs of wear, stretching, or damage. Ensure the timing marks are aligned correctly.
Fixing a P0306 Code
The repair for a P0306 code depends entirely on the underlying cause. Here are some common solutions:
- Replace Spark Plugs and Wires: If the spark plugs are worn or damaged, replace them with new ones. Consider replacing the spark plug wires as well.
- Clean or Replace Fuel Injectors: Clean clogged fuel injectors using a fuel injector cleaning kit. If the injector is faulty, replace it with a new one.
- Repair Vacuum Leaks: Repair any leaks found in the intake manifold or vacuum hoses. Replace damaged components as necessary.
- Address Compression Issues: Repairing low compression often requires more involved work, such as replacing piston rings, valves, or even rebuilding the engine. Consult a qualified mechanic for these repairs.
- Replace Faulty Ignition Coil: If the ignition coil for cylinder 6 is faulty, replace it with a new one.
- Replace Timing Belt/Chain: If the timing belt or chain is worn, stretched, or damaged, replace it immediately. Ensure the timing marks are aligned correctly during installation.
- Replace Faulty O2 Sensor: If a faulty oxygen sensor is contributing to the misfire, replace it with a new one.
Expert Insight:
“While DIY repairs can be tempting, remember that misdiagnosing or incorrectly fixing a P0306 code can lead to further engine damage and costly repairs down the line,” says John Miller, a certified master mechanic with over 20 years of experience. “If you’re unsure about any step of the diagnosis or repair process, it’s best to seek professional help from a qualified mechanic.”
Conclusion
Addressing an OBD2 code P0306 promptly is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and preventing further engine damage. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic steps, you can effectively troubleshoot the problem and determine the appropriate solution. Remember, while DIY repairs are possible, seeking professional help is recommended for complex issues to ensure your vehicle’s longevity and your safety.
FAQs about OBD2 Code P0306
1. Can I still drive with a P0306 code?
It’s not recommended to drive for extended periods with a P0306 code. Driving with a misfire can damage your catalytic converter and lead to further engine problems.
2. How much does it cost to fix a P0306 code?
The repair cost varies greatly depending on the underlying cause. Simple fixes like spark plug replacements can cost under $100, while major repairs like engine work can cost thousands of dollars.
3. Can bad gas cause a P0306 code?
While rare, contaminated fuel can cause misfires. If you suspect bad gas, try adding a fuel system cleaner or draining and refilling your fuel tank.
4. How do I reset the check engine light after fixing a P0306 code?
You can reset the check engine light using an OBD2 acura device or by disconnecting the battery for a few minutes. However, the light will come back on if the underlying issue isn’t resolved.
5. Is a P0306 code serious?
Yes, a P0306 code indicates a potentially serious engine issue. Ignoring it can lead to costly repairs and further damage to your vehicle.
Need more help with your OBD2 codes? Check out these resources:
For personalized assistance with your car diagnostic needs, don’t hesitate to reach out to our expert team:
- WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880
- Email: [email protected]
We offer 24/7 support to help you get back on the road safely.