OBD2 uses a variety of sensors to monitor your vehicle’s performance and emissions. Understanding what sensors does obd2 use can help you diagnose car problems and maintain your vehicle’s health. This article dives deep into the world of OBD2 sensors, explaining their functions and importance. do 1995 vehicles have obd2 sensors
Decoding the OBD2 Sensor Network
The OBD2 system, mandatory in most vehicles since 1996, acts as a window into your car’s internal workings. It relies on a network of sensors strategically placed throughout the engine and other key systems. These sensors continuously monitor various parameters, providing crucial data to the vehicle’s computer (ECU) and allowing the OBD2 scanner to retrieve diagnostic information.
The Core OBD2 Sensors: Engine Performance and Emissions
- Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor): Measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This data helps the ECU adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion and reduced emissions. A faulty O2 sensor can lead to decreased fuel efficiency and increased emissions.
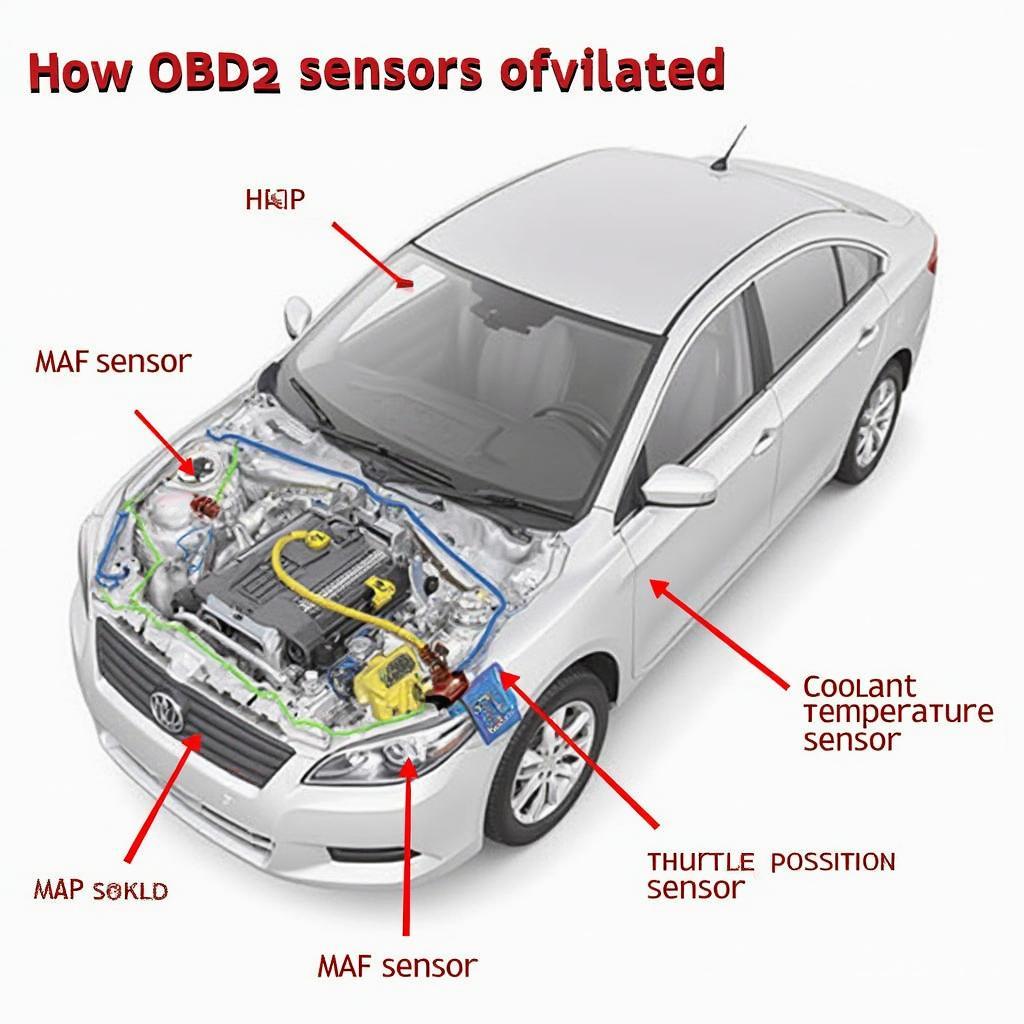
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor: Determines the amount of air entering the engine. The ECU uses this information to calculate the correct fuel injection amount. A malfunctioning MAF sensor can result in poor engine performance and increased fuel consumption.
- Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor: Measures the pressure inside the intake manifold. This data is used to calculate engine load and adjust fuel delivery accordingly. Problems with the MAP sensor can lead to rough idling, hesitation, and reduced power.
- Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS): Monitors the engine coolant temperature. The ECU uses this information to control the engine’s warm-up cycle, fuel injection, and cooling fan operation. A faulty CTS can cause overheating, poor fuel economy, and starting problems.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): Measures the position of the throttle plate, indicating how much air is entering the engine. The ECU uses this data to control fuel injection and ignition timing. A malfunctioning TPS can result in poor acceleration, hesitation, and a high idle.
Beyond the Basics: Other Important OBD2 Sensors
While the above sensors are considered core components of the OBD2 system, there are several other crucial sensors that contribute to the overall picture of your vehicle’s health:
- Camshaft Position Sensor: Determines the position of the camshaft, which is essential for precise ignition timing and valve operation.
- Crankshaft Position Sensor: Measures the position and speed of the crankshaft, providing vital information for ignition timing and fuel injection.
- Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS): Measures the speed of the vehicle, which is used by the speedometer, cruise control, and other systems.
- Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) System Sensor: Monitors the EVAP system, which prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere.
What if My OBD2 Scanner Shows a Sensor Fault?
Don’t panic! A sensor fault code doesn’t always mean the sensor itself is bad. Sometimes, the problem lies in the wiring, connectors, or other related components. how to get rid of a permanent obd2 code will help you.
Expert Insights on OBD2 Sensors
“Understanding the role of each sensor is crucial for accurate diagnostics,” says automotive expert, Dr. Emily Carter. “A holistic approach, considering the interplay between different sensors and systems, often leads to quicker and more effective troubleshooting.”
Conclusion: Mastering OBD2 for Enhanced Vehicle Maintenance
Understanding what sensors does obd2 use empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance. By recognizing the function and importance of each sensor, you can effectively use an obd2 diag scan tool to diagnose issues, prevent costly repairs, and ensure optimal performance and longevity.
FAQ
- How many sensors does OBD2 use? The number of sensors varies depending on the make and model of the vehicle.
- Can I replace an OBD2 sensor myself? Yes, with the right tools and knowledge, many OBD2 sensors can be replaced at home.
- What is the most common OBD2 sensor failure? The oxygen sensor is often cited as one of the most common OBD2 sensor failures.
- How often should I check my OBD2 system? It’s a good idea to check your OBD2 system whenever you experience any unusual car behavior or as part of regular maintenance.
- Can an OBD2 scanner diagnose all car problems? No, an OBD2 scanner primarily focuses on engine and emissions-related problems.
- What is a “pending code” on an OBD2 scanner? A pending code indicates a potential problem that hasn’t yet become a full-fledged fault.
- Where can I find more information about specific OBD2 codes? Online resources and repair manuals can provide detailed information about specific OBD2 codes.
Need help with your car diagnostics? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our 24/7 customer support team is always ready to assist you.