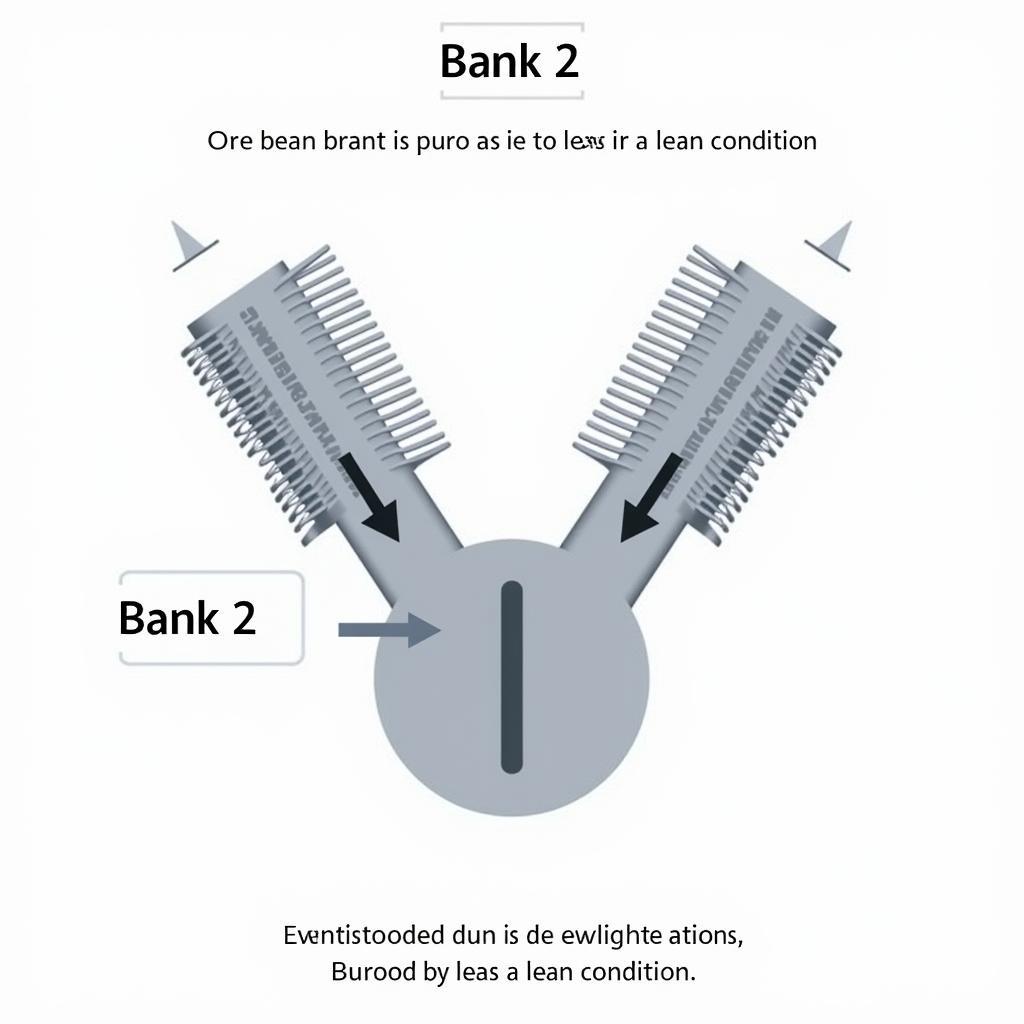
The dreaded check engine light can strike fear into any driver’s heart, especially when accompanied by a cryptic OBD2 code like P0178. This code, indicating a “Fuel System Too Lean (Bank 2),” can signal a range of issues within your vehicle’s engine management system. But fear not, this comprehensive guide will demystify P0178, explaining its meaning, causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions.
A “lean” condition occurs when the air-fuel mixture in your engine’s combustion chamber has too much air compared to fuel. This imbalance disrupts the optimal combustion process, potentially leading to reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and even engine damage if left unaddressed. “Bank 2” refers to the side of the engine that doesn’t house cylinder one.
Common Symptoms of OBD2 Code P0178
While the check engine light is often the first indicator, you might experience other symptoms accompanying a P0178 code:
- Rough Idle: The engine might feel shaky or vibrate excessively when idling.
- Misfires: The engine may misfire, causing a jerking sensation during acceleration.
- Hesitation on Acceleration: You might notice a delay or lag in engine response when you press the accelerator.
- Increased Emissions: A lean condition can disrupt the catalytic converter’s efficiency, leading to increased harmful emissions.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A lean mixture burns hotter and less efficiently, potentially reducing your gas mileage.
What Causes a P0178 Code?
Numerous culprits can contribute to a lean condition in bank 2. Some of the most common causes include:
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold, vacuum hoses, or PCV valve can disrupt the air-fuel ratio by allowing unmetered air into the engine.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor(s): Oxygen sensors monitor the exhaust gases and provide feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture. A malfunctioning sensor, particularly on bank 2, can lead to inaccurate readings and a lean condition.
- Fuel Injector Problems: A clogged, dirty, or failing fuel injector on bank 2 can restrict fuel flow, creating a lean mixture.
- Fuel Pressure Issues: Low fuel pressure, often caused by a weak fuel pump or a clogged fuel filter, can starve the engine of fuel.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust manifold or exhaust pipes before the oxygen sensors can confuse the sensors and lead to inaccurate readings.
- EVAP System Malfunction: Issues with the evaporative emissions control (EVAP) system, such as a stuck open purge valve, can introduce fuel vapors into the intake manifold, disrupting the air-fuel ratio.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Problems: The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. A dirty or faulty MAF sensor can provide incorrect readings to the ECU, leading to an improper air-fuel mixture.
Diagnosing OBD2 Code P0178
Accurately diagnosing the root cause of a P0178 code requires a systematic approach:
- Read the Code: Start by connecting an OBD2 scanner to your vehicle’s diagnostic port and reading the stored code(s). Note any additional codes present, as they can provide valuable clues.
- Inspect for Vacuum Leaks: Visually inspect all vacuum hoses, the intake manifold, and the PCV valve for cracks, loose connections, or damage. You can also use a carburetor cleaner spray around these areas while the engine is running—any changes in engine idle speed might indicate a leak.
- Check Fuel Pressure: Use a fuel pressure gauge to ensure the fuel pump delivers adequate pressure. Compare your readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Inspect and Test Oxygen Sensors: Locate the oxygen sensors on bank 2 (refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for specific locations). Visually inspect the sensors for damage or contamination. If necessary, use a multimeter to test their resistance and voltage output according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Examine Fuel Injectors: Check the fuel injectors on bank 2 for signs of clogging or malfunction. You can listen for the characteristic “clicking” sound of the injectors firing while the engine is running.
- Inspect the EVAP System: Check the EVAP system for leaks or malfunctions, paying attention to the purge valve and charcoal canister.
“When diagnosing a P0178 code, always prioritize the simpler and more common causes first,” advises John Miller, ASE Certified Master Technician. “Start with visual inspections, then move on to more involved testing procedures. Remember, a thorough diagnosis is key to a successful repair.”
Fixing a P0178 Code: Common Solutions
Once you’ve pinpointed the cause of your P0178 code, you can implement the appropriate solution:
- Repair Vacuum Leaks: Replace any cracked, damaged, or loose vacuum hoses, intake manifold gaskets, or PCV valve components.
- Replace Faulty Oxygen Sensor(s): If you’ve determined that an oxygen sensor on bank 2 is faulty, replace it with a new one that meets OEM specifications.
- Clean or Replace Fuel Injectors: If clogged fuel injectors are the culprit, consider cleaning them using a fuel injector cleaning kit. However, if cleaning doesn’t resolve the issue, replacement might be necessary.
- Address Fuel Pressure Problems: Replace a weak or failing fuel pump. If the fuel filter is clogged, replace it with a new one.
- Repair Exhaust Leaks: Address any leaks in the exhaust manifold, pipes, or gaskets to ensure accurate oxygen sensor readings.
- Repair or Replace EVAP Components: Fix any leaks or replace malfunctioning components within the EVAP system, such as the purge valve or charcoal canister.
- Clean or Replace MAF Sensor: If the MAF sensor is dirty, carefully clean it using MAF sensor cleaner. If cleaning doesn’t resolve the issue or the sensor is damaged, replace it with a new one.
After addressing the problem, clear the code using your OBD2 scanner and test drive your vehicle to confirm that the code doesn’t reappear.
Conclusion
While a P0178 code can seem daunting, understanding its meaning, causes, and solutions can empower you to address the issue effectively. Remember, a systematic diagnostic approach and prompt repairs are crucial to restoring your vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, and overall health. If you’re unsure about any step of the diagnosis or repair process, don’t hesitate to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic.