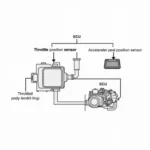
The OBD2 controller, often referred to as the engine control unit (ECU), plays a crucial role in modern vehicles. This sophisticated computer system manages a wide array of engine and transmission functions, ensuring optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. More importantly, it serves as the communication hub for accessing valuable diagnostic information through the OBD2 port.
What Does an OBD2 Controller Do?
The OBD2 controller constantly monitors various sensors throughout your vehicle, collecting data on everything from engine speed and temperature to oxygen levels and throttle position. Based on this data, it makes real-time adjustments to parameters like:
- Fuel Injection: Determining the precise amount of fuel delivered to the engine for combustion.
- Ignition Timing: Controlling the timing of the spark plugs to ignite the air-fuel mixture.
- Variable Valve Timing: Adjusting the timing of the engine valves to optimize performance and efficiency.
- Emissions Control: Managing systems like the EGR valve and catalytic converter to minimize harmful emissions.
- Transmission Shifting: Controlling the shift points and pressure in automatic transmissions.
Beyond these core functions, the OBD2 controller also plays a vital role in:
- Storing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): When a fault is detected, the controller logs a specific code that pinpoints the issue.
- Illuminating Warning Lights: Triggering the “Check Engine” light and other warning indicators on the dashboard to alert the driver of potential problems.
- Enabling Communication with OBD2 Scanners: Allowing access to stored DTCs, live data streams, and other diagnostic information.
Accessing the OBD2 Controller with a Scanner
The OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, provides a standardized interface to connect an OBD2 scanner to the controller. This allows you to:
- Read and Clear DTCs: Retrieve stored trouble codes to identify the root cause of warning lights or performance issues. Once the problem is fixed, you can clear the codes to turn off the warning lights.
- View Live Data Streams: Monitor real-time sensor readings like engine RPM, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor voltage, and more. This helps diagnose intermittent problems or fine-tune performance modifications.
- Perform Advanced Functions: Depending on the scanner and vehicle model, you may be able to access advanced functions like actuator tests, adaptations, and module coding.
Common Issues with OBD2 Controllers
While OBD2 controllers are generally reliable, they can experience issues like:
- Software Corruption: Faulty updates or electrical glitches can corrupt the controller’s software, leading to malfunctions.
- Communication Errors: Problems with wiring, connectors, or the OBD2 port itself can disrupt communication between the controller and the scanner.
- Hardware Failure: Extreme temperatures, vibrations, or component aging can cause physical damage to the controller.
If you suspect an issue with your OBD2 controller, it’s crucial to have it diagnosed and repaired by a qualified mechanic.
Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
The market offers a wide range of OBD2 scanners, from basic code readers to professional-grade diagnostic tools. The right scanner for you depends on your needs and budget:
- Basic Code Readers: Affordable and easy to use, ideal for reading and clearing DTCs.
- Mid-Range Scanners: Offer additional features like live data viewing and some advanced functions.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: Provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including module coding and bi-directional control.
When choosing a scanner, consider factors like:
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the scanner supports your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Features: Determine the essential features you need based on your diagnostic goals.
- User Interface: Opt for a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear display.
- Software Updates: Choose a scanner that offers regular software updates to ensure compatibility with newer vehicles.
The OBD2 Controller: Essential for Modern Diagnostics
The OBD2 controller serves as the gateway to your vehicle’s inner workings, providing valuable insights into its health and performance. Understanding how it works and utilizing an OBD2 scanner empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance, diagnose problems accurately, and ensure optimal operation.