Electronic Throttle Body (ETB) OBD2 codes can be a real headache for car owners. These codes, often starting with P0120 or P2100, indicate a problem somewhere in your car’s throttle control system. But what exactly do these codes mean, and how can you fix them?
This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of ETB OBD2 codes, demystifying their meaning, potential causes, and solutions. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a car enthusiast looking to understand your vehicle better, this article is your one-stop resource for all things ETB OBD2 codes.
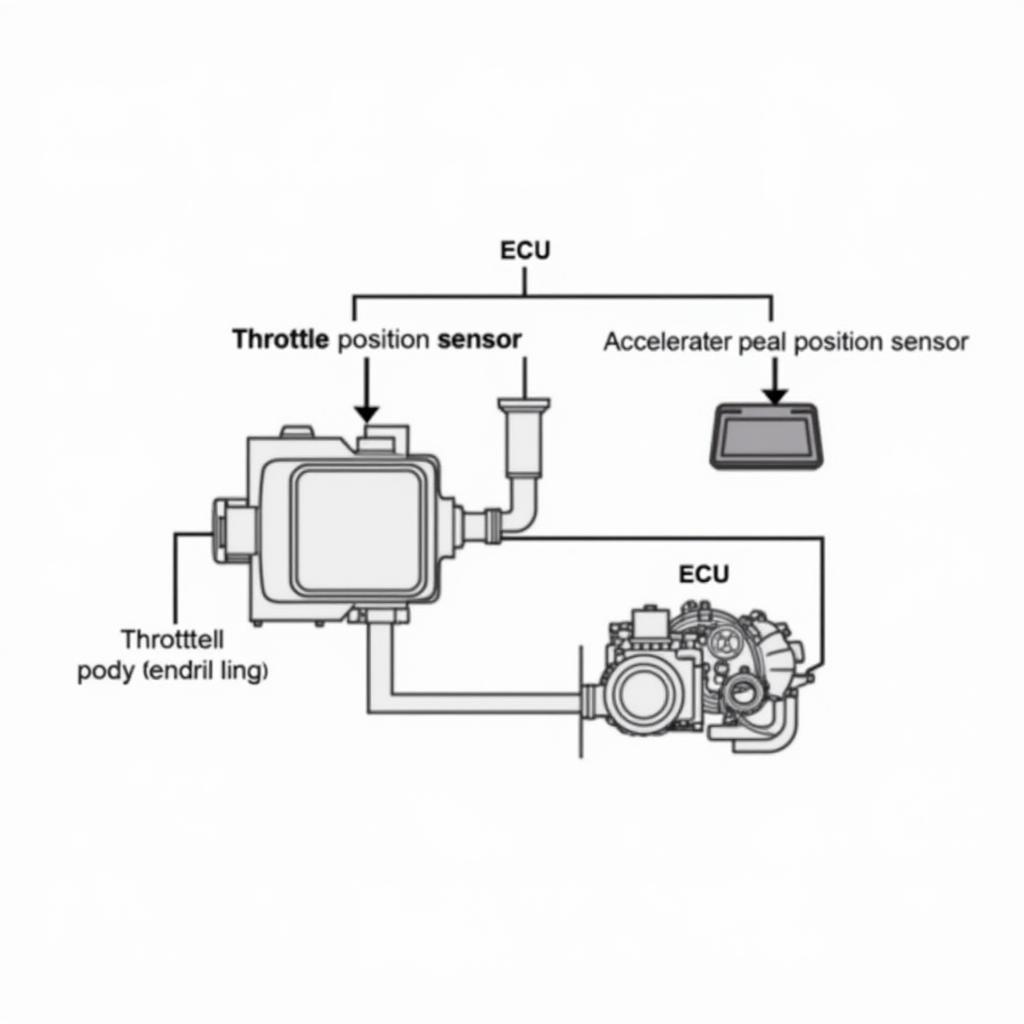
What is an ETB System and How Does it Work?
Before we dive into the codes themselves, it’s crucial to understand what the ETB system does. In modern vehicles, gone are the days of a physical cable connecting your gas pedal to the throttle plate. Instead, we have the ETB system, a drive-by-wire setup that offers improved responsiveness, fuel efficiency, and integration with other vehicle systems like cruise control and traction control.
Here’s a breakdown:
- Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor: This sensor measures how far you press the gas pedal.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The brain of the operation, the ECU receives data from the pedal sensor and other sensors, crunches the numbers, and sends commands to the throttle body.
- Throttle Body: This component houses the throttle plate, a butterfly valve that controls the amount of air entering the engine.
- Throttle Position Sensor: This sensor tells the ECU the exact position of the throttle plate, ensuring it aligns with your pedal input.
Common ETB OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
When the ECU detects an inconsistency in the ETB system—say, a discrepancy between pedal position and throttle plate angle—it triggers an ETB OBD2 code. Here are some of the most frequent ones:
- P0120 – Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit Malfunction: This generic code points to a problem with the throttle position sensor circuit.
- P0121 – Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit Range/Performance Problem: This code indicates an issue with the signal from the throttle position sensor, potentially a faulty sensor or wiring issue.
- P0122 – Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit Low Input: This code suggests the ECU is receiving a lower-than-expected voltage signal from the throttle position sensor.
- P0123 – Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit High Input: The inverse of P0122, this code means the ECU is receiving a higher voltage signal than expected.
- P2100 – Throttle Actuator Control Motor Circuit/Open: This code indicates a problem with the throttle actuator control motor circuit, which controls the throttle plate.
What Causes ETB OBD2 Codes?
A range of issues can trigger ETB OBD2 codes. Some common culprits include:
- Dirty Throttle Body: Carbon buildup on the throttle plate or its housing can restrict airflow and trigger codes.
- Faulty Throttle Position Sensor: A malfunctioning sensor can send incorrect signals to the ECU, leading to performance issues.
- Worn-Out Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor: Similar to a faulty throttle position sensor, a worn-out accelerator pedal position sensor can disrupt the signal flow.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring within the ETB system can cause communication errors between components.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold or other vacuum hoses can disrupt airflow and trigger ETB codes.
- Faulty ECU: In rare cases, a malfunctioning ECU can be the root cause of ETB issues.
How to Diagnose and Fix ETB OBD2 Codes
Diagnosing ETB OBD2 codes requires a systematic approach:
- Read the Code(s): Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the specific code(s) stored in your vehicle’s ECU.
- Inspect the Throttle Body: Check the throttle body for dirt and carbon buildup. Clean it thoroughly if necessary.
- Check the Wiring: Inspect all wiring and connectors within the ETB system for damage, corrosion, or looseness.
- Test the Sensors: Use a multimeter to test the throttle position sensor and accelerator pedal position sensor for proper voltage readings.
- Check for Vacuum Leaks: Inspect the intake manifold and vacuum hoses for leaks using a visual inspection or a smoke test.
- Consult a Mechanic: If the problem persists, it’s best to consult with a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and repair.
Preventing ETB OBD2 Codes
While not all ETB issues are preventable, some regular maintenance can go a long way:
- Regular Throttle Body Cleaning: Cleaning the throttle body every 30,000 miles or as part of a tune-up can prevent carbon buildup.
- Inspecting Wiring and Connectors: Periodically checking the wiring and connectors in the ETB system for signs of wear and tear can help identify potential issues early.
- Addressing Issues Promptly: Addressing any drivability issues like rough idling or hesitation promptly can prevent minor problems from escalating into major ones.
Conclusion
ETB OBD2 codes might seem daunting, but understanding their meaning and potential causes empowers you to address them effectively. By following the diagnosis and prevention tips outlined in this guide, you can keep your car’s throttle control system running smoothly and avoid those unexpected trips to the mechanic.
Remember, a well-maintained ETB system translates to a smoother, more responsive, and more fuel-efficient driving experience.
FAQs
Q: Can I drive my car with an ETB OBD2 code?
A: While you might be able to drive short distances, it’s not recommended. Driving with a faulty ETB system can lead to reduced performance, poor fuel economy, and potentially dangerous driving conditions.
Q: How much does it cost to fix an ETB OBD2 code?
A: The cost can vary significantly depending on the specific issue and labor costs in your area. A simple throttle body cleaning might cost under $100, while replacing a faulty throttle body could range from $300 to $700 or more.
Q: Can I clean the throttle body myself?
A: Yes, cleaning the throttle body is a relatively straightforward DIY task. However, if you’re not comfortable working on your car, it’s best to leave it to a professional.
Q: What tools do I need to diagnose ETB OBD2 codes?
A: You’ll need an OBD2 scanner, a multimeter, and basic hand tools. A smoke machine can be helpful for diagnosing vacuum leaks.
Q: Are there any risks associated with cleaning the throttle body?
A: While generally safe, using the wrong cleaning products or being overly aggressive can damage the throttle body. It’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions or consult a professional if unsure.
Need More Help with ETB OBD2 Codes?
If you’re facing persistent ETB OBD2 codes or need expert assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out. Contact our dedicated support team via WhatsApp at +1(641)206-8880 or email us at [email protected]. We’re available 24/7 to assist you with all your car diagnostic needs.