The OBD2 code P0230 signals a problem within your vehicle’s fuel pump circuit. This code specifically indicates a malfunction with the fuel pump’s primary control circuit, which is responsible for supplying power to the fuel pump itself. Encountering this code usually means your car’s engine control module (ECM) has detected a voltage reading outside the normal range, signifying an issue in the electrical pathway to your fuel pump.
Decoding the P0230 Code: What Does It Mean for Your Car?
The fuel pump is a vital component in your car’s fuel delivery system. Its job is to draw fuel from the tank and deliver it to the engine for combustion. The P0230 code suggests an electrical problem is disrupting this process. Here’s a breakdown:
- Fuel Pump Relay: This relay acts as a switch, controlling the flow of power to the fuel pump. A faulty relay can interrupt the circuit.
- Fuel Pump: While the code focuses on the circuit, the fuel pump itself could be faulty and drawing too much or too little current.
- Wiring and Connectors: Damage, corrosion, or loose connections within the fuel pump’s wiring harness can disrupt the electrical flow.
- ECM Issues: In rare cases, a problem with the ECM itself might be misinterpreting signals and triggering the P0230 code.
Common Symptoms of a P0230 Code
Identifying the P0230 code early is crucial. Ignoring it can lead to more serious engine problems. Look out for these common symptoms:
- Check Engine Light: The most obvious sign, your check engine light will illuminate.
- Difficulty Starting: A malfunctioning fuel pump circuit can prevent adequate fuel from reaching the engine, making starting difficult or impossible.
- Engine Stalling: Intermittent power supply to the fuel pump can cause the engine to stall while driving.
- Reduced Engine Performance: Insufficient fuel delivery can lead to a loss of power, hesitation, and poor acceleration.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A struggling fuel pump can consume more power, leading to reduced fuel efficiency.
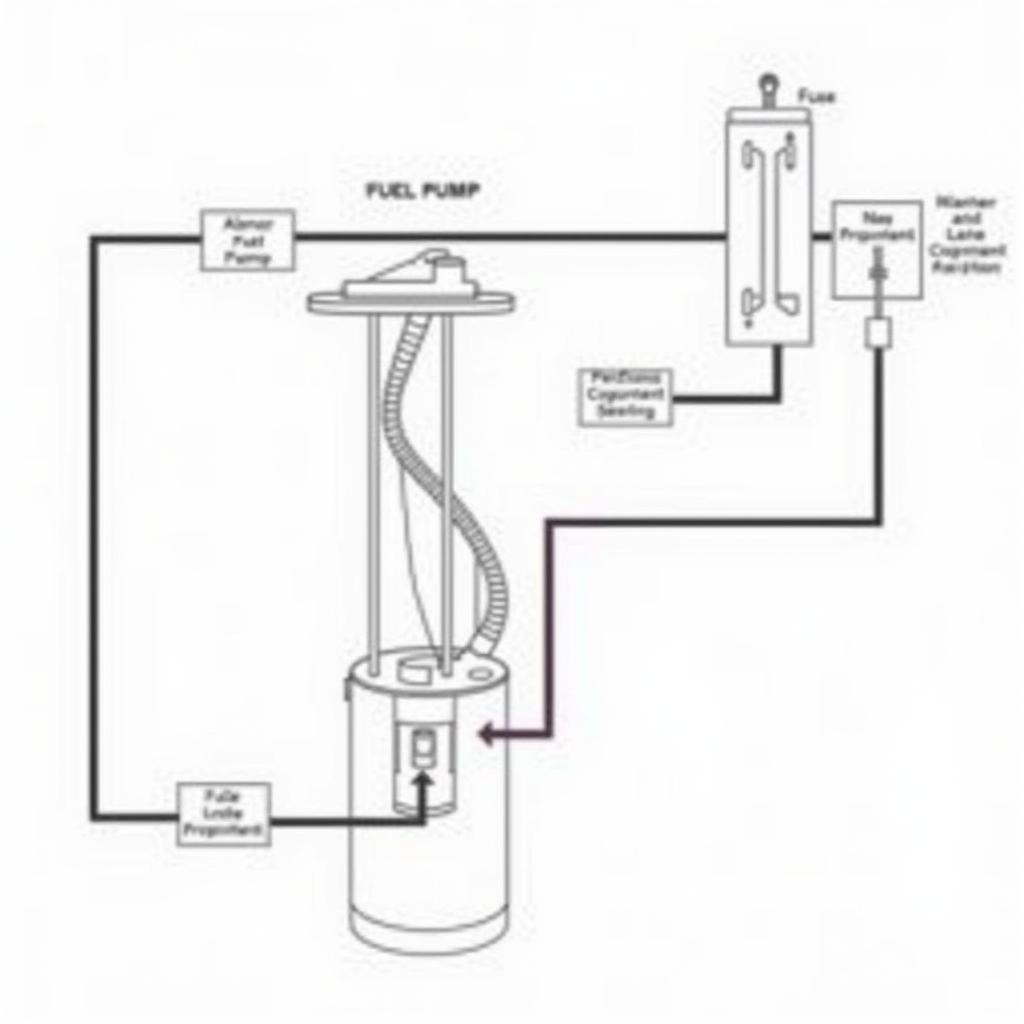 Fuel Pump Circuit Diagram
Fuel Pump Circuit Diagram
Diagnosing and Troubleshooting the P0230 Code
Accurately diagnosing the P0230 code requires a systematic approach:
- Check for Other Codes: Scan your vehicle’s computer for any additional OBD2 codes. These can provide valuable clues and point to related issues.
- Inspect the Fuel Pump Relay: Locate the fuel pump relay and check for any signs of damage, burning, or loose connections. Test the relay for proper function.
- Examine the Fuel Pump Fuse: Locate and visually inspect the fuel pump fuse for any signs of a blown fuse. If necessary, test the fuse with a multimeter for continuity.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Thoroughly examine the wiring harness leading to the fuel pump, looking for any frayed wires, corrosion, or loose connections. Pay close attention to areas where the harness might rub against other components.
- Test Fuel Pump Pressure: Using a fuel pressure gauge, verify if the fuel pump is delivering adequate pressure. Low pressure indicates a problem with the pump or its circuit.
- Test Fuel Pump Voltage: Use a multimeter to test the voltage at the fuel pump connector. This will help determine if the pump is receiving the correct voltage supply.
Expert Insights on the P0230 Code
“Many car owners jump to replacing the fuel pump when they encounter a P0230 code,” says automotive expert John Miller, “However, it’s crucial to remember that this code points to an electrical circuit issue. While a faulty pump is a possibility, it’s essential to rule out other components like the relay, fuse, and wiring before assuming the worst.”
He adds, “Regular vehicle maintenance, including inspections of the fuel system and wiring, can help prevent many electrical problems that lead to codes like the P0230.”
Conclusion: Addressing the P0230 Code
The OBD2 code P0230 signals a potential issue with your vehicle’s fuel pump circuit. Addressing this code promptly is essential to prevent further engine problems and ensure your car runs smoothly. While the diagnostic process can seem daunting, following the steps outlined above and seeking professional help when needed will help you get to the root of the problem and back on the road quickly and safely.
FAQs:
1. Can I still drive my car with a P0230 code?
While it might be possible to drive short distances with a P0230 code, it’s not recommended. Doing so could worsen the issue and lead to further damage.
2. How much does it cost to fix a P0230 code?
The cost of repair varies greatly depending on the underlying cause and whether you need professional assistance. Replacing a relay or fuse is relatively inexpensive, while a new fuel pump can be more costly.
3. Is it safe to replace the fuel pump myself?
Replacing a fuel pump can be a complex procedure. Unless you have experience working on car mechanics, it’s best to leave this task to a qualified mechanic.
4. Can a bad battery cause a P0230 code?
While a weak battery might contribute to the issue, it’s unlikely to be the sole cause of a P0230 code.
5. How can I prevent a P0230 code in the future?
Regular vehicle maintenance, including inspections of the fuel system, wiring, and electrical components, is the best way to prevent a P0230 code from occurring.
Need More Help?
We’re here to support you every step of the way. If you need further assistance diagnosing or resolving a P0230 code, don’t hesitate to contact our expert team through WhatsApp at +1(641)206-8880 or email us at [email protected]. We offer 24/7 customer support to help you get back on the road safely.


