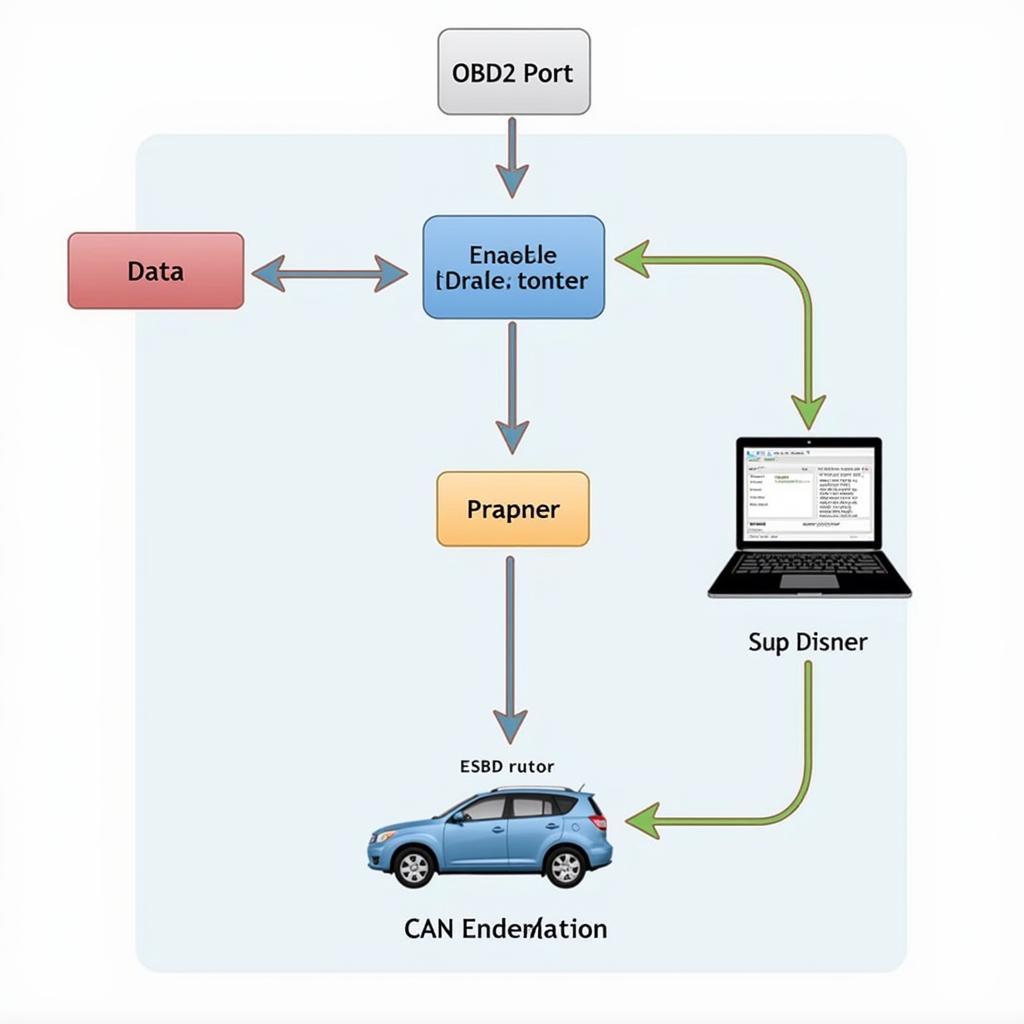
The On-Board Diagnostics (OBD2) system in your car is a technological marvel that allows mechanics and car enthusiasts alike to delve into the inner workings of their vehicles. At its core, the OBD2 system relies on communication protocols to transmit data between the various electronic control units (ECUs) in your car and a diagnostic tool, such as an OBD2 scanner. One such protocol, pivotal in modern vehicles, is the Controller Area Network, better known as CAN protocol.
Understanding OBD2 Protocols
Before we dive into the specifics of the CAN protocol, it’s crucial to understand the broader context of OBD2 protocols. Simply put, these protocols are standardized sets of rules and procedures that dictate how data is exchanged within a vehicle’s network. They ensure that different components, even those manufactured by different companies, can “speak” the same language and share information seamlessly. Think of it as the language your car’s brain uses to communicate.
Over the years, several OBD2 protocols have emerged, each with its strengths and limitations. Some of the most common ones include:
- SAE J1850: Primarily used in older vehicles from American manufacturers like Ford and GM.
- ISO 9141-2: Commonly found in European and Asian vehicles, particularly older models.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Another popular choice for European and Asian carmakers, often used in conjunction with CAN.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): The dominant protocol in modern vehicles, known for its speed, efficiency, and reliability.
The specific protocol(s) used in your vehicle depend on its make, model, and year of manufacture.
The Rise of CAN Protocol in OBD2
The CAN protocol has become the gold standard in OBD2 communication, and for good reason. Developed by Bosch in the 1980s, CAN was specifically designed for automotive applications, addressing the growing complexity of electronic systems in vehicles. Here are some of the key advantages of CAN protocol:
- High-Speed Data Transfer: CAN enables rapid data exchange between ECUs, allowing for real-time monitoring and control of critical systems.
- Robustness and Reliability: CAN is highly resistant to electromagnetic interference and data errors, ensuring accurate and reliable communication even in harsh environments.
- Efficient Use of Bandwidth: CAN’s messaging system prioritizes data based on importance, optimizing bandwidth usage and preventing network congestion.
- Flexibility and Scalability: CAN can support a large number of ECUs on the network, making it ideal for modern vehicles with increasingly sophisticated electronics.
How CAN Protocol Works in OBD2
To grasp how CAN protocol functions within the OBD2 framework, envision your car’s electronic systems as a network of interconnected devices, each with a specific role to play. The CAN protocol acts as the messenger, facilitating the exchange of information between these devices through a two-wire bus system.
When an ECU wants to transmit data, it packages the information into a short message with a specific identifier (ID). This ID acts as an address label, indicating the intended recipient(s) of the message. All ECUs on the network receive the message simultaneously, but only those with the corresponding ID will process it.
CAN protocol utilizes a “collision detection” mechanism to ensure data integrity. If multiple ECUs attempt to transmit simultaneously, the ECU with the higher priority message gets precedence, preventing data collisions and ensuring smooth communication.
Accessing CAN Protocol Data with an OBD2 Scanner
For car owners and mechanics, the ability to tap into the wealth of information transmitted via the CAN protocol is invaluable. This is where an OBD2 scanner equipped with CAN capabilities comes into play. By connecting to your car’s OBD2 port, the scanner can:
- Read and Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identify and diagnose issues with your vehicle’s engine, transmission, emissions system, and more.
- Monitor Live Data Streams: Access real-time sensor readings, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor voltage, and more, to analyze vehicle performance.
- Perform Actuator Tests: Command specific components, such as solenoids, actuators, and relays, to verify their functionality.
- Access Advanced Diagnostics: Depending on the scanner and vehicle, you can delve into module-specific diagnostics, programming, and configurations.
Common Issues Related to OBD2 CAN Protocol
While CAN protocol is renowned for its reliability, issues can still arise. Some common problems include:
- Wiring Faults: Damaged or corroded wiring in the CAN bus system can disrupt communication between ECUs.
- Faulty ECUs: A malfunctioning ECU can disrupt the CAN network, preventing data transmission or generating erroneous data.
- Software Glitches: Software bugs in ECUs or the OBD2 scanner itself can lead to communication errors.
Troubleshooting these issues often requires specialized knowledge and diagnostic tools. If you suspect a problem with your vehicle’s CAN protocol, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic or automotive electrician.
Conclusion
The OBD2 CAN protocol plays a critical role in the functionality of modern vehicles, enabling seamless communication between electronic systems and providing a window into your car’s health and performance. Understanding the basics of CAN protocol and its significance in OBD2 diagnostics can empower you to make more informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance and repair.
FAQs
1. Is my car compatible with CAN protocol?
Most vehicles manufactured after 2008 use CAN protocol as the primary communication standard. You can check your owner’s manual or use an OBD2 scanner to confirm compatibility.
2. Can I use any OBD2 scanner to access CAN data?
Not all OBD2 scanners support CAN protocol. Ensure the scanner you choose explicitly states its CAN capabilities.
3. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner can’t connect to my car?
Double-check the scanner’s compatibility, ensure it’s properly connected to the OBD2 port, and verify that your vehicle’s ignition is switched on.
4. Can I damage my car by using an OBD2 scanner with CAN support?
Using a reputable OBD2 scanner according to instructions is generally safe. However, it’s crucial to avoid modifying or reprogramming ECUs unless you have the expertise to do so.
5. Where can I find more information about OBD2 CAN protocol for my specific car model?
Consult your vehicle’s service manual, online forums dedicated to your car model, or contact your vehicle manufacturer’s customer support.
Need More Help?
For any further assistance or inquiries, don’t hesitate to reach out to our expert team. We’re available 24/7 via WhatsApp at +1(641)206-8880 or email us at [email protected].
You can also explore more insightful articles on OBD2 diagnostics and related topics on our website. For instance:
- obd2 iso canbus protocol failed: Learn about potential reasons for CAN protocol failures and how to address them.
- can my obd2 protocol be vpn: Explore the possibilities and implications of accessing your car’s OBD2 system remotely.
- access diagnostics through obd2 port: Discover the range of diagnostics and information accessible through the OBD2 port.
- obd2 adapter pcb board: Delve into the hardware components that enable OBD2 communication and their functionalities.
- obd2 bcm: Understand the role of the Body Control Module (BCM) in vehicle electronics and its interaction with the OBD2 system.