An OBD2 scanner can unlock a treasure trove of information about your vehicle, including the crucial air fuel ratio (AFR). Understanding your car’s air fuel ratio OBD2 readings can help you optimize performance, improve fuel economy, and even diagnose potential problems. Let’s dive into the world of air fuel ratio and how your OBD2 scanner can help you monitor it. obd2 air fuel ratio
What is Air Fuel Ratio (AFR) and Why Does it Matter?
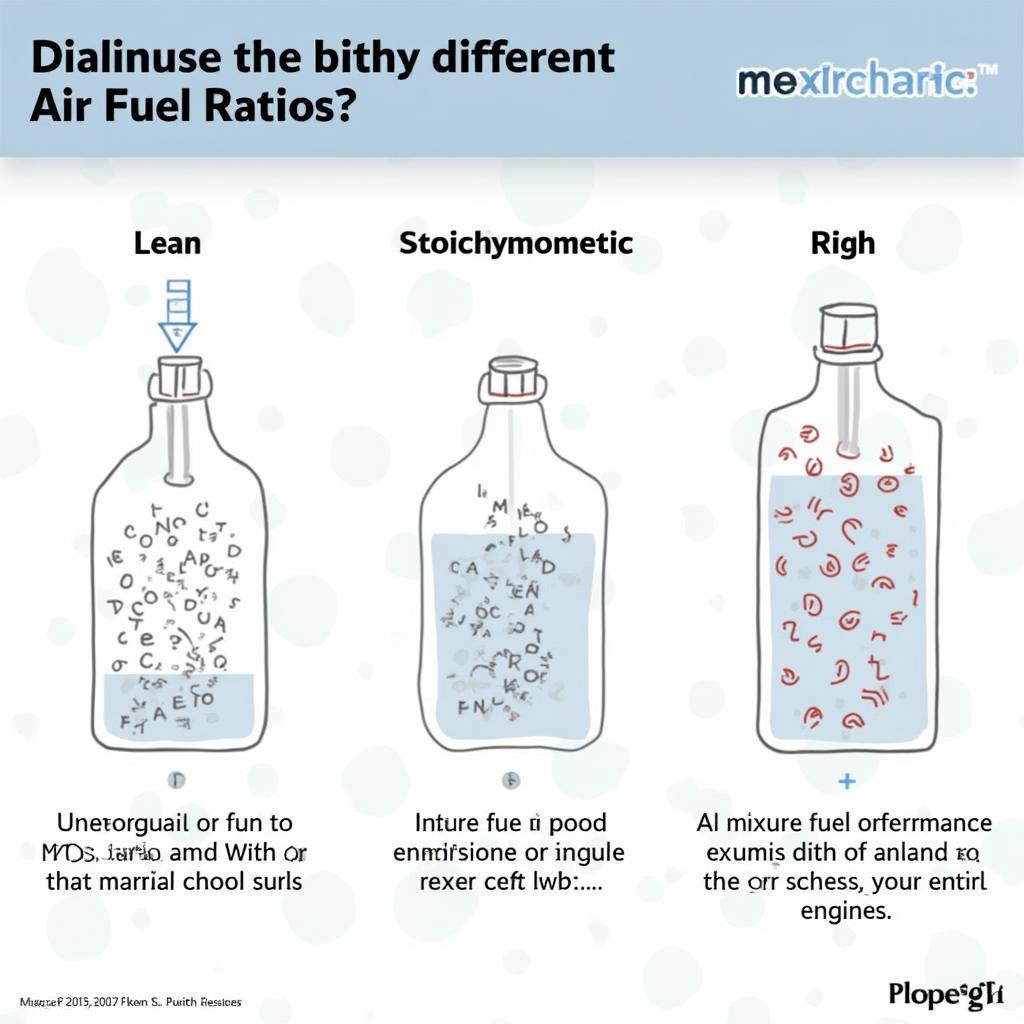
The air fuel ratio is the proportion of air to fuel that enters the engine’s cylinders. A perfect or stoichiometric AFR is the ideal balance for complete combustion, maximizing power and minimizing emissions. This ratio varies depending on the fuel type, but for gasoline engines, it’s typically around 14.7:1, meaning 14.7 parts of air to 1 part of fuel.
A rich mixture (less air, more fuel) is needed for acceleration and high power output. Conversely, a lean mixture (more air, less fuel) is generally used during cruising for better fuel efficiency. Monitoring your afr obd2 can provide valuable insights into your engine’s performance.
How Does an OBD2 Scanner Read Air Fuel Ratio?
While not all OBD2 scanners directly display AFR, they can provide data that helps calculate it. The oxygen sensor (O2 sensor) plays a crucial role here. It measures the amount of unburned oxygen in the exhaust gases, which is then used by the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the air fuel mixture. Your OBD2 scanner can read the O2 sensor data and other parameters like Short Term Fuel Trim (STFT) and Long Term Fuel Trim (LTFT), which indicate how the ECU is adjusting the fuel injection to maintain the desired AFR.
Understanding these readings can help you pinpoint potential issues like a faulty O2 sensor, a vacuum leak, or a failing fuel injector. For example, consistently high STFT and LTFT values may indicate a lean condition.
Using OBD2 to Diagnose Air Fuel Ratio Problems
Changes in your driving habits or modifications to your vehicle can influence AFR. If you notice unusual fluctuations or consistently rich or lean readings, it’s crucial to investigate further. A professional mechanic can utilize advanced diagnostic tools in conjunction with your OBD2 readings to pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
Common OBD2 Codes Related to Air Fuel Ratio
Several OBD2 codes directly relate to air fuel ratio issues. For instance, the obd2 code p2a00 indicates a problem with the Air/Fuel Ratio Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Bank 1 Sensor 1. Other codes, while not directly related to AFR, can indirectly impact it, such as those related to the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor or the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor.
Can Any OBD2 Scanner Read Air Fuel Ratio?
Not all OBD2 scanners provide the same level of detail. While basic scanners may only show generic codes, more advanced scanners offer access to real-time data like O2 sensor readings and fuel trims. Some high-end scanners even provide a calculated afr obd2 reading. If monitoring AFR is a priority, ensure your OBD2 scanner has this capability. Do certain car models allow for more comprehensive AFR readings? For example, does camaro obd2 read air fuel ratio in detail? Researching your specific vehicle model can help determine the data your OBD2 scanner can access.
Knowing the wiring specifics of your car can also be helpful. For example, understanding the civic obd2 air fuel ratio wiring can assist in troubleshooting.
Conclusion
Monitoring your air fuel ratio obd2 readings is crucial for optimal vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. By understanding how your OBD2 scanner interacts with your vehicle’s systems, you can effectively diagnose potential problems and ensure your engine is running smoothly.
FAQ
- What is the ideal air fuel ratio? The stoichiometric ratio for gasoline engines is typically 14.7:1.
- Can I adjust my air fuel ratio? Adjusting AFR typically requires professional tuning equipment and expertise.
- What causes a lean air fuel ratio? Causes can include vacuum leaks, faulty fuel injectors, or a malfunctioning MAF sensor.
- What causes a rich air fuel ratio? Causes can include a faulty O2 sensor, a clogged fuel filter, or a leaking fuel injector.
- How can I improve my air fuel ratio? Regular maintenance, including replacing worn-out sensors and filters, can help maintain the proper AFR.
- Do I need a special OBD2 scanner for air fuel ratio? Some advanced scanners provide direct AFR readings or data to calculate it.
Have more questions? Check out our other helpful resources on our site or contact our 24/7 customer support team via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected], or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA.