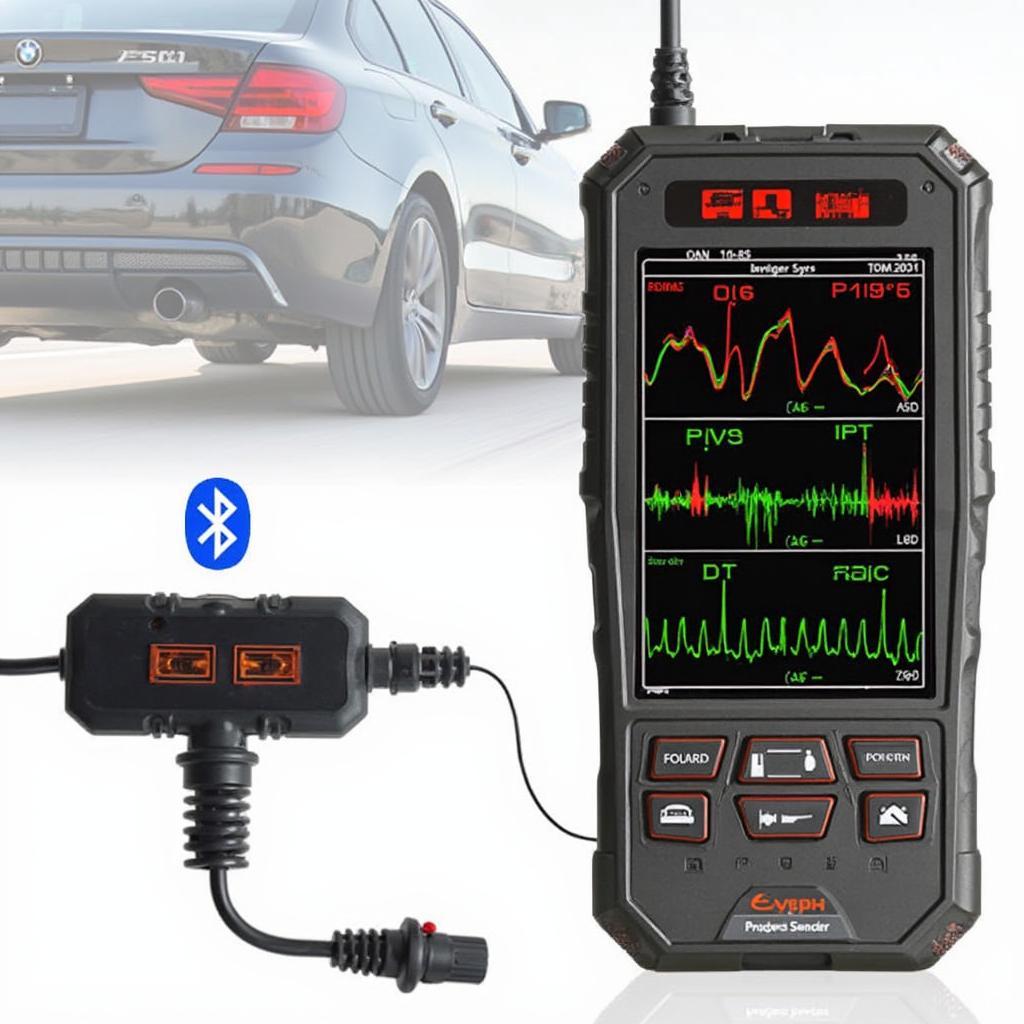
Can OBD2 Bluetooth scanners tell you which O2 sensor is faulty? This is a common question for car owners trying to diagnose check engine lights. While these handy tools provide valuable diagnostic information, the answer isn’t a simple yes or no. Let’s dive into the details and understand how these scanners interact with your car’s oxygen sensors.
Decoding the OBD2 and O2 Sensor Relationship
OBD2 scanners, especially Bluetooth versions, offer a convenient way to access your car’s diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes act like clues, pointing towards potential issues within your vehicle’s systems, including the oxygen sensors. obd2 parameter readings provides a comprehensive overview of these parameters.
How OBD2 Scanners Interact with O2 Sensors
An OBD2 scanner doesn’t directly pinpoint a specific faulty O2 sensor like pointing a finger at it. Instead, it provides the DTCs related to the oxygen sensor system. For example, a code like P0135 indicates a problem with the O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Bank 1 Sensor 1. This tells you the circuit related to the first sensor on Bank 1 has an issue, narrowing down the location.
Understanding Oxygen Sensor DTCs
Different DTCs relate to various oxygen sensor problems, including:
- Heater circuit malfunctions
- Slow response times
- Circuit voltage issues
- Sensor lean/rich conditions
By understanding these codes, you can deduce which sensor or part of the circuit is likely at fault. toyota tundra obd2 pid can help with understanding specific PIDs related to oxygen sensors in Toyota Tundra vehicles.
Pinpointing the Culprit: Using OBD2 Data Effectively
While the DTC provides a starting point, interpreting the live data from your OBD2 scanner is crucial. This involves looking at the voltage readings and waveforms of the oxygen sensors. making sense of obd2 data stream offers valuable insights into understanding OBD2 data streams.
Analyzing O2 Sensor Voltage and Waveforms
A healthy oxygen sensor’s voltage should fluctuate between 0.1 and 0.9 volts. A consistently low or high reading, or a lack of fluctuation, suggests a problem. Comparing the readings from different sensors can help isolate the faulty one.
Why Can’t OBD2 Always Pinpoint the Exact Sensor?
Sometimes, the DTC might only indicate a general problem within the oxygen sensor system, not a specific sensor. This can happen due to wiring issues, a faulty oxygen sensor controller, or other related components. In such cases, further diagnosis may be needed.
“Using an OBD2 scanner is like having a conversation with your car,” says automotive expert John Miller. “It tells you what’s wrong, but sometimes you need to ask follow-up questions to get the full story.”
Beyond the Scanner: Further Diagnostic Steps
If the OBD2 scanner doesn’t provide a definitive answer, consider these steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the wiring and connectors of the suspected sensors for damage or corrosion.
- Professional Diagnosis: A qualified mechanic can use advanced diagnostic tools to pinpoint the exact issue. conector obd2 jetta a4 can assist in locating the OBD2 connector in a Jetta A4 for easier diagnostics.
“Don’t jump to conclusions based solely on the OBD2 codes,” advises Sarah Chen, a seasoned mechanic. “A comprehensive diagnosis, including a visual inspection, is essential for accurate troubleshooting.”
Can OBD2 Bluetooth scanners tell you which O2 sensor needs replacing? While they don’t always pinpoint the exact sensor, they provide valuable information that significantly narrows down the possibilities. By understanding the DTCs, analyzing live data, and potentially performing further diagnostics, you can effectively identify and fix oxygen sensor issues, keeping your car running smoothly.
obd2 sensor list offers a comprehensive list of OBD2 sensors, providing additional resources for your diagnostic journey.
FAQ
- Can I replace an oxygen sensor myself? Yes, with the right tools and knowledge, it’s a manageable DIY task.
- How often should oxygen sensors be replaced? Generally, every 60,000 to 90,000 miles.
- What are the symptoms of a bad oxygen sensor? Decreased fuel efficiency, rough idling, and a check engine light are common signs.
- Are all OBD2 scanners the same? No, they vary in features and functionality. Some offer more advanced data analysis capabilities.
- Can a bad O2 sensor damage my car? Yes, it can lead to catalytic converter damage and other issues if left unaddressed.
- What does Bank 1 and Bank 2 mean for O2 sensors? Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine with cylinder #1, while Bank 2 is the opposite side.
- How can I clear O2 sensor codes after replacing the sensor? You can use an OBD2 scanner to clear the codes or disconnect the battery for a short period.
Need support? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We have a 24/7 customer support team.