A computador de bordo OBD2 funciona by monitoring your car’s engine, transmission, and other crucial systems. It uses sensors to collect data, which it then analyzes for potential problems. If an issue is detected, the OBD2 system stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in its memory. This code can then be accessed using an OBD2 scanner to pinpoint the source of the problem, allowing for faster and more efficient repairs.
Understanding the Computador de Bordo OBD2 System
The OBD2 system, often referred to as a “computador de bordo,” is a standardized system found in most vehicles manufactured after 1996. Its primary function is to monitor emissions and ensure optimal engine performance. But how does a computador de bordo OBD2 funciona in practice? It’s a complex network of sensors and electronic control units (ECUs) constantly communicating with each other. These sensors gather data on various parameters, including engine speed, coolant temperature, oxygen levels, and fuel pressure. This data is then sent to the car’s computer, which uses sophisticated algorithms to analyze and interpret it.
Key Components of an OBD2 System
Several key components work together to ensure the OBD2 system functions correctly:
- Electronic Control Units (ECUs): The “brains” of the operation, ECUs process data from the sensors and make adjustments to control various systems.
- Sensors: These devices gather data from different parts of the vehicle and transmit it to the ECUs.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): When a problem is detected, the OBD2 system generates a DTC, which is a unique code that identifies the specific fault.
- OBD2 Port: A standardized 16-pin connector located inside the vehicle, typically under the dashboard, used to connect an OBD2 scanner.
How to Use a Computador de Bordo OBD2 Scanner
Accessing the information stored within your car’s computador de bordo requires an OBD2 scanner. These handy devices plug into the OBD2 port and allow you to read and interpret DTCs.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Read the Codes: The OBD2 scanner will display any stored DTCs.
- Interpret the Codes: Use a reliable resource, such as OBDFree, to understand the meaning of the codes.
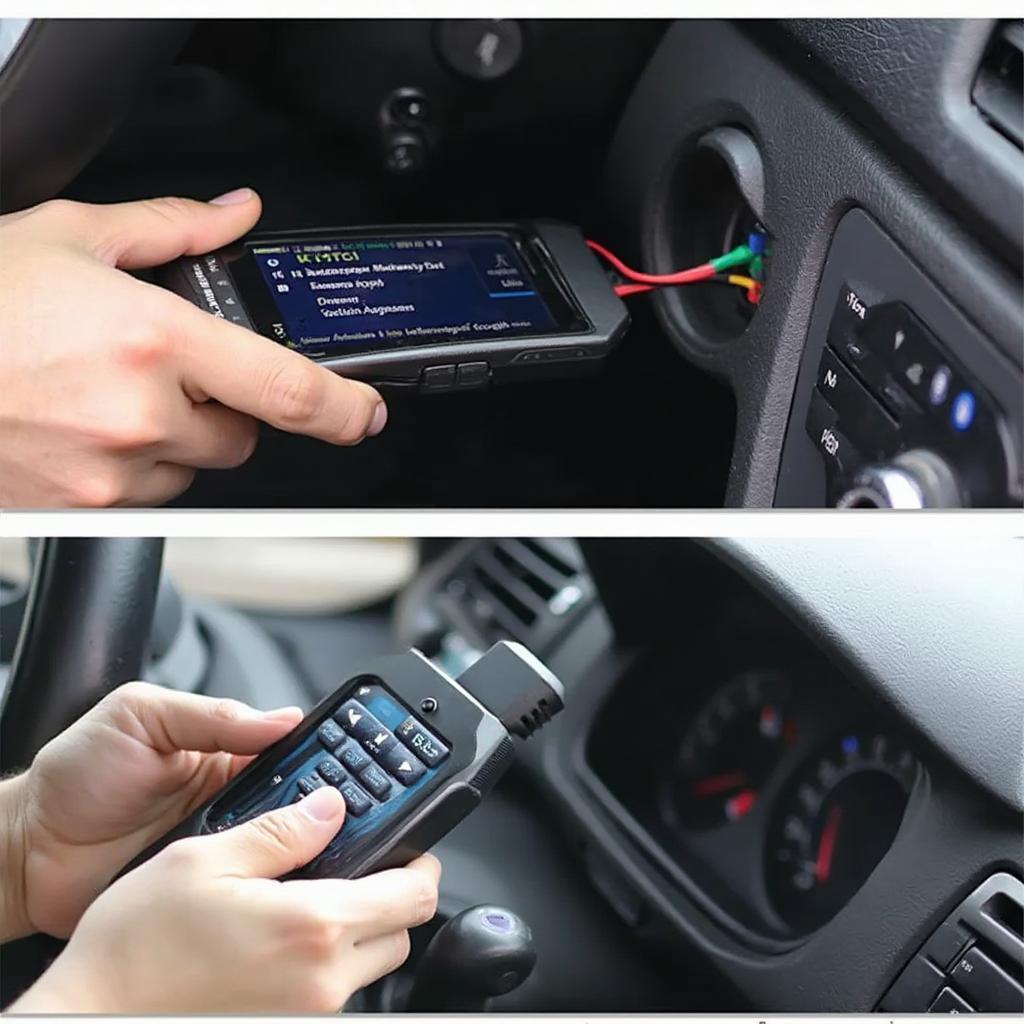 Using an OBD2 Scanner to Access Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Using an OBD2 Scanner to Access Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner offers numerous advantages:
- Early Problem Detection: Identify potential issues before they become major problems, saving you time and money on repairs.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Diagnose and fix problems that may be affecting your vehicle’s fuel economy.
- Enhanced Vehicle Performance: Optimize your engine’s performance by identifying and addressing any underlying issues.
- Empowerment: Gain a deeper understanding of your vehicle’s health and performance.
“Regularly using an OBD2 scanner is like giving your car a regular check-up. It allows you to catch potential problems early on and keep your car running smoothly,” says Michael Johnson, Automotive Diagnostics Specialist.
Common OBD2 Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding some common OBD2 trouble codes can be helpful:
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0172: System Too Rich (Bank 1)
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Your Computador de Bordo OBD2
The computador de bordo OBD2 funciona as a crucial system for monitoring your vehicle’s health. By understanding how it works and utilizing an OBD2 scanner, you can take proactive steps to maintain your vehicle’s performance, improve fuel efficiency, and save money on costly repairs. Remember to use reputable resources like OBDFree for accurate DTC interpretations and valuable information on OBD2 scanners.
FAQ
- What does “computador de bordo OBD2” mean? It refers to the On-Board Diagnostics system.
- Where is the OBD2 port located? It’s usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- How often should I use an OBD2 scanner? Periodically, especially if the check engine light illuminates.
- What should I do if I get a DTC? Consult a mechanic or use a reliable resource to understand the code.
- Are all OBD2 scanners the same? No, they vary in features and capabilities.
- Can I fix the problem myself after reading the code? It depends on your mechanical skills and the complexity of the problem.
- What if my car was manufactured before 1996? It may have a different diagnostic system.
Need support? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.