If your 2000 Dodge Ram 1500 is experiencing a loss of power and your OBD2 scanner isn’t providing any helpful codes, you’re not alone. This is a common issue that can stem from a variety of factors, and pinpointing the culprit often requires a methodical approach. This article will guide you through the potential causes of power loss in your 2000 Dodge Ram 1500, even when the OBD2 scanner doesn’t offer a clear diagnosis.
While the OBD2 system is designed to alert you to engine and emissions-related problems, some issues might not trigger a specific code, especially if they’re mechanical or electrical in nature. Here’s a breakdown of what could be causing your Ram’s power loss:
Common Causes of Power Loss in a 2000 Dodge Ram 1500
1. Fuel System Issues
Fuel Pump: A failing fuel pump might not be delivering sufficient fuel to the engine, resulting in reduced power.
Fuel Filter: A clogged fuel filter restricts fuel flow and can lead to similar symptoms.
Fuel Injectors: Malfunctioning fuel injectors can disrupt the proper air-fuel mixture, impacting engine performance.
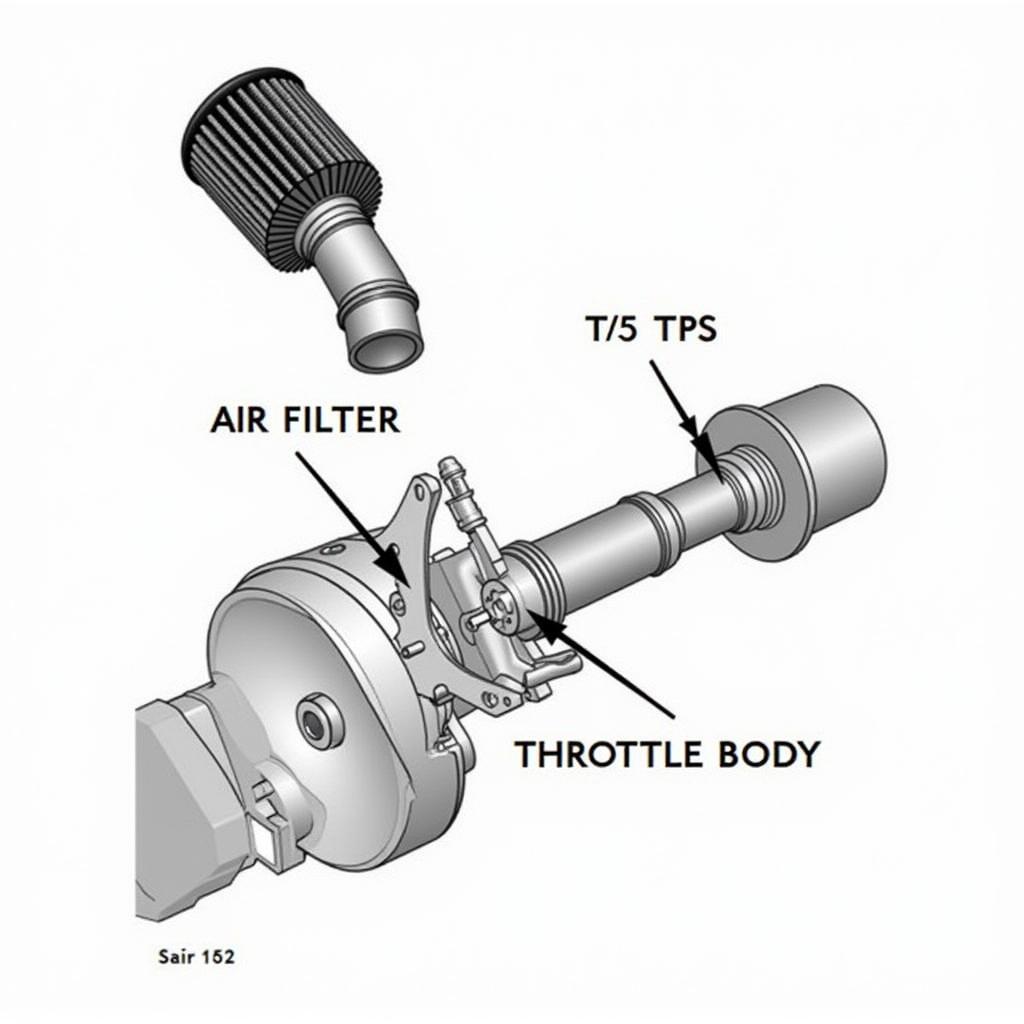
2. Air Intake and Sensor Problems
Air Filter: A severely clogged air filter can choke the engine, restricting airflow and reducing power.
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor: The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. If it’s dirty or faulty, it can send incorrect data to the engine control unit (ECU), leading to an improper air-fuel mixture.
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): The TPS relays the position of the throttle pedal to the ECU. A faulty TPS can disrupt the engine’s response to throttle input, resulting in poor acceleration and reduced power.
3. Ignition System Faults
Spark Plugs: Worn-out or fouled spark plugs can cause misfires, leading to power loss and reduced fuel efficiency.
Ignition Coils: Failing ignition coils can disrupt the spark delivery to the spark plugs, resulting in similar symptoms as faulty spark plugs.
4. Exhaust System Restrictions
Catalytic Converter: A clogged catalytic converter creates exhaust back pressure, hindering engine performance and potentially leading to a loss of power.
5. Transmission Problems
Slipping Transmission: A slipping transmission can cause a noticeable loss of power, especially during acceleration.
Troubleshooting Power Loss Without OBD2 Codes
-
Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the engine bay for any loose connections, damaged hoses, or obvious signs of wear and tear.
-
Check for Basic Maintenance: Ensure your air filter is clean and your spark plugs are in good condition.
-
Listen for Unusual Sounds: Pay attention to any unusual noises coming from the engine, such as hissing (vacuum leak), knocking, or rattling.
-
Monitor Fuel Consumption: A sudden decrease in fuel efficiency could indicate a fuel system problem.
-
Check Transmission Fluid: Ensure your transmission fluid is at the proper level and in good condition.
Conclusion
While a lack of OBD2 codes can make diagnosing power loss in your 2000 Dodge Ram 1500 more challenging, it’s essential to remember that not all issues trigger error codes. By systematically examining the potential culprits and employing some basic troubleshooting steps, you can often narrow down the problem. If you’re unable to pinpoint the cause, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic with experience in diagnosing and repairing Dodge vehicles. They can utilize advanced diagnostic tools and techniques to identify the root cause of your power loss and get your Ram back on the road running smoothly.