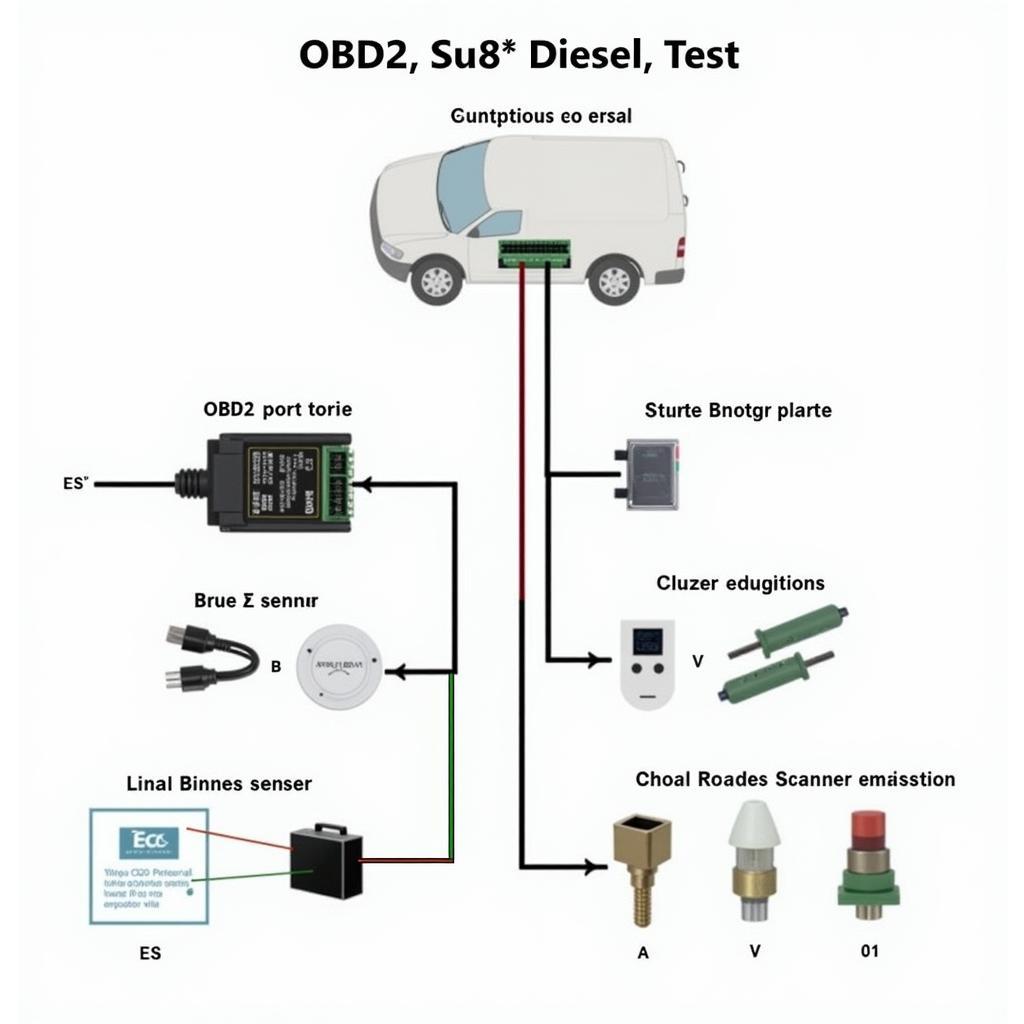
The eco OBD2 diesel test is a crucial part of vehicle maintenance, especially for diesel engine owners. It provides insights into your engine’s performance, emissions, and overall health, which can be vital for optimizing fuel efficiency and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Understanding OBD2 and Diesel Emissions
Before delving into the specifics of the eco OBD2 diesel test, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of OBD2 systems and their role in diesel emissions control.
What is OBD2?
OBD2, short for On-Board Diagnostics, is a standardized system that monitors various aspects of your vehicle’s engine and emissions control systems. It uses a network of sensors to collect data, which is then processed by the Engine Control Unit (ECU).
Diesel Emissions and Their Impact
Diesel engines, while known for their fuel efficiency and torque, produce different types of emissions compared to gasoline engines. These include:
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Contribute to smog and acid rain.
- Particulate Matter (PM): Fine soot particles that can cause respiratory problems.
- Hydrocarbons (HC): Unburned fuel that contributes to smog.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A poisonous gas.
To mitigate these emissions, modern diesel vehicles incorporate sophisticated systems like:
- Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF): Traps soot particles from the exhaust gas.
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR): Uses AdBlue (Diesel Exhaust Fluid) to convert NOx into harmless nitrogen and water.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR): Redirects a portion of exhaust gases back into the engine to lower combustion temperatures and reduce NOx emissions.
How Eco OBD2 Diesel Tests Work
An eco OBD2 diesel test uses the OBD2 port to communicate with your vehicle’s ECU and retrieve diagnostic information related to emissions. This information can include:
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Indicates the air-to-fuel ratio in the exhaust, helping determine combustion efficiency.
- DPF Soot Load: Shows the level of soot accumulated in the DPF, indicating its regeneration status.
- EGR Valve Position: Verifies if the EGR valve is functioning correctly to control NOx emissions.
- AdBlue System Status: Monitors the AdBlue level, injection rate, and overall system health for SCR systems.
Why Eco OBD2 Diesel Tests Are Important
Regular eco OBD2 diesel tests offer several benefits:
- Identify Potential Issues Early: Detecting problems like a clogged DPF or a faulty EGR valve early on can prevent costly repairs down the line.
- Optimize Fuel Efficiency: A properly functioning emissions system ensures optimal combustion and fuel economy.
- Reduce Environmental Impact: By monitoring and maintaining your vehicle’s emissions systems, you contribute to cleaner air and a healthier environment.
- Pass Emissions Tests: In many regions, passing an emissions test is mandatory for vehicle registration.
Performing an Eco OBD2 Diesel Test
You can have a professional mechanic conduct the test or perform it yourself using an OBD2 scanner. If you choose the DIY route, here are the general steps:
- Locate Your OBD2 Port: It’s typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the OBD2 Scanner: Ensure the scanner is compatible with diesel vehicles and supports enhanced diagnostics for emissions systems.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Access the Emissions Data: Navigate through the scanner’s menu to find the emissions-related data you want to check.
- Interpret the Results: Compare the readings with the manufacturer’s specifications or consult a mechanic if you notice any anomalies.
Pro Tip: For in-depth analysis and troubleshooting, consider using an advanced OBD2 scanner that offers live data streaming, graphing capabilities, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
kess obd2 how to use
Common Eco OBD2 Diesel Test Fault Codes
Here are some frequently encountered fault codes related to diesel emissions systems:
- P0401: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected.
- P2002: Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Efficiency Below Threshold Bank 1.
- P2463: Diesel Particulate Filter Restriction – Soot Accumulation.
- P20EE: SCR NOx Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold Bank 1.
Note: These are just a few examples, and the specific codes may vary depending on the vehicle make and model.
Eco OBD2 Diesel Test: FAQs
Q: How often should I get an eco OBD2 diesel test?
A: It’s recommended to have your diesel vehicle’s emissions system checked at least once a year or as part of your regular service schedule.
Q: Can I use any OBD2 scanner for an eco diesel test?
A: Not all OBD2 scanners are created equal. Make sure to use one that is compatible with diesel vehicles and supports enhanced diagnostics for emissions-related systems. You can find reliable OBD2 scanners from reputable brands like Amazon Sike One OBD2 Scanner.
Q: What should I do if my vehicle fails an eco OBD2 diesel test?
A: If your vehicle fails an eco OBD2 test, it’s crucial to address the underlying issue promptly. This might involve repairs or replacements of faulty components within the emissions system. Consult a qualified mechanic for a thorough diagnosis and recommended course of action.
Conclusion
In conclusion, eco OBD2 diesel tests are an indispensable tool for maintaining the health, performance, and environmental friendliness of your diesel vehicle. By understanding how these tests work and their importance, you can ensure optimal engine performance, extend the lifespan of your vehicle’s emissions control systems, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Remember, regular maintenance is key to a healthy and efficient diesel engine.