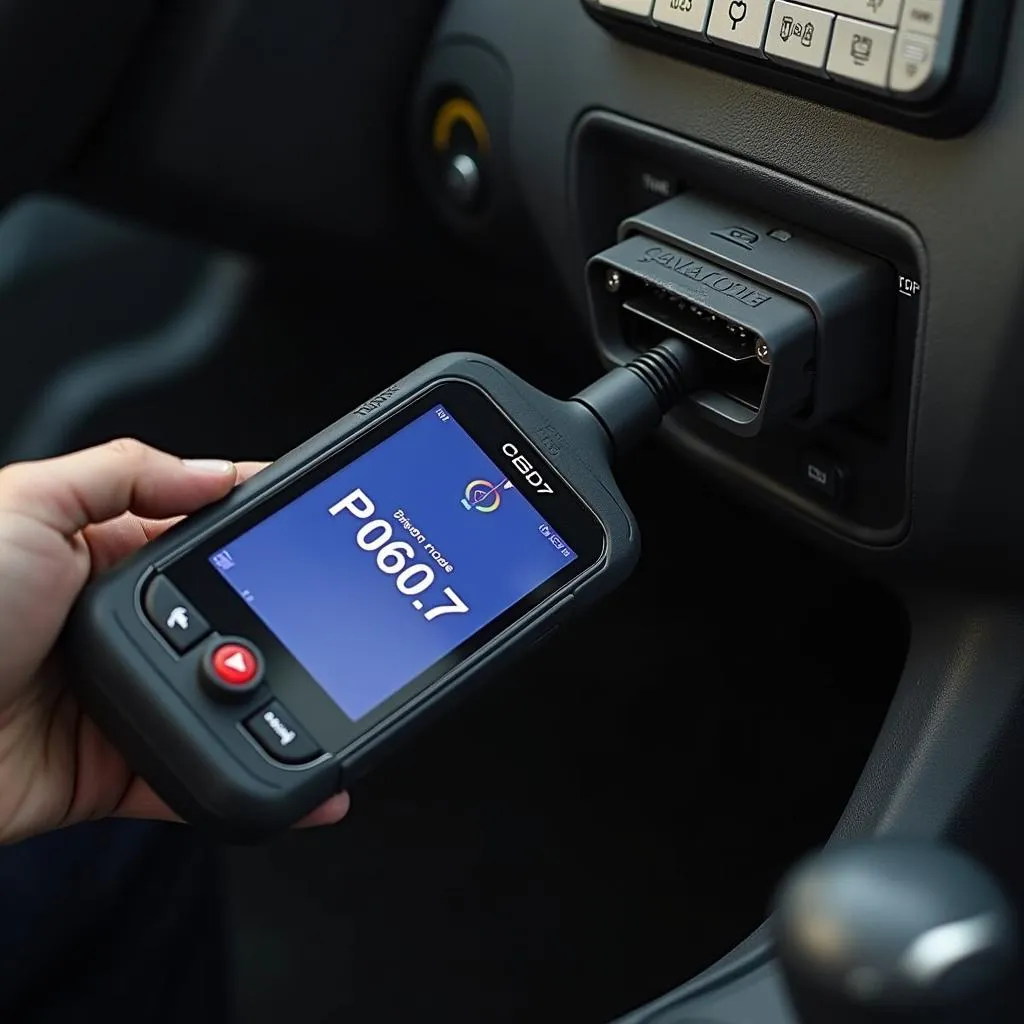
The OBD2 fault code P0607 indicates a problem with your vehicle’s Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM) memory. This code specifically points to a performance issue within the control module itself, rather than a problem with a specific sensor or component.
While encountering any OBD2 code can be concerning, understanding what P0607 means and its potential causes is crucial for proper diagnosis and repair. This article will delve deeper into OBD2 code P0607, its symptoms, common causes, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions.
What Does OBD2 Code P0607 Mean?
The code P0607 falls under the category of “Control Module” codes, indicating an internal fault detected within the ECM/PCM. This fault relates to the module’s ability to perform its primary functions, which include:
- Monitoring engine sensors: The ECM/PCM constantly receives data from various sensors throughout the engine, such as the oxygen sensor, mass airflow sensor, and throttle position sensor.
- Controlling engine actuators: Based on the sensor data, the ECM/PCM adjusts the operation of engine components like the fuel injectors, ignition system, and variable valve timing system to optimize performance and emissions.
- Storing and adapting to data: The ECM/PCM learns from driving conditions and adjusts its control strategies to maintain optimal performance over time.
When the ECM/PCM detects an internal performance error, it triggers the P0607 code, indicating a potential problem with its memory, processing power, or communication with other modules.
Symptoms of OBD2 Code P0607
While the check engine light illuminating on your dashboard is the most obvious symptom of code P0607, you might experience various other driving issues, including:
- Rough engine idle: The engine might vibrate or shake noticeably when the vehicle is stopped.
- Reduced engine performance: You might notice a decrease in power and acceleration.
- Poor fuel economy: A malfunctioning ECM/PCM can lead to inefficient fuel consumption.
- Stalling: The engine might suddenly shut off while idling or driving.
- Difficulty starting: The engine might crank slowly or require multiple attempts to start.
- Transmission shifting problems: In some cases, the ECM/PCM issue can affect the transmission’s shifting patterns.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other problems within your vehicle. Therefore, a proper diagnosis using an OBD2 scanner is crucial to confirm P0607 as the root cause.
Common Causes of OBD2 Code P0607
Several factors can contribute to the P0607 code, ranging from simple electrical issues to more complex internal module malfunctions:
- Loose or corroded ECM/PCM connectors: A poor connection between the ECM/PCM and the vehicle’s wiring harness can disrupt communication and trigger the code.
- Damaged wiring harness: Frayed, broken, or shorted wires within the harness can also interrupt data transmission to and from the module.
- Low battery voltage: The ECM/PCM requires a stable voltage supply to function correctly. A weak battery or faulty charging system can lead to voltage fluctuations and trigger the code.
- Faulty ECM/PCM: Internal damage to the module itself, such as a failed memory chip or processor, can cause the P0607 code.
- Software issues: In some cases, corrupted or outdated software within the ECM/PCM can lead to performance issues and trigger the code.
Diagnosing OBD2 Code P0607
Diagnosing the P0607 code requires a systematic approach to pinpoint the exact cause:
-
Read the code: Connect an OBD2 scanner to your vehicle’s OBD2 port and retrieve the stored codes. Note any other codes present, as they might be related to the P0607 code.
-
Check for technical service bulletins (TSBs): Manufacturers often issue TSBs addressing known issues with specific vehicle models. Consult your vehicle’s manufacturer or a reliable online database for any TSBs related to the P0607 code and your vehicle.
-
Inspect the ECM/PCM connectors and wiring: Visually inspect the connectors for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Check the wiring harness for any visible damage.
-
Test the battery and charging system: Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage and charging system output. Ensure the battery is fully charged and the alternator is providing the correct voltage.
Potential Solutions for OBD2 Code P0607
Once you have identified the cause of the P0607 code, you can proceed with the appropriate repair:
- Clean or repair connectors and wiring: Clean any corroded connectors with electrical contact cleaner. Repair or replace damaged wiring within the harness.
- Replace the battery or repair the charging system: If the battery is weak or the charging system is faulty, replace or repair them accordingly.
- Reprogram or replace the ECM/PCM: If the module itself is faulty, you might need to reprogram it with updated software or replace it entirely. Reprogramming usually requires specialized equipment and software available at dealerships or specialized repair shops.
Preventing OBD2 Code P0607
While not all causes of P0607 are preventable, regular vehicle maintenance can minimize the risk:
- Regular battery maintenance: Have your battery tested regularly and replace it when necessary.
- Inspect and clean battery terminals: Corrosion on battery terminals can lead to voltage drops. Clean them periodically with a battery terminal cleaner.
- Address electrical issues promptly: Don’t ignore warning signs like flickering lights or dimming dashboard displays, as they can indicate electrical problems that might affect the ECM/PCM.
Conclusion
The OBD2 fault code P0607 signifies a potential issue with your vehicle’s ECM/PCM, a critical component responsible for managing your engine’s performance. While encountering this code can be concerning, understanding its meaning, causes, and possible solutions will equip you to address the issue effectively. Remember, a proper diagnosis using an OBD2 scanner and a systematic approach to troubleshooting are crucial for resolving the P0607 code and restoring your vehicle’s performance.
Frequently Asked Questions about OBD2 Code P0607
Q: Can I drive my car with a P0607 code?
A: While you might be able to drive for a short distance, it’s not recommended. Driving with a P0607 code can lead to further damage to your vehicle’s engine and other components.
Q: How much does it cost to fix a P0607 code?
A: The cost of repair varies depending on the underlying cause. Simple fixes like cleaning connectors or replacing a battery are relatively inexpensive. However, replacing the ECM/PCM can be costly.
Q: Can I fix the P0607 code myself?
A: If you have experience with vehicle repair and are comfortable working with electrical components, you might be able to fix simple issues like cleaning connectors or replacing a battery. However, more complex repairs like reprogramming or replacing the ECM/PCM often require specialized tools and knowledge. It’s best to consult with a qualified mechanic for complex repairs.
Q: Can a bad battery cause a P0607 code?
A: Yes, a weak or failing battery can cause voltage fluctuations that can trigger the P0607 code.
Q: How do I prevent the P0607 code from recurring?
A: Regular vehicle maintenance, including battery care, prompt attention to electrical issues, and addressing any other related codes, can help prevent the P0607 code from recurring.
Need further assistance with OBD2 codes or have questions about diagnostic tools? Our team of experts at OBDFree is here to help. Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880 or Email: [email protected]. We provide 24/7 customer support to address your automotive needs.