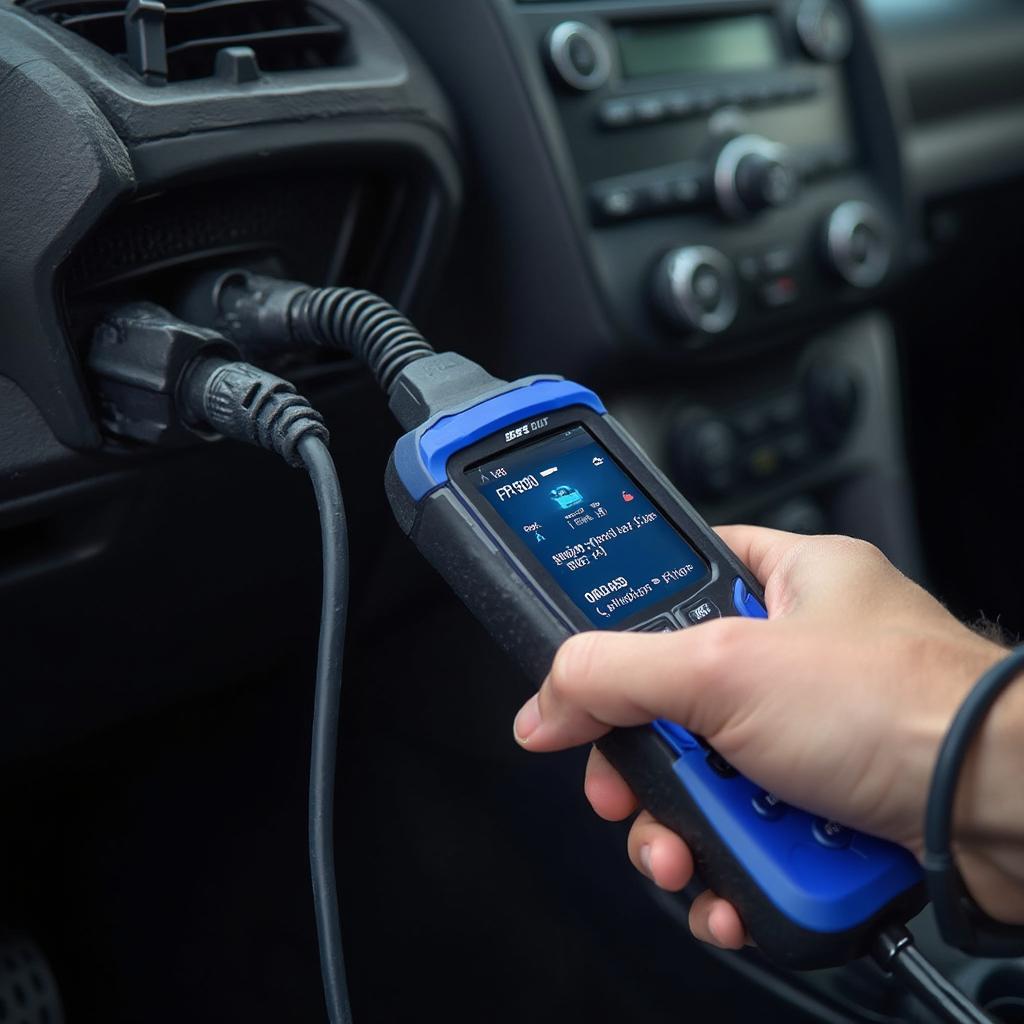
A Ford OBD2 code P0300 indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire, a common yet potentially serious issue. Understanding this code, its causes, and how to address it is crucial for maintaining your Ford’s performance and longevity. This guide will provide you with everything you need to know about the P0300 code in your Ford vehicle.
What Does P0300 Mean on a Ford?
The P0300 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) specifically points to a random or multiple cylinder misfire. This means the engine’s computer, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM), has detected irregularities in the combustion process across multiple cylinders, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact faulty cylinder. While the P0300 code is generic, its manifestation and diagnostic procedures can vary slightly among different Ford models.
Common Causes of P0300 in Ford Vehicles
A P0300 code can stem from various issues, ranging from simple fixes like a faulty spark plug to more complex problems like vacuum leaks or internal engine damage. Here’s a breakdown of common culprits:
- Faulty Spark Plugs or Wires: Worn-out spark plugs or damaged wires can disrupt the ignition process, leading to misfires.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold or vacuum hoses can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, causing improper combustion.
- Fuel System Issues: Problems with the fuel pump, fuel filter, or fuel injectors can restrict fuel delivery, resulting in misfires.
- Low Compression: Worn piston rings, damaged valves, or a blown head gasket can lead to low compression in the cylinders, hindering combustion.
- Ignition Coil Problems: A failing ignition coil can prevent the spark plugs from firing correctly.
- Camshaft or Crankshaft Sensor Issues: Faulty sensors can provide inaccurate information to the PCM, affecting engine timing and leading to misfires.
- EGR Valve Problems: A malfunctioning EGR valve can disrupt the exhaust gas recirculation process, affecting combustion.
Diagnosing a P0300 Code in Your Ford
Diagnosing a P0300 code requires a systematic approach. Start with the easier checks and progress to more complex ones:
- Visual Inspection: Look for loose or damaged vacuum hoses, spark plug wires, and other visible signs of damage.
- Check Spark Plugs and Wires: Inspect the spark plugs for wear and tear. Replace them if necessary, along with the wires if they show signs of damage.
- Scan for Other Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to check for other codes that might be accompanying the P0300. These additional codes can provide valuable clues.
- Check Fuel Pressure: Ensure the fuel pump is delivering adequate pressure. A faulty fuel pump or clogged fuel filter can cause lean fuel conditions, leading to misfires.
- Compression Test: A compression test will reveal if there are any issues with the cylinder’s ability to hold pressure. Low compression can indicate internal engine problems.
How to Fix a P0300 Code
Once you’ve identified the cause of the P0300 code, the appropriate repair can be made. Here are some potential solutions:
- Replace Spark Plugs and Wires: This is often the easiest and most effective fix.
- Repair Vacuum Leaks: Seal any leaks in the intake manifold or vacuum hoses.
- Address Fuel System Issues: Replace a faulty fuel pump, fuel filter, or fuel injectors as needed.
- Repair or Replace Ignition Coil: If a faulty ignition coil is identified, replace it.
- Replace Camshaft or Crankshaft Sensors: Replace faulty sensors.
- Address EGR Valve Issues: Clean or replace the EGR valve.
What if the P0300 Code Persists?
If the P0300 code returns after repairs, consider consulting a qualified Ford technician for a more in-depth diagnosis. They have access to specialized equipment and the expertise to pinpoint more complex issues.
Conclusion: Resolving Your Ford’s P0300 Code
Addressing the P0300 code promptly is essential for preventing further damage and restoring your Ford’s optimal performance. By understanding the potential causes and following the diagnostic steps outlined, you can effectively tackle this issue and ensure a smooth and efficient ride.
FAQs
- Is it safe to drive with a P0300 code? It’s best to avoid driving extensively with a P0300 code as it can lead to catalytic converter damage and reduced fuel efficiency.
- Can bad gas cause a P0300 code? Yes, contaminated or low-quality fuel can contribute to misfires.
- How much does it cost to fix a P0300 code? The cost varies depending on the underlying cause and can range from a few dollars for spark plugs to hundreds or even thousands for more extensive repairs.
- Can I fix a P0300 code myself? Simple fixes like replacing spark plugs can be done DIY, but more complex issues require professional attention.
- What other codes are often associated with P0300? Codes like P0301-P0308 (cylinder-specific misfire codes) often accompany P0300.
- Can a vacuum leak cause a P0300 code? Yes, a vacuum leak can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to misfires and a P0300 code.
- How can I prevent a P0300 code in the future? Regular maintenance, including timely spark plug replacements and fuel system checks, can help prevent future P0300 codes.
Need further assistance? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our 24/7 customer service team is ready to help.