Connecting your OBD2 scanner directly to the CAN bus might seem daunting, but with the right knowledge, a homemade OBD2 CAN bus hard wired connection is entirely achievable. This guide provides a detailed walkthrough of the process, addressing common questions and concerns.
Understanding the CAN Bus and OBD2
Before diving into a hard-wired connection, it’s crucial to understand the basics of the Controller Area Network (CAN bus) and On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2). The CAN bus is a robust vehicle communication system that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) to communicate with each other. OBD2 is a standardized system that utilizes the CAN bus to provide access to vehicle diagnostic data. A hard-wired connection bypasses the standard OBD2 port and taps directly into the CAN bus, offering a more direct and potentially faster connection.
Why Choose a Homemade OBD2 CAN Bus Hard Wired Connection?
Several reasons might lead someone to opt for a homemade hard-wired connection. Perhaps you’re working on a custom project, building a race car data logger, or simply want a cleaner, more permanent setup. A hard-wired connection eliminates the need for a dangling OBD2 cable and can provide a more reliable connection in demanding environments.
Advantages of a Hard-Wired Setup
- Reduced clutter: Eliminates the OBD2 connector and cable.
- Enhanced reliability: Less susceptible to connection issues due to vibrations or loose connectors.
- Potential for faster data transfer: Direct connection to the CAN bus can offer improved data throughput.
- Customization: Allows for tailored installations for specific projects.
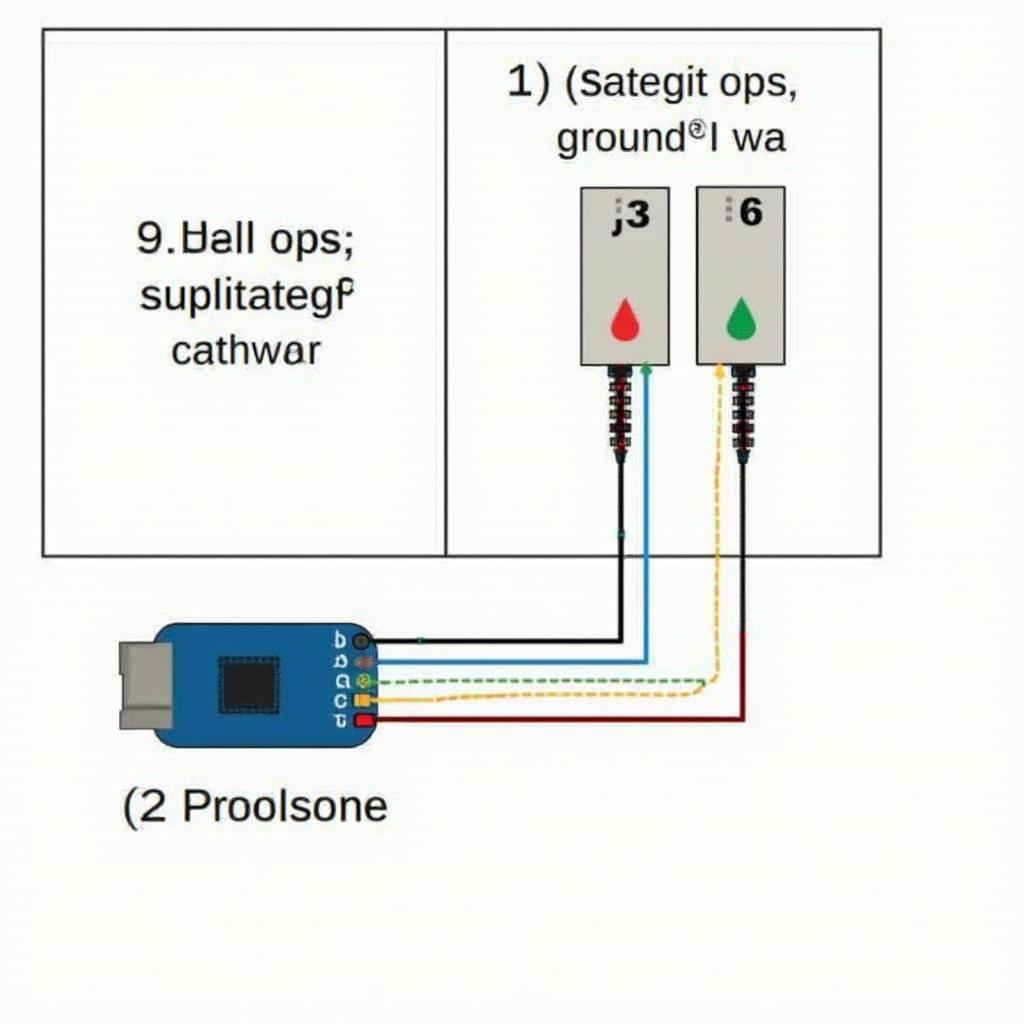 Homemade OBD2 CAN Bus Hard Wired Connection Diagram
Homemade OBD2 CAN Bus Hard Wired Connection Diagram
How to Create a Homemade OBD2 CAN Bus Hard Wired Connection
Creating a homemade OBD2 CAN bus hard wired connection requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Locate the CAN bus wires: Consult your vehicle’s wiring diagram to identify the CAN high (CANH) and CAN low (CANL) wires. These wires are typically twisted together.
- Tap into the CAN bus: Carefully splice into the CANH and CANL wires using appropriate connectors or soldering techniques. Ensure proper insulation to prevent short circuits.
- Connect to your device: Connect the tapped CANH and CANL wires to your OBD2 scanner, data logger, or other device.
- Ground connection: Establish a solid ground connection for your device.
- Testing the connection: Use an OBD2 software application to verify that the connection is established and data is being transmitted correctly.
What tools do I need for a homemade OBD2 CAN bus hard-wired setup?
You’ll need basic tools like wire strippers, crimpers, or a soldering iron, along with connectors and heat shrink tubing. A multimeter is also essential for testing continuity and ensuring proper connections.
Safety Precautions and Considerations
Working with vehicle electronics requires caution. Always disconnect the vehicle’s battery before making any connections to prevent damage to the electronics. Double-check all connections before reconnecting the battery. Incorrect wiring can lead to communication errors or even damage to the vehicle’s electronic systems.
Is a homemade OBD2 CAN bus hard-wired connection safe?
With proper precautions and correct wiring, a homemade connection is safe. However, negligence can lead to potential risks. Always ensure proper insulation and grounding.
“A solid understanding of the CAN bus protocol is paramount when attempting a hard-wired connection,” advises John Miller, Senior Automotive Engineer at Apex Automotive Solutions. “Improper wiring can have detrimental effects on the vehicle’s electronic systems.”
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- No communication: Verify the CANH and CANL connections, ground connection, and the compatibility of your device.
- Intermittent communication: Check for loose connections or damaged wires.
- Incorrect data: Ensure that the correct CAN bus protocol is being used.
Conclusion
A homemade OBD2 CAN bus hard wired connection can be a valuable solution for specific applications. By following the steps outlined in this guide and taking the necessary safety precautions, you can successfully establish a direct and reliable connection to your vehicle’s CAN bus. Remember to always consult your vehicle’s wiring diagram and double-check all connections before reconnecting the battery.
FAQ
- Can I connect any OBD2 scanner to a hard-wired CAN bus? Most OBD2 scanners should work, but compatibility can vary.
- What gauge wire should I use? 22-24 gauge wire is typically suitable for CAN bus connections.
- Do I need a specific type of connector? Various connectors can be used, including crimp connectors and solder joints.
- What if I damage the CAN bus? Incorrect wiring can damage the CAN bus, so careful planning and execution are essential.
- Is it legal to modify my vehicle’s wiring? Regulations may vary depending on your location. Check local laws before modifying your vehicle’s wiring.
- Where can I find my vehicle’s wiring diagram? Vehicle-specific repair manuals or online resources often provide wiring diagrams.
- What software can I use to monitor CAN bus data? Several OBD2 software applications are available for monitoring and logging CAN bus data.
“When working with vehicle electronics, safety should always be the top priority,” emphasizes Sarah Johnson, Electrical Systems Specialist at AutoTech Diagnostics. “Always disconnect the battery and double-check your connections to prevent damage.”
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We have a 24/7 customer support team ready to help. You can also find more helpful articles and guides on our website, OBDFree. We recommend checking out our articles on “Understanding OBD2 Protocols” and “Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs”.