OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a crucial system in modern vehicles. It acts like a car’s doctor, constantly monitoring various systems and alerting you to potential problems. But how does OBD2 know there is a misfire, a common engine issue? Let’s dive deep into the intricate workings of this diagnostic marvel.
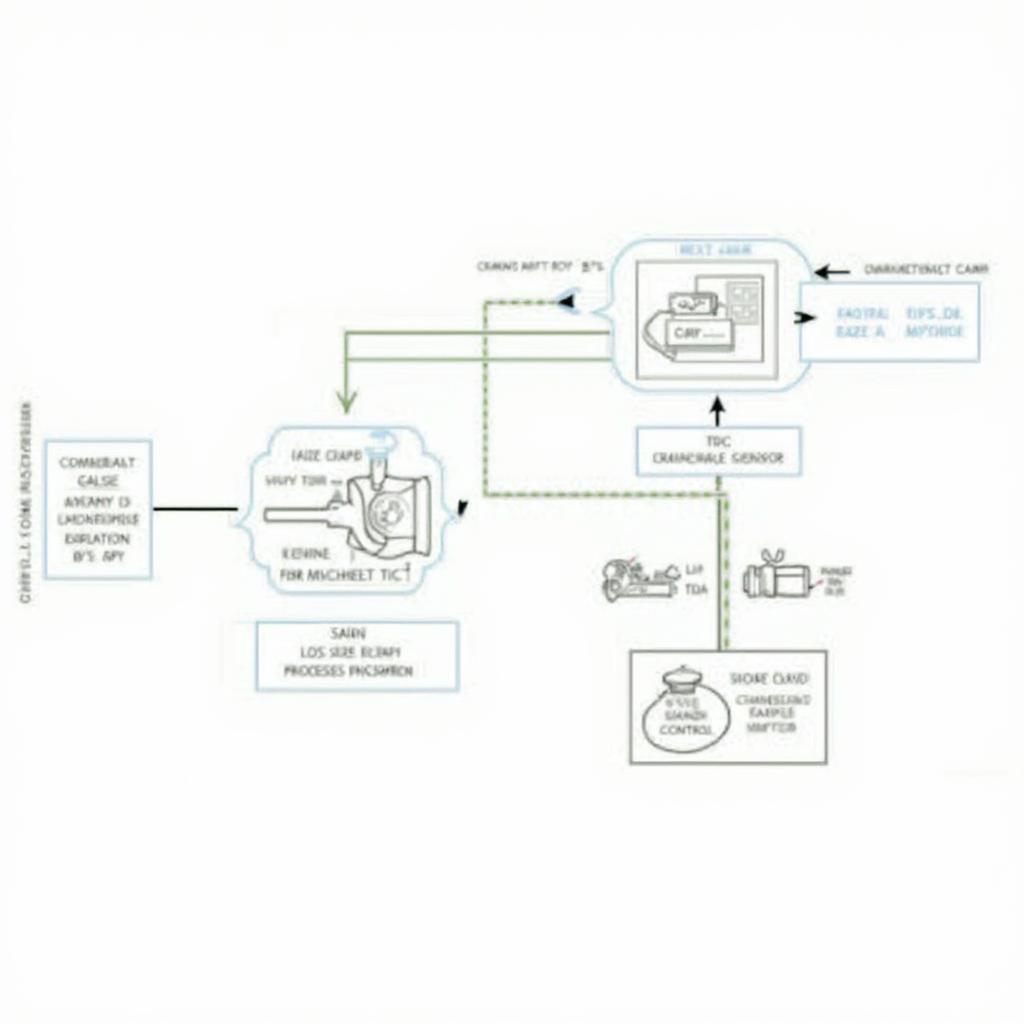
The primary way OBD2 detects a misfire is through the crankshaft position sensor (CKP). This sensor carefully tracks the rotational speed of the crankshaft. A consistent rotation is vital for smooth engine operation. When a cylinder misfires, it disrupts this smooth rotation, causing a slight, but detectable, fluctuation in the crankshaft speed. The CKP picks up on these variations and relays this information to the engine control module (ECM), also known as the powertrain control module (PCM). The ECM/PCM is essentially the brain of the car’s engine management system. It takes the input from the CKP and uses sophisticated algorithms to determine if the fluctuation is indeed a misfire.
The Role of the Crankshaft Position Sensor
The CKP is incredibly sensitive. It can detect even the slightest variations in crankshaft speed, allowing for quick and accurate misfire detection. This quick detection is crucial for preventing further damage to the engine and the catalytic converter. For example, a consistent misfire in a specific cylinder can quickly overheat the catalytic converter.
Understanding Misfire Counts and Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Once the ECM/PCM confirms a misfire, it logs a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), specifically a P0300 series code. For example, P0301 indicates a misfire in cylinder 1, P0302 in cylinder 2, and so on. The ECM/PCM also keeps track of the number of misfires, known as misfire counts. This helps determine the severity and frequency of the misfire. The Actron OBD2 scanner, for instance, can be highly useful in retrieving these codes and data. You can learn how to use one effectively through resources like actron obd2 scanner how to use.
Other Contributing Factors to Misfire Detection
While the CKP is the primary method for misfire detection, the OBD2 system also utilizes other sensors to provide a comprehensive analysis. These include the camshaft position sensor, the mass airflow sensor (MAF), and the oxygen sensors. These sensors provide additional data that help pinpoint the cause of the misfire. For instance, a faulty MAF sensor can lead to an incorrect air/fuel mixture, which can cause misfires. Similarly, understanding obd2 mode 10 can offer deeper insights into the diagnostic process.
Pinpointing the Culprit: Beyond the Code
Identifying the underlying cause of the misfire requires further investigation. While the OBD2 system provides valuable clues through the DTCs, it doesn’t pinpoint the exact problem. A misfire can be caused by a variety of issues, such as faulty spark plugs, worn ignition coils, a vacuum leak, low fuel pressure, or even mechanical problems within the engine.
“A common misconception is that the OBD2 code tells you exactly what part to replace. In reality, the code is just the starting point of the diagnostic process,” says John Smith, a certified automotive technician with over 20 years of experience.
“Understanding the information the OBD2 system provides is key to efficient and accurate diagnostics. This knowledge can save you time and money,” adds Jane Doe, an automotive engineer specializing in engine management systems. Accessing the OBD2 port on various vehicles, like the polaris rzr obd2 port, can be the first step towards understanding these systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how OBD2 knows there is a misfire involves appreciating the complex interplay between various sensors and the ECM/PCM. The CKP plays a vital role by detecting fluctuations in crankshaft speed caused by misfires. This information is then processed by the ECM/PCM, which generates specific DTCs and misfire counts. While the OBD2 system provides valuable diagnostic information, further investigation is usually necessary to pinpoint the root cause of the misfire. With this knowledge, you can effectively address engine issues and ensure optimal vehicle performance. Remember the crucial role of reliable OBD2 software, especially for specialized vehicles. Resources like the best bluetooth obd2 software for p can provide valuable guidance. And, if you’re dealing with OBD2 issues on a specific vehicle like the Ram 1500, checking out the ram 1500 obd2 resource can be beneficial.
FAQ
- What is a misfire? A misfire occurs when a cylinder in the engine fails to combust the air/fuel mixture properly.
- What are the common symptoms of a misfire? Rough idling, reduced power, poor fuel economy, and flashing check engine light.
- Can I drive with a misfire? It’s best to avoid driving with a misfire as it can damage the engine and catalytic converter.
- How much does it cost to fix a misfire? The cost varies depending on the cause, but it can range from a simple spark plug replacement to more complex repairs.
- How can I prevent misfires? Regular maintenance, including spark plug replacements and fuel system cleaning, can help prevent misfires.
- What is the role of the camshaft position sensor in misfire detection? It helps the ECM/PCM determine which cylinder is misfiring.
- Can a bad oxygen sensor cause a misfire? Not directly, but it can lead to an incorrect air/fuel mixture, which can contribute to misfires.
For support, contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We have a 24/7 customer service team.