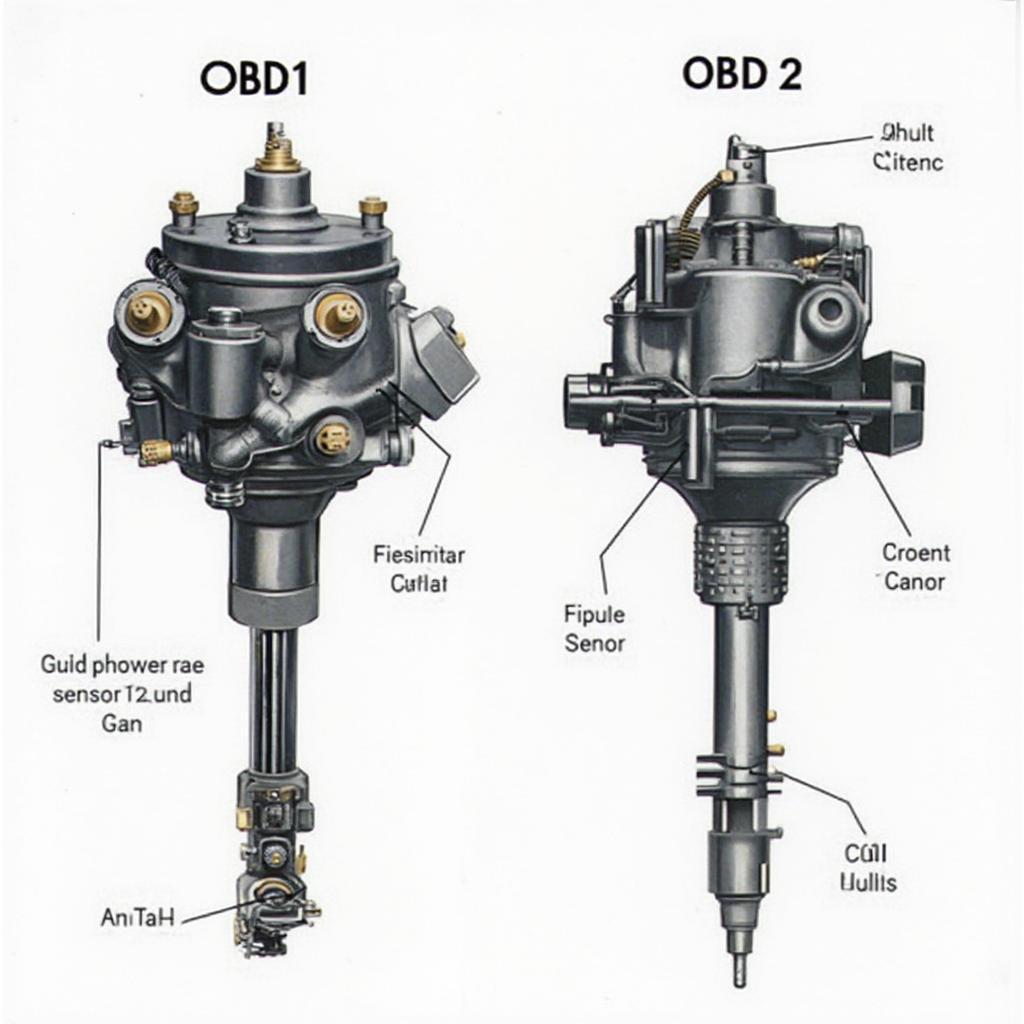
Swapping an OBD1 ignition distributor into an OBD2 automatic car is a complex process, often attempted to address performance issues or compatibility with older engine management systems. However, directly installing an OBD1 distributor in an OBD2 vehicle isn’t a plug-and-play operation and requires significant modifications that can affect the vehicle’s emissions system and overall drivability. This article explores the complexities involved and provides alternative solutions.
Understanding the Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2 Systems
Before diving into the process, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental differences between OBD1 and OBD2 systems. OBD1, or On-Board Diagnostics Generation 1, is a simpler system primarily focused on monitoring emissions components. OBD2, introduced in 1996, is a more sophisticated system with enhanced diagnostic capabilities and stricter emission standards. A key difference lies in how the ignition timing is controlled. OBD1 systems often rely on the distributor for ignition timing, while OBD2 systems utilize the engine control module (ECM) for precise control, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Challenges of Installing an OBD1 Distributor in an OBD2 Car
The primary challenge lies in the incompatibility of the two systems. OBD2 vehicles use a crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sensor to determine ignition timing, which the ECM manages. OBD1 distributors lack the necessary components to interact with the OBD2 ECM. Simply swapping the distributor won’t work, and attempting to bypass the OBD2 system can lead to various problems, including:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) illumination: The ECM will detect the missing signals and trigger the CEL, indicating a fault.
- Poor engine performance: Incorrect ignition timing can lead to misfires, rough idling, and reduced power.
- Failed emissions tests: Altering the emissions system can result in failing emissions tests, making the vehicle illegal to operate in many jurisdictions.
- Transmission issues: In automatic cars, the ECM communicates with the transmission control module (TCM). Disrupting this communication can negatively impact shifting performance and even cause damage.
Exploring Alternatives and Solutions
Rather than attempting a direct swap, consider these alternatives for achieving your desired outcome:
- Using a standalone engine management system: This allows you to bypass the OBD2 system entirely and control the engine parameters, including ignition timing, with a separate aftermarket system. This is a complex modification requiring expertise.
- Converting to an OBD1 ECM: In some cases, it’s possible to convert the entire engine management system to OBD1. This typically involves swapping the ECM, wiring harness, and other components. This is also a complex procedure and might not be suitable for all vehicles.
- Addressing the underlying issue: If performance problems are the motivation for the swap, diagnosing and fixing the root cause within the OBD2 system is the recommended approach. This may involve replacing faulty sensors, addressing vacuum leaks, or other repairs.
Why Professional Help is Recommended
Modifying the engine management system is a complex undertaking that requires specialized knowledge and tools. Incorrectly performing these modifications can lead to significant problems and costly repairs. Consulting a qualified mechanic experienced with OBD systems is highly recommended. They can accurately diagnose the issue, recommend the best course of action, and ensure the modifications are performed correctly.
Conclusion
While the idea of putting an OBD1 ignition distributor in an OBD2 automatic car might seem appealing, it’s not a straightforward process and can lead to numerous complications. Exploring alternative solutions like using a standalone engine management system or addressing the underlying performance issues is often a better approach. Consulting with a qualified mechanic is crucial for ensuring the modifications are done correctly and avoiding potential problems. Understanding the complexities of these systems is key to making informed decisions about your vehicle’s performance and maintenance.
FAQ
-
Can I just plug an OBD1 distributor into an OBD2 car? No, the two systems are incompatible and a direct swap won’t work.
-
What problems can arise from trying to bypass the OBD2 system? Problems can include a check engine light, poor engine performance, failed emissions tests, and transmission issues.
-
What are some alternatives to swapping the distributor? Alternatives include using a standalone engine management system, converting to an OBD1 ECM, or addressing the underlying issue causing the performance problems.
-
Should I attempt these modifications myself? Modifying the engine management system is complex and best left to qualified mechanics.
-
Why is it important to understand the difference between OBD1 and OBD2? Understanding the differences helps you make informed decisions about repairs and modifications, and avoids potentially damaging your vehicle.
-
What is a standalone engine management system? It’s an aftermarket system that replaces the factory ECM and allows for custom tuning of engine parameters.
-
What should I do if my car is experiencing performance issues? The best course of action is to have a qualified mechanic diagnose the problem and recommend the appropriate repairs.
Situations & Questions
Scenario: You have an older engine you want to put into your OBD2 car. The engine has an OBD1 distributor.
Question: Can I use the OBD1 distributor with my OBD2 car?
Answer: As explained above, direct swapping is not recommended. Explore alternatives like a standalone engine management system or consider if converting your car to OBD1 is feasible.
Scenario: Your OBD2 car is experiencing performance problems and you suspect the distributor.
Question: Could an OBD1 distributor fix my performance issues?
Answer: It’s unlikely. An OBD1 distributor won’t solve the problem and will likely create more issues. Have a mechanic diagnose the actual cause of the performance problems.
Further Reading and Resources
For more information on OBD systems and car diagnostics, explore these resources on our website:
- OBD2 Codes Explained
- How to Use an OBD2 Scanner
- Common Car Performance Problems and Solutions
Need Help?
For expert advice and assistance with your car diagnostics, contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, or Email: [email protected]. Our 24/7 customer support team is ready to help.