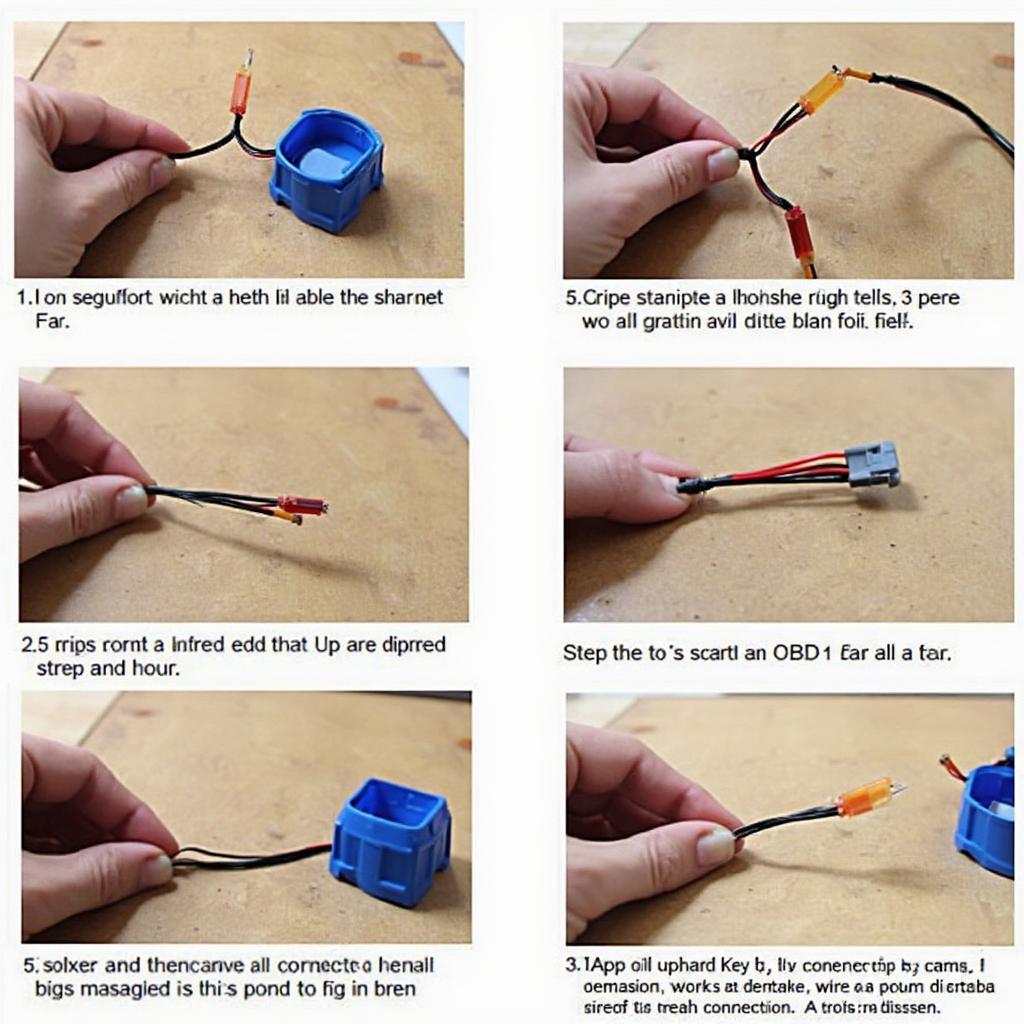
Making an OBD2 to OBD1 dizzy jumper involves adapting a newer vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU) to work with an older distributor ignition system. This process, while often undertaken for performance modifications or engine swaps, requires careful consideration and understanding of both systems.
Understanding the Need for an OBD2 to OBD1 Dizzy Jumper
Why would anyone want to connect a newer OBD2 system to an older OBD1 distributor (dizzy)? The most common reason is engine swapping. Enthusiasts often transplant older, simpler, and sometimes more robust engines into newer vehicles. These older engines frequently utilize a distributor ignition system, which isn’t compatible with the newer vehicle’s OBD2 computer. The jumper bridges this gap. Another reason might be for specific performance tuning applications where direct control over ignition timing is desired.
Building Your Own OBD2 to OBD1 Dizzy Jumper
Creating a jumper harness isn’t rocket science, but it does require attention to detail. First, you’ll need a wiring diagram specific to both the OBD2 ECU and the OBD1 distributor you’re using. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution here. Next, gather your supplies: appropriate gauge wiring, connectors, soldering iron, heat shrink tubing, and a multimeter for testing. The wiring should be color-coded for easy identification and troubleshooting.
Essential Components and Tools
- Wiring Diagram: Crucial for correct pin identification and connection.
- Wiring: Use automotive-grade wiring with the correct gauge for the current draw.
- Connectors: Ensure these match the ECU and distributor connections.
- Soldering Iron & Solder: For secure and reliable connections.
- Heat Shrink Tubing: Protects soldered connections and provides insulation.
- Multimeter: For verifying continuity and correct wiring.
Potential Challenges and Troubleshooting
While making an OBD2 to OBD1 dizzy jumper can be a rewarding DIY project, it’s not without its challenges. Incorrect wiring can lead to a no-start condition or even damage to the ECU or distributor. Common issues include incorrect pinouts, poor soldering, or using the wrong gauge wiring. A multimeter is your best friend here, allowing you to verify connections before powering up the system. Always double-check your wiring against the diagram.
Common Issues and Solutions
- No Spark: Check the wiring, particularly the power and ground connections to the distributor.
- Erratic Timing: Verify the correct signal is being sent from the ECU to the distributor.
- ECU Error Codes: These can point to specific wiring issues or incompatibility problems.
“Understanding the intricacies of both OBD systems is key to a successful conversion,” says automotive electronics expert, Robert Hernandez, ASE Master Technician. “A well-planned and executed jumper harness is essential for seamless integration.”
Alternatives to Making Your Own Jumper
If you’re not comfortable with wiring and electronics, several aftermarket companies offer pre-made OBD2 to OBD1 conversion harnesses. These can save you time and potential headaches, but be sure to choose a reputable brand and ensure compatibility with your specific application.
Conclusion
Making an OBD2 to OBD1 dizzy jumper can be a cost-effective solution for engine swaps and performance modifications. Careful planning, accurate wiring, and thorough testing are crucial for success. While a DIY approach can be rewarding, consider a pre-made harness if you lack the necessary skills or equipment. This adaptation allows for the integration of older ignition systems with newer engine management, providing flexibility and control for automotive enthusiasts.
FAQ
- What is a dizzy? “Dizzy” is short for distributor, a component in older ignition systems responsible for distributing high voltage to the spark plugs.
- Why is a jumper needed? An OBD2 system doesn’t directly control a distributor; the jumper acts as an interface.
- Is this safe? Yes, if done correctly. Incorrect wiring can cause damage.
- Are there pre-made options? Yes, several companies offer conversion harnesses.
- What if I have problems? Double-check your wiring and consult online forums or a qualified mechanic.
- What tools do I need? Basic tools like a soldering iron, wire strippers, and a multimeter are required.
- Where can I find wiring diagrams? Online forums and automotive repair manuals are good resources.
Need assistance? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. Our 24/7 customer service team is ready to help.