Mitsubishi vehicles, known for their reliability and performance, utilize a sophisticated onboard diagnostic system (OBD2). This system acts as your car’s internal communication network, constantly monitoring various sensors and components. When an issue arises, the OBD2 system generates specific error codes, often displayed as a combination of letters and numbers, which act as vital clues for diagnosing and resolving car problems. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of Mitsubishi OBD2 error codes, equipping you with the knowledge to decipher these cryptic messages and take control of your vehicle’s health.
Decoding the Language of Your Mitsubishi: What are OBD2 Error Codes?
Imagine your Mitsubishi’s OBD2 system as a vigilant watchdog, always on the lookout for any signs of trouble. When it detects an anomaly, whether it’s a malfunctioning sensor, an emissions issue, or a problem with the engine, it logs a specific code in its memory. This code, known as an OBD2 error code, is essentially a standardized alphanumeric representation of the detected issue.
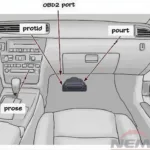
These codes are not meant to be cryptic puzzles but rather invaluable tools for mechanics and car owners alike. By connecting an OBD2 scanner to your Mitsubishi’s diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, you can retrieve these codes and gain insights into the potential root cause of your car troubles.
Common Mitsubishi OBD2 Error Codes and Their Meanings
While the specific codes and their interpretations can vary slightly depending on the model year and region, here are some of the most frequently encountered Mitsubishi OBD2 error codes:
P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- Possible Causes: This code often indicates an issue with the air-fuel mixture in engine bank 1, meaning the engine is running on too much air and not enough fuel. This could be due to a vacuum leak, a faulty mass airflow sensor (MAF), or a problem with the oxygen sensor.
P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- Possible Causes: As the code suggests, this points to a misfire occurring in one or more cylinders. Potential culprits include worn spark plugs, faulty ignition coils, a vacuum leak, or even internal engine problems.
P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- Possible Causes: This code usually signals a problem with the catalytic converter’s efficiency in converting harmful exhaust gases into less harmful substances. A failing catalytic converter, a faulty oxygen sensor, or an exhaust leak could be the underlying cause.
P0135: O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- Possible Causes: This code points to a problem with the heating element within the oxygen sensor, which helps it reach operating temperature quickly. A faulty oxygen sensor, wiring issues, or a blown fuse in the heater circuit are common culprits.
P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
- Possible Causes: This code typically indicates a small leak in the evaporative emissions (EVAP) system, which is responsible for preventing fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. A loose gas cap, a cracked EVAP hose, or a faulty purge or vent valve are often the source of the leak.
Don’t Panic, Take Action: What to Do When Your Mitsubishi Throws a Code
It’s important to remember that seeing an OBD2 error code on your Mitsubishi’s dashboard doesn’t necessarily signify a catastrophic problem. However, it’s crucial not to ignore these warning signs. Timely diagnosis and intervention can often prevent minor issues from escalating into costly repairs.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on what to do:
-
Note the Code: When the Check Engine Light illuminates, make a note of the specific code or codes displayed on your OBD2 scanner. If you don’t have a scanner, most auto parts stores will retrieve the codes for you.
-
Research the Code: Use a reliable online resource or a Mitsubishi-specific repair manual to research the meaning of the code and its potential causes. Understanding the code will give you a better idea of the problem’s severity.
-
Check for Simple Fixes: Before assuming the worst, inspect your vehicle for any obvious issues that might trigger the code. For example, ensure the gas cap is securely tightened, as a loose gas cap is a common cause of EVAP system leaks (P0442).
-
Consider DIY Repairs: If you’re mechanically inclined and the potential fixes seem manageable, you might consider tackling the repair yourself. However, always refer to reputable repair manuals and exercise caution.
-
Seek Professional Help: If the problem appears complex, or if you’re unsure about DIY repairs, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic specializing in Mitsubishi vehicles. They have the expertise, tools, and diagnostic equipment to pinpoint the issue accurately and perform the necessary repairs.
Expert Insight: “Ignoring OBD2 codes is like ignoring a fever. It might go away on its own, or it could be a sign of something serious. Early diagnosis is key to protecting your Mitsubishi’s health and your wallet,” says John Miller, a veteran Mitsubishi mechanic with over 20 years of experience.
OBDFree: Your Trusted Partner in Mitsubishi Diagnostics
Navigating the world of OBD2 codes can seem daunting, but remember, you’re not alone. OBDFree is here to provide you with the resources and support you need to understand and address your Mitsubishi’s needs. From comprehensive code definitions and troubleshooting tips to expert advice and product recommendations, we’re your trusted partner in keeping your Mitsubishi running smoothly for miles to come.
FAQs – Mitsubishi OBD2 Error Codes
Q: Can I still drive my Mitsubishi with the Check Engine Light on?
A: While it’s possible to drive short distances with the Check Engine Light on, it’s not advisable. Ignoring the light could lead to further damage and more costly repairs down the line.
Q: Will disconnecting the battery reset the OBD2 codes?
A: Disconnecting the battery may temporarily clear the codes and turn off the Check Engine Light. However, the codes will reappear if the underlying problem persists.
Q: Are all OBD2 scanners compatible with Mitsubishi vehicles?
A: Most standard OBD2 scanners will work with Mitsubishi vehicles. However, for more advanced features and model-specific diagnostics, consider investing in a Mitsubishi-compatible scanner or code reader.
Q: Can I prevent OBD2 error codes from occurring?
A: While you can’t prevent all error codes, regular maintenance, including timely oil changes, spark plug replacements, and inspections, can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering issues.
Q: How often should I get my Mitsubishi’s OBD2 system checked?
A: It’s a good practice to have your Mitsubishi’s OBD2 system scanned at least once a year or as part of your regular maintenance schedule.
Need Further Assistance?
For personalized guidance and expert support in diagnosing and resolving your Mitsubishi’s OBD2 error codes, don’t hesitate to reach out to our dedicated team.
Contact Us:
WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880
Email: [email protected]
Our team of automotive specialists is available 24/7 to assist you with all your Mitsubishi diagnostic needs.