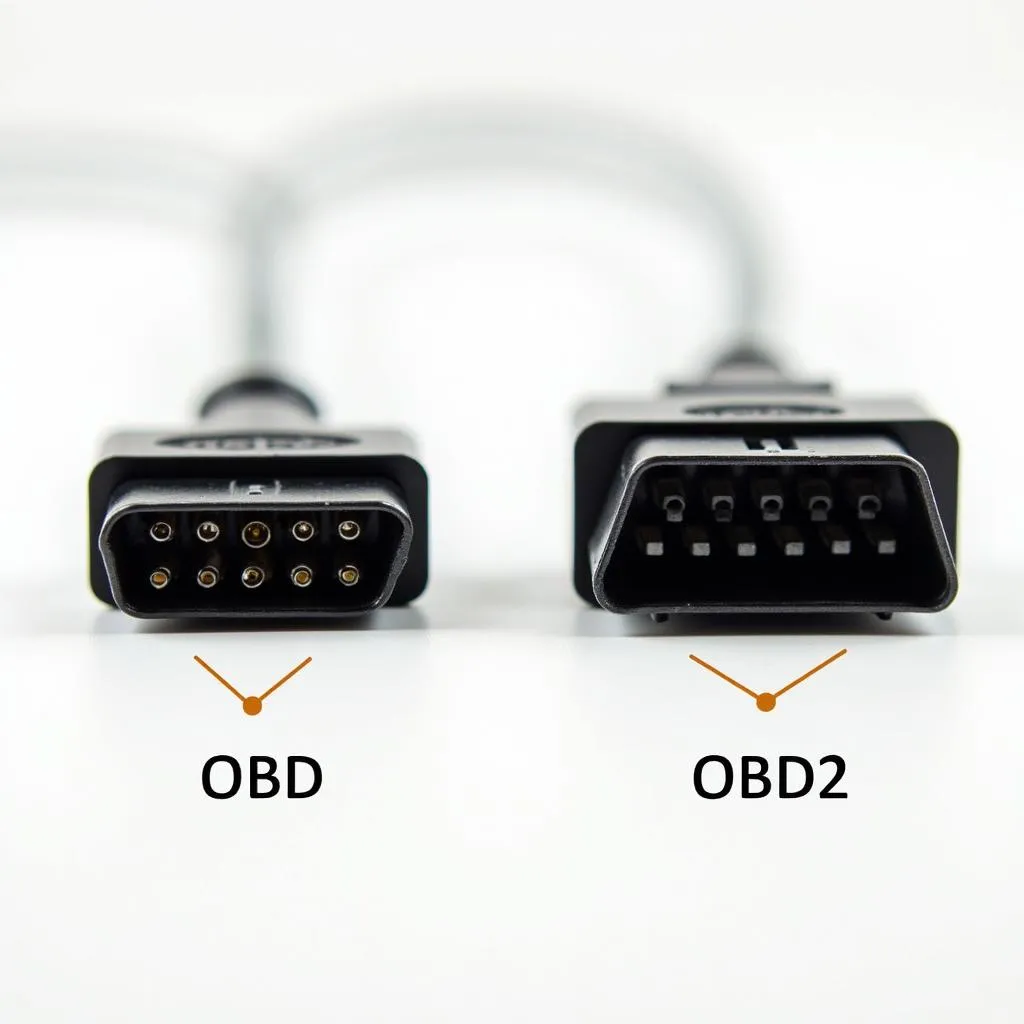
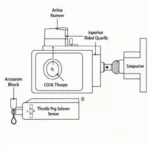
The automotive world can feel like a labyrinth of acronyms and technical jargon, and one common point of confusion for car owners is the difference between OBD and OBD2. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct systems with significant variations in capabilities and applications. This article delves into the evolution from OBD to OBD2, highlighting the key differences and providing clarity for car enthusiasts and everyday drivers alike.
A Historical Perspective: From OBD to OBD2
The genesis of On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) can be traced back to the 1960s, driven by the need to monitor emissions control systems in vehicles. Early OBD systems were rudimentary, often limited to illuminating a “check engine” light when a problem arose. The information provided was minimal, offering little insight into the nature or severity of the issue.
The introduction of OBD2 in the mid-1990s revolutionized vehicle diagnostics. Mandated for all cars and light trucks sold in the United States from 1996 onwards, OBD2 standardized the diagnostic connector, communication protocols, and error codes across different makes and models. This standardization marked a significant leap forward, empowering mechanics and car owners with a unified system for understanding and addressing vehicle issues.
Key Differences Between OBD and OBD2
While both OBD and OBD2 aim to identify malfunctions within a vehicle’s systems, several crucial differences set them apart:
1. Standardization:
- OBD: Lacked standardization, leading to inconsistencies in connectors, protocols, and error codes across vehicle manufacturers.
- OBD2: Introduced standardized connectors, communication protocols (such as SAE J1850 and ISO 9141), and a universal set of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), ensuring interoperability across different vehicle makes and models.
2. Diagnostic Capabilities:
- OBD: Primarily focused on monitoring emissions-related components, offering limited diagnostic capabilities.
- OBD2: Expanded diagnostic scope to encompass a wider range of vehicle systems, including engine, transmission, airbags, ABS, and more, providing comprehensive insights into vehicle health.
3. Data Richness:
- OBD: Provided limited data, often restricted to basic information about the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) status.
- OBD2: Enables access to a wealth of real-time data, including engine RPM, speed, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and more, facilitating in-depth analysis and troubleshooting.
The Significance of OBD2 in the Modern Automotive Landscape
The advent of OBD2 has had a profound impact on the automotive industry, transforming the way vehicles are diagnosed, repaired, and maintained. Some of the key benefits include:
- Simplified Diagnostics: The standardized nature of OBD2 makes it easier for mechanics to diagnose and repair vehicle issues, regardless of make or model.
- Improved Repair Efficiency: Access to detailed diagnostic information and real-time data enables quicker and more efficient repairs, reducing downtime and labor costs.
- Empowered Car Owners: OBD2 scanners have become increasingly affordable and user-friendly, allowing car owners to perform basic diagnostics, monitor vehicle health, and even clear error codes.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of OBD2
Understanding the distinctions between OBD and OBD2 is crucial in navigating the complexities of modern vehicle diagnostics. OBD2’s standardization, expanded diagnostic capabilities, and data richness have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering a universal language for understanding and addressing vehicle issues. As technology advances, OBD2 will continue to evolve, ushering in a new era of sophisticated diagnostics and enhanced vehicle insights.