The obd1 and obd2 data link connector are essential interfaces for vehicle diagnostics. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a car enthusiast, understanding the differences and functionalities of these connectors is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. This article will explore the evolution from OBD1 to OBD2, delve into the specifics of each data link connector, and provide valuable insights for utilizing them effectively.
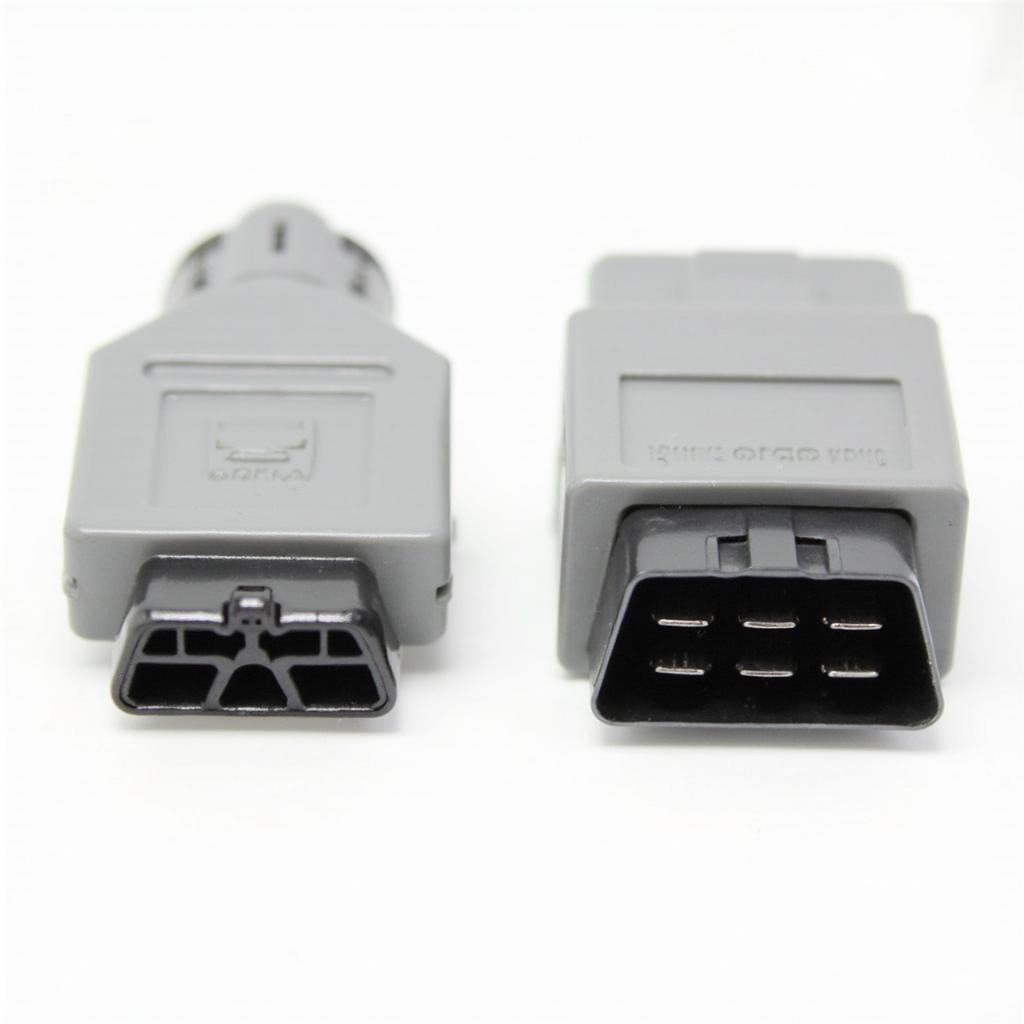 Comparing OBD1 and OBD2 Connectors
Comparing OBD1 and OBD2 Connectors
From OBD1 to OBD2: A Leap in Diagnostics
Before the standardization of OBD2, manufacturers used proprietary OBD1 systems. This meant different connectors, protocols, and diagnostic procedures, making troubleshooting complex. obd1 obd2 vr6 systems were often manufacturer-specific, requiring specialized equipment for each car make and model. With the advent of OBD2 in 1996 in the United States, a universal standard emerged, simplifying diagnostics across different vehicles. This standardization brought numerous advantages, including improved emission monitoring, easier troubleshooting, and access to a wider range of diagnostic tools.
What is an OBD1 Data Link Connector?
OBD1 connectors lack standardization, varying significantly between manufacturers. Locating the connector can be challenging, often requiring consultation of the vehicle’s service manual. These connectors transmitted limited diagnostic information primarily focusing on engine performance.
What is an OBD2 Data Link Connector?
The OBD2 data link connector is a standardized 16-pin connector typically located under the dashboard, near the steering column. This standardized interface allows a single OBD2 scanner to communicate with various vehicle makes and models, providing access to a wealth of diagnostic information related to engine performance, emissions, transmission, and other systems. Accessing the OBD2 connector is significantly easier due to its standardized location.
Decoding the OBD2 Data Link Connector
The OBD2 connector’s 16 pins are not all used in every vehicle. Specific pins are assigned for different functionalities, allowing manufacturers some flexibility while maintaining compatibility with standard OBD2 scanners. Understanding the pin assignments can help you troubleshoot connection issues or utilize advanced diagnostic features.
Common OBD2 Connector Pin Functions:
- Pin 4 & 5: Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (Controller Area Network)
- Pin 7: ISO 9141-2 K-Line
- Pin 14: CAN Low (Controller Area Network)
- Pin 16: Battery Power
“The OBD2 standard revolutionized automotive diagnostics, empowering both professionals and car owners with accessible and standardized troubleshooting capabilities,” says Michael Stevens, Automotive Diagnostics Engineer.
Using the OBD2 Data Link Connector
Connecting an OBD2 scanner to the data link connector is straightforward. Simply locate the connector under the dashboard, plug in the scanner, and turn the ignition on. The scanner will then communicate with the vehicle’s onboard computer, retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and other relevant data.
1996 2003 obd2 gm 1996-2003 obd2
Common Uses of OBD2 Scanners:
- Retrieving DTCs: Identifying the source of malfunctions
- Monitoring Real-Time Data: Observing sensor readings and system performance
- Performing Emissions Tests: Checking for compliance with environmental regulations
- Resetting the Check Engine Light: After repairs, clearing the DTCs and turning off the warning light
“Investing in a reliable OBD2 scanner is essential for any car owner. It empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and avoid costly surprises,” adds Maria Rodriguez, Certified Automotive Technician.
Conclusion
Understanding the obd1 and obd2 data link connector is fundamental for effective vehicle diagnostics. The standardization of OBD2 has greatly simplified troubleshooting, providing car owners and professionals with valuable tools for maintaining and repairing vehicles. By familiarizing yourself with the connector, its pinout, and the capabilities of OBD2 scanners, you can enhance your understanding of your vehicle’s health and address potential issues efficiently. difference between obd1 and obd2 connector and actron obd2 scanner instructions are important resources for furthering your understanding. obd2 connector online may help you locate further information.
FAQ
- Where can I find the OBD2 connector in my car?
- What does the check engine light mean?
- Can I fix my car myself using an OBD2 scanner?
- What are the different types of OBD2 scanners?
- How do I choose the right OBD2 scanner for my needs?
- What do the different OBD2 codes mean?
- Where can I find more information on specific OBD2 codes?
When you need assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our address at 789 Elm Street, San Francisco, CA 94102, USA. We have a 24/7 customer support team.