So you’ve found yourself in a bit of a bind. You’ve got an OBD1 car (model year 1995 or older) but with a newer, OBD2 engine (model year 1996 or newer) under the hood. Now, what happens when it’s time for emissions testing? This isn’t an uncommon scenario, especially for those who’ve done engine swaps. Let’s break down the challenges and solutions for passing emissions with an OBD1 car and OBD2 engine.
The OBD1 and OBD2 Disconnect
The heart of the issue lies in how emissions testing works. OBD1 cars have a different diagnostic system than OBD2 vehicles. While both systems monitor emissions-related components, they speak different languages. Your OBD1 car’s computer system simply can’t communicate with the OBD2 engine’s control system in the way emissions testing equipment expects.
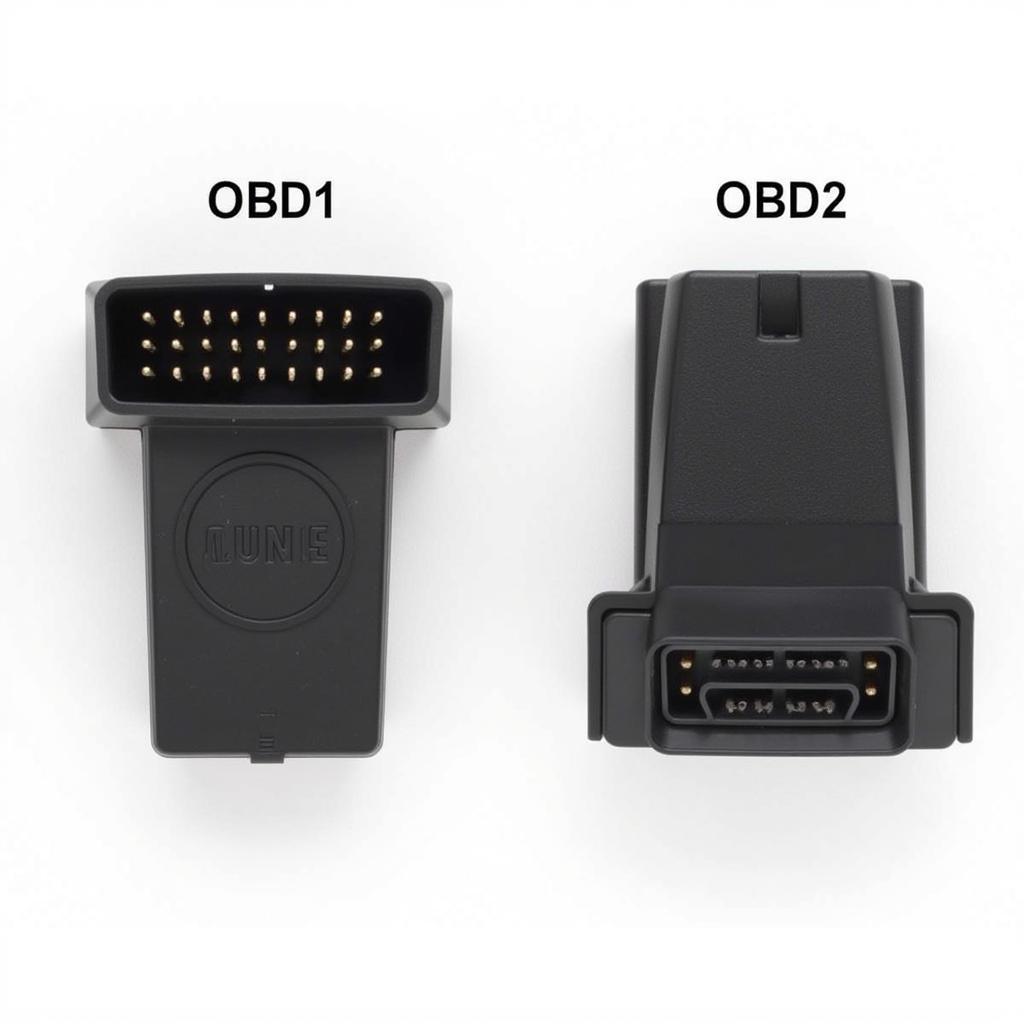 OBD1 and OBD2 Connector Differences
OBD1 and OBD2 Connector Differences
Challenges of Emissions Testing
This incompatibility presents a significant hurdle during emissions testing. When the testing equipment plugs into your OBD2 engine’s port, it won’t be able to retrieve the necessary data from your OBD1 car’s system. This usually results in an automatic fail, even if your engine is running perfectly and within emissions standards.
Finding a Solution
Don’t despair! There are potential solutions to overcome this OBD1-OBD2 mismatch:
- Check with Your Local DMV: Regulations vary, and some states may have exemptions or specific procedures for vehicles with engine swaps.
- Consult a Specialist: A qualified mechanic specializing in engine swaps and emissions systems can assess your situation and advise on the best course of action. They might recommend:
- OBD2 ECU Conversion: This involves replacing your OBD1 engine control unit (ECU) with a compatible OBD2 ECU. It’s a complex procedure that requires expertise and careful tuning to ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s other systems.
- Standalone Engine Management System: For highly modified vehicles or situations where an OBD2 ECU swap isn’t feasible, a standalone engine management system can be installed. This system bypasses your car’s factory computer and allows for complete control over engine parameters, including emissions-related settings.
- Emissions Testing Exemption: In some areas, you might be eligible to apply for an emissions testing exemption if you can demonstrate that converting your vehicle to meet the OBD2 standard is technically infeasible or prohibitively expensive.
Moving Forward: Getting Your OBD1 Car Emissions-Ready
Successfully navigating the emissions testing process with an OBD1 car and OBD2 engine requires careful planning and expert advice. It’s crucial to:
- Research Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with your state’s specific requirements for engine swaps and emissions testing.
- Consult with Professionals: Engage qualified mechanics and emissions specialists to understand the available options and get accurate estimates for the necessary modifications.
- Keep Detailed Records: Maintain comprehensive documentation of the engine swap, including parts used, modifications made, and any tuning adjustments. This information can be invaluable when dealing with emissions testing officials or if you need to apply for an exemption.
Navigating the world of OBD1 and OBD2 can seem daunting, but with the right information and guidance, you can get your car emissions-ready and legally on the road. Remember, professional help is essential for ensuring your vehicle complies with all safety and emissions standards.